Abstract
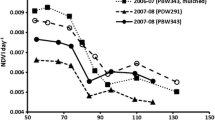
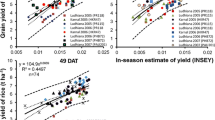
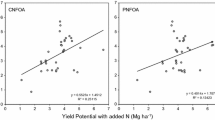
Blanket fertilizer nitrogen (N) recommendations for large irrigated wheat tracts lead to low N-use efficiency due to field-to-field variability in soil N supply and seasonal variability in yield. To achieve high N use efficiency, a site-specific N management strategy using GreenSeeker™ optical sensor was evaluated. We conducted seven field experiments during 2004–2006 at three locations to define relationships between in-season sensor measurements and yield of wheat and to know whether response of wheat to fertilizer N can be estimated by sensor measurements. During 2005–2007, four field experiments were conducted to assess the sensor-based N management strategy and to work out prescriptive N management to be followed prior to applying sensor-guided fertilizer dose. We observed robust relationships between in-season sensor-based estimates of yield at Feekes 5–6 and 7–8 stages and actual wheat yields. Response of wheat to fertilizer N defined by the sensor was highly correlated with harvest response index. Sensor-guided fertilizer N applications resulted in high yield levels and high N-use efficiency. Application of 90 kg N ha-1 at planting or in two equal doses at planting and crown root initiation stage was the appropriate prescriptive fertilizer N management. This study reveals that high N-use efficiency in irrigated wheat can be achieved by replacing blanket fertilizer recommendation by an optical sensor-based N management strategy consisting of applying moderate amount of fertilizer N at planting and crown root initiation stages and sensor-guided fertilizer N dose at Feekes 5–6 or 7–8 stages of wheat.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari C, Bronson KF, Panaullah GM, Regmi AP, Saha PK, Dobermann A, Olk DC, Hobbs PR, Pasuquin E (1999) On-farm N supply and N nutrition in the rice–wheat system of Nepal and Bangladesh. Field Crops Res 64:273–286. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00063-5
Aparicio N, Villegas D, Araus JL, Casadesús J, Royo C (2002) Relationship between growth traits and spectral vegetation indices in durum wheat. Crop Sci 42:1547–1555. doi:10.2135/cropsci2002.1547
Báez-González AD, Chen P, Tiscareño-López M, Srinivasan R (2002) Using satellite and field data with crop growth modeling to monitor and estimate maize yield in Mexico. Crop Sci 42:1943–1949. doi:10.2135/cropsci2002.1943
Baligar VC, Fageria NK, He ZL (2001) Nutrient use efficiency in plants. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 32:921–950. doi:10.1081/CSS-100104098
Bijay-Singh, Yadvinfrt-Singh (2003) Nitrogen management in rice–wheat system in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. In: Singh Y, Singh B, Nayyar VK, Jagmohan-Singh (eds) Nutrient management for sustainable rice–wheat crop** system. National Agricultural Technology Project, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, and Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana. pp 99–114
Bremner JM (1965a) Total nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Agronomy monograph 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1149–1178
Bremner JM (1965b) Inorganic forms of nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Agronomy monograph 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1179–1237
Campbell JB (2002) Introduction to remote sensing, 3rd edn. The Guilford Press, New York
Chaudhary TN, Katoch KK (1981) Fertiliser-N management for wheat in coarse textured soils. Fert News 26(12):36–39
Dobermann A, Witt C, Abdulrachman S, Gines HC, Nagarajan R, Son TT, Tan PS, Wang GH, Chien NV, Thoa VTK, Phung CS, Stalin P, Muthukrishanan P, Ravi V, Babu M, Sethanathan GC, Adviento MAA (2003) Soil fertility and indigenous nutrient supply in irrigated domains of Asia. Agron J 95:913–927. doi:10.2134/agronj2003.0913
Doerge TA, Roth RI, Gardner BR (1991) Nitrogen fertilizer management in Arizona, College of Agriculture, The University of Arizona, Tucson. p 87
Fox RH, Roth GW, Iversen KV, Piekielek WP (1989) Soil and tissue nitrate tests compared for predicting soil nitrogen availability to corn. Agron J 81:971–974. doi:10.2134/agronj1989.00021962008100060025x
Giller KE, Chalk P, Dobermann A, Hammond L, Heffer P, Ladha JK, Nyamudeza P, Maene L, Ssali H, Freney J (2004) Emerging technologies to increase the efficiency of use of fertilizer nitrogen. In: Mosier AR, Syers JK, Freney J (eds) Agriculture and the nitrogen cycle: assessing the impacts of fertilizer use on food production and the environment, SCOPE 65 (Scientific Committee on Problems of the Environment). Island Press, Washington, pp 35–51
Hong SD, Fox RH, Piekielek WP (1990) Field evaluation of several chemical indexes of soil nitrogen availability. Plant Soil 123:83–88. doi:10.1007/BF00009929
IAEA (2000) Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer application in irrigated wheat: Results of a co-ordinated research project organized by the joint FAP/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture 1994–1998, IAEA TECDOC-1164. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, p 245
Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute (2007) Agricultural Research Data Book, IASRI, Library Avenue, New Delhi. p. 333
Johnson GV, Raun WR (2003) Nitrogen response index as a guide to fertilizer management. J Plant Nutr 26:249–262. doi:10.1081/PLN-120017134
Justes E, Meynard JM, Mary B, Plénet D (1997) Management of N nutrition: diagnosis using stem base extract: JUBIL method. In: Lemaire G (ed) Diagnosis of the Nitrogen Status in Crops. Springer, Berlin, pp 163–187
Katyal JC, Bijay-Singh, Vlek PLG, Buresh RJ (1987) Efficient nitrogen use as affected by urea application and irrigation sequence. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:366–370. doi:10.2136/sssaj1987.03615995005100020020x
Khosla R, Alley MM (1999) Soil-specific nitrogen management on mid-Atlantic coastal plain soils. Better Crops 83(3):6–7
Kranz WL, Kanwar RS (1995) Spatial distribution of leachate losses due to pre-plant tillage methods. In: Clean water–clean environment—21st century. Proceedings of Conference Working Group on Water Quality, vol 2. American Society of Agricultural Engineering, St Joseph. pp 107–110
Ladha JK, Pathak H, Krupnik TJ, Six J, van Kessel C (2005) Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen in cereal production: retrospect and prospects, Adv Agron 87:85–156. doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(05)87003-8
Large EC (1954) Growth stages in cereals. Plant Pathol 3:128–129
Lemaire G, Gastal F (1997) N uptake and distribution in plant canopies. In: Lemaire G (ed) Diagnosis of the nitrogen status in crops. Springer, Germany, pp 3–43
Li F, Miao Y, Zhang F, Cui Z, Li R, Chen X, Zhang H, Schrodner J, Raun WR, Jia L (2009) In-season optical sensing improves nitrogen use efficiency for winter wheat. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:1566–1574. doi:10.2136/sssaj2008.0150
Ma BL, Morrison MJ, Dwyer L (1996) Canopy light reflectance and field greenness to assess nitrogen fertilization and yield of maize. Agron J 88:915–920. doi:10.2134/agronj1996.00021962003600060011x
Ma BL, Lianne LM, Dwyer M, Costa C, Cober ER, Morrison MJ (2001) Early prediction of soybean yield from canopy reflectance measurements. Agron J 93:1227–1234. doi:10.2134/agronj2001.1227
Magdoff FR, Jokela WE, Fox RH, Griffin GF (1990) A soil test for nitrogen availability in the northeastern United States. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 21:1103–1115. doi:10.1080/00103629009368293
Meelu OP, Saggar S, Maskina MS, Rekhi RS (1987) Time and source of nitrogen application in rice and wheat. J Agril Sci Camb 109:387–391. doi:10.1017/S0021859600080813
Mullen RW, Freeman KW, Raun WR, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Solie JB (2003) Identifying an in-season response index and the potential to increase wheat yield with nitrogen. Agron J 95:347–351. doi:10.2134/agronj2003.0347
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate, USDA Cir. 939, US Govt. Print Office, Washington
Ortiz-Monasterio JIR, Sayre KD, Pena J, Fischer RA (1994) Improving the nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated spring wheat in the Yaqui Valley of Mexico. Trans 15th World Cong Soil Sci 5b:348–349
Peñuelas J, Gamon JA, Fredeen AL, Merino J, Field CB (1994) Reflectance indices associated with physiological changes in nitrogen- and water-limited sunflower leaves. Remote Sens Environ 48:135–146. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(94)90136-8
Raun WR, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Solie JB, Lukina EV, Thomason WE, Schepers JS (2001) In-season prediction of potential grain yield in winter wheat using canopy reflectance. Agron J 93:131–138. doi:10.2134/agronj2001.931131x
Raun WR, Solie JB, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Mullen RW, Freeman KW, Thomason WE, Lukina EV (2002) Improving nitrogen use efficiency in cereal grain production with optical sensing and variable rate application. Agron J 94:815–820. doi:10.2134/agronj2002.0815
Schröder JJ, Neeteson JJ, Oenema O, Struik PC (2000) Does the crop or the soil indicate how to save nitrogen in maize production? Reviewing the state of the art. Field Crops Res 66:151–164. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(00)00072-1
Thenkabail PS, Smith RB, DePauw E (2000) Hyperspectral vegetation indices and their relationships with agricultural crop characteristics. Remote Sens Environ 71:158–182. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(99)00067-X
Walkley A (1947) A critical examination of a rapid method for determining organic carbon in soils: effect of variations in digestion conditions and of inorganic soil constituents. Soil Sci 63:251–263
Yadvinder-Singh, Bijay-Singh, Ladha JK, Singh JP, Choudhary OP (2007) Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency for sustainable rice-wheat production system in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. In: Abrol YP, Raghuram N, Sachdev MS (eds) Agricultural nitrogen use and its environmental implications. I.K. International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, pp 139–164
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock DH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice, 3rd edn. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños
Acknowledgments
The financial and technical support received from the USDA and encouragement from Dr. Ryan Moore to undertake this study is gratefully acknowledged. The first author acknowledges the financial support received from Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi in the form of National Professor project to continue the work on GreenSeeker optical sensor. Thanks are due to Drs. James Schepers, Arnall Brain, and Bram Govaerts for technical support at different times and useful discussions during the course of the studies. We take the opportunity to thank Punjab Agricultural University (Ludhiana), Directorate of Wheat Research-ICAR (Karnal) and Project Directorate for Crop** System Research-ICAR (Modipuram) for providing the necessary facilities used in conducting the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bijay-Singh, Sharma, R.K., Jaspreet-Kaur et al. Assessment of the nitrogen management strategy using an optical sensor for irrigated wheat. Agronomy Sust. Developm. 31, 589–603 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0005-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0005-5