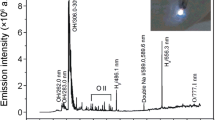
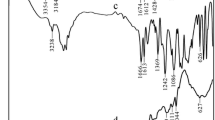
Abstract
In this work, a novel chitosan/P(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid-co-acrylic amide) (CS/P(AMPS-co-AM)) hydrogel was successfully prepared by a simple one-step method using glow-discharge-electrolysis plasma (GDEP) initiated copolymerization, in which N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide was used as a cross-linking agent. A copolymerization mechanism of AMPS and AM onto CS initiated by GDEP was proposed. The structure, thermal stability and morphology of CS/P(AMPS-co-AM) hydrogel were characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), TG/DTG, and scanning electron microscope (SEM). This hydrogel was employed as an absorbent for the removal of methylene blue (MB) and malachite green (MG) from aqueous solutions. The effects of pH, contact time and equilibrium concentration on the dye adsorption were investigated batchwise. FTIR and XRD indicated that AM and AMPS were grafted onto the CS backbone successfully, forming copolymer. TG/DTG suggested that grafted AMPS and AM onto CS could change the thermal stability of the CS. SEM showed a unique three-dimensional porous structure for the CS/P(AMPS-co-AM) hydrogel. The optimum pH for the removal of cationic dyes was 5.8, and time of adsorption equilibrium was achieved in 90 min. The CS/P(AMPS-co-AM) hydrogel exhibited a very high adsorption potential, and its adsorption capacities calculated based on the Langmuir isotherm for MB and MG were 1,538.5 and 917.4 mg g−1, respectively. The dye adsorption data fitted well to the pseudo-second-order model and Langmuir model at 25 °C with pH 5.8.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh RL, Singh PK, Singh RP (2015) Enzymatic decolorization and degradation of azo dyes—a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 104:21–31
Wang SM, Guan Y, Wang LP, Zhao W, He H, **ao J, Yang SG, Sun C (2015) Fabrication of a novel bifunctional material of BiOI/Ag3VO4 with high adsorption–photocatalysis for efficient treatment of dye wastewater. Appl Catal B 168–169:448–457
Raghu S, Lee CW, Chellammal S, Palanichamy S, Basha CA (2009) Evaluation of electrochemical oxidation techniques for degradation of dye effluents—a comparative approach. J Hazard Mater 171:748–754
Muthukumar M, Sargunamani D, Selvakumar N (2005) Statistical analysis of the effect of aromatic, azo and sulphonic acid groups on decolouration of acid dye effluents using advanced oxidation processes. Dyes Pigments 65:151–158
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 201–202:68–93
Punzi M, Anbalagan A, Börner RA, Svensson BM, Jonstrup M, Mattiasson B (2015) Degradation of a textile azo dye using biological treatment followed by photo-Fenton oxidation: evaluation of toxicity and microbial community structure. Chem Eng J 270:290–299
Ungureanu G, Santos S, Boaventura R, Botelho C (2015) Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. J Environ Manag 151:326–342
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085
Yu J, Yang GG, Pan YP, Lu QF, Yang W, Gao JZ (2014) Poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel induced by glow-discharge electrolysis plasma and its adsorption properties for cationic dyes. Plasma Sci Technol 16:767–776
Wang L, Zhang JP, Wang AQ (2011) Fast removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite composite. Desalination 266:33–39
Liu PF, Gao WJ, Zhang QS, Chen K, Zhang J, Chen L, Zhang XY, Wang K (2015) Temperature-sensitive hydrogel modified by polymerizable liquid crystal AAc-Brij-58: optical and protein adsorption/desorption behaviors. React Funct Polym 89:1–8
Wang L, Zhang JP, Wang AQ (2008) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/montmorillonite superadsorbent nanocomposite. Colloids Surf A 322:47–53
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Wang AQ (2010) Enhanced adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/vermiculite hydrogel composites. J Environ Sci 22:486–493
Luo JW, Han GC, **e MJ, Cai ZR, Wang XY (2015) Quaternized chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite resin and its adsorption behavior. Iran Polym J 24:531–539
Bekçi Z, Özveri C, Seki Y, Yurdakoç K (2008) Sorption of malachite green on chitosan bead. J Hazard Mater 154:254–261
**ng Y, Sun XM, Li BH (2009) Poly(methacrylic acid)-modified chitosan for enhancement adsorption of water-soluble cationic dyes. Polym Eng Sci 49:272–280
Nguyen NT, Liu JH (2013) Fabrication and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan hydrogel thin films via UV irradiation. Eur Polym J 49:4201–4211
Gad YH (2008) Preparation and characterization of poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid)/chitosan hydrogel using gamma irradiation and its application in wastewater treatment. Radiat Phys Chem 77:1101–1107
Wang XY, Zhou MH, ** XL (2012) Application of glow discharge plasma for wastewater treatment. Electrochim Acta 83:501–512
Joshi AA, Locke BR, Arce P, Finney WC (1995) Formation of hydroxyl radicals, hydrogen peroxide and aqueous electrons by pulsed streamer corona discharge in aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 41:3–30
Harada K, Iwaski T (1974) Syntheses of amino acids from aliphatic carboxylic acid by glow discharge electrolysis. Nature 250:426–428
Malik MA, Ghaffar A, Malik SA (2001) Water purification by electrical discharges. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 10:82–91
Brisset JL, Moussa D, Doubla A, Hnatiuc E, Hnatiuc B, Youbi GK, Herry JM, Naïtali M, Bellon-Fontaine MN (2008) Chemical reactivity of discharges and temporal post-discharges in plasma treatment of aqueous media: examples of gliding discharge treated solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:5761–5781
Friedrich JF, Mix R, Schulze RD, Meyer-Plath A, Joshi R, Wettmarshausen S (2008) New plasma techniques for polymer surface modification with monotype functional groups. Plasma Process Polym 5:407–423
Lu QF, Yu J, Gao JZ, Yang W, Li Y (2011) Glow-discharge electrolysis plasma induced synthesis of polyvinylpyrrolidone/acrylic acid hydrogel and its adsorption properties for heavy-metal ions. Plasma Process Polym 8:803–814
Yu J, Pan YP, Lu QF, Yang W, Gao JZ, Li Y (2012) Synthesis and swelling behaviors of P(AMPS-co-AAc) superabsorbent hydrogel produced by glow-discharge electrolysis plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33:219–235
Mukhopadhyay P, Sarkar K, Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharyya A, Mishra R, Kundu PP (2014) pH sensitive N-succinyl chitosan grafted polyacrylamide hydrogel for oral insulin delivery. Carbohydr Polym 112:627–637
Bao Y, Ma JZ, Li N (2011) Synthesis and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(AA-co-AM-co-AMPS)/MMT superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 84:76–82
Malik MA, Ahmed M, Rehman E, Naheed R, Ghaffar A (2003) Synthesis of superabsorbent copolymers by pulsed corona discharges in water. Plasmas Polym 8:271–279
Mukhopadhyay P, Sarkar K, Soam S, Kundu PP (2013) Formulation of pH-responsive carboxymethyl chitosan and alginate beads for the oral delivery of insulin. J Appl Polym Sci 129:835–845
Bhattacharyya R, Ray SK (2014) Micro- and nano-sized bentonite filled composite superabsorbents of chitosan and acrylic copolymer for removal of synthetic dyes from water. Appl Clay Sci 101:510–520
Ahn JS, Choi HK, Cho CS (2001) A novel mucoadhesive polymer prepared by template polymerization of acrylic acid in the presence of chitosan. Biomaterials 22:923–928
Zhou JQ, Wang JW (2009) Immobilization of alliinase with a water soluble–insoluble reversible N-succinyl-chitosan for allicin production. Enzyme Microb Technol 45:299–304
Zhang JP, Wang Q, Wang AQ (2007) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite superabsorbent composites. Carbohydr Polym 68:367–374
Limparyoon N, Seetapan N, Kiatkamjornwong S (2011) Acrylamide/2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid and associated sodium salt superabsorbent copolymer nanocomposites with mica as fire retardants. Polym Degrad Stab 96:1054–1063
Pourjavadi A, Tehrani ZM, Salimi H, Banazadeh A, Abedini N (2015) Hydrogel nanocomposite based on chitosan-g-acrylic acid and modified nanosilica with high adsorption capacity for heavy metal ion removal. Iran Polym J 24:725–734
Wang Y, Wang W, Wang A (2013) Efficient adsorption of methylene blue on an alginate-based nanocomposite hydrogel enhanced by organo-illite/smectite clay. Chem Eng J 228:132–139
Vimonses V, Lei S, ** B, Chow CWK, Saint C (2009) Adsorption of Congo red by three Australian kaolins. Appl Clay Sci 43:465–472
Lorenc-Grabowska E, Gryglewicz G (2007) Adsorption characteristics of Congo red on coal-based mesoporous activated carbon. Dyes Pigments 74:34–40
Chen ZH, Zhang JA, Fu JW, Wang MH, Wang XZ, Han RP, Xu Q (2014) Adsorption of methylene blue onto poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) nanotubes: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics analysis. J Hazard Mater 273:263–271
Li XL, Li YF, Zhang SD, Ye ZF (2012) Preparation and characterization of new foam adsorbents of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan composites and their removal for dye and heavy metal from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 183:88–97
Şölener M, Tunali S, Özcan AS, Özcan A, Gedikbey T (2008) Adsorption characteristics of lead(II) ions onto the clay/poly(methoxyethyl)acrylamide (PMEA) composite from aqueous solutions. Desalination 223:308–322
Kumar PS, Ramalingam S, Senthamarai C, Niranjanaa M, Vijayalakshmi P, Sivanesan S (2010) Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 261:52–60
Mahdavinia GR, Aghaie H, Sheykhloie H, Vardini MT, Etemadi H (2013) Synthesis of CarAlg/MMt nanocomposite hydrogels and adsorption of cationic crystal violet. Carbohydr Polym 98:358–365
Panic VV, Madzarevic ZP, Volkov-Husovic T, Velickovic SJ (2013) Poly(methacrylic acid) based hydrogels as sorbents for removal of cationic dye basic yellow 28: kinetics, equilibrium study and image analysis. Chem Eng J 217:192–204
Ngah WSW, Ariff NFM, Hashim A, Hanafiah MAKM (2010) Malachite green adsorption onto chitosan coated bentonite beads: isotherms, kinetics and mechanism. Clean Soil Air Water 38:394–400
Peng Q, Liu MX, Zheng JW, Zhou CR (2015) Adsorption of dyes in aqueous solutions by chitosan–halloysite nanotubes composite hydrogel beads. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 201:190–201
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21367023 and 21567025), Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (Nos. 1308RJZA144 and 1208RJZA161), Scientific Research Project in Higher Education Institutions of Gansu Province (No. 2013-019), and Key Project of Young Teachers’ Scientific Research Promotion of Northwest Normal University (No. NWNU-LKQN-12-9), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Li, Y., Lu, Q. et al. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption of cationic dyes by CS/P(AMPS-co-AM) hydrogel initiated by glow-discharge-electrolysis plasma. Iran Polym J 25, 423–435 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-016-0434-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-016-0434-8