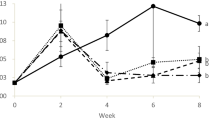
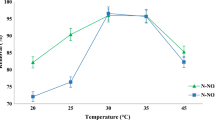
Abstract
This investigation was carried out to remove total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) in aquaculture system by employing immobilized heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial consortium. The bacterial consortium was immobilized on biodegradable and low cost, wood powder. Among the three wood powders tested, Thespesia populnae wood powder showed the highest (99%) nitrifying activity. Nitrifying bacteria immobilized Thespesia populnae wood powder at three different concentrations was applied in a 100-L tank stocked with Labeo rohita for TAN removal. The experiment tanks with the addition of immobilized wood powder were observed TAN concentration below 0.15 ± 0.1 mg/l. This was lower than the control tank without the addition of immobilized wood powder. A highest average body weight gain of Labeo rohita was observed in experiment tanks. The haematology profile in experiment tanks revealed a highest Hb and RBC count, reduction in WBC count and low blood ammonia concentration, which was contrary in control tanks. Histological study showed that severe gill damage occurred in control group, whereas experiment fishes possessed normal gill morphology. The immobilized wood powder was also applied in one hectare aquaculture earthen pond and observed a complete TAN elimination within 24 h. The present study reveals that the heterotrophic nitrifiers immobilized on wood powder could carry out efficient nitrification and thus eliminates TAN from aquaculture pond water and enhances fish growth.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ha, H.P.; Thu, N.H.; Thanh, T.H.; Tung, T.T.; Phuong, D.L.; Cong, L.T.N.: Isolation and selection of nitrifying bacteria with high biofilm formation for treatment of ammonium polluted aquaculture water. J. Vietnam. Environ. 8(1), 33–40 (2016)
Devi, P.A.; Padmavathy, P.; Aanand, S.; Aruljothi, K.: Review on water quality parameters in freshwater cage fish culture. Int. J. Appl. Res. 3(5), 114–120 (2017)
Kesharwani, S.; Dube, K.K.; Khan, R.: Effect of dichlorvos (nuvan) on behaviour, haematology and histology of freshwater teleost Labeo rohita. Int. J. Sci. Res. Methodol. 8(3), 132–146 (2018)
Jasmin, J.; Rahman, M.D.; Rahman, M.D.: Haematological changes in Labeo rohita (H.) due to exposure of pesticides, Difenoconazole and Thiamethoxam. Int. J. Contemp. Res. Rev. 9(1), 20199–20205 (2018)
Tzollas, N.M.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Anthemidis, A.N.; Stratis, J.A.: A new approach to indophenol blue method for determination of ammonium in geothermal waters with high mineral content. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 90(2), 115–126 (2010)
Moustafa, G.G.; Shaaban, F.E.; Hadeed, A.H.A.; Elhady, W.M.: Immunotoxicological, biochemical, and histopathological studies on roundup and stomp herbicides in Nile catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Vet. World 9(6), 638–642 (2016)
Gross, A.; Nemirovsky, A.; Zilberg, D.; Khaimov, A.; Brenner, A.; Snir, E.; Ronen, Z.; Nejidat, A.: Soil nitrifying enrichment as biofilter starters in intensive recirculating saline water aquaculture. Aquaculture 223(1–4), 51–62 (2003)
Ogbonna, J.F.; Chinomso, A.A.: Determination of the concentration of ammonia that could have lethal effect on fish pond. Asian Res. Publ. Netw. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 5(2), 1–5 (2010)
Padmavathi, P.; Sunitha, K.; Veeraiah, K.: Efficacy of probiotics in improving water quality and bacterial flora in fish ponds. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 6(49), 7471–7478 (2012)
Karthik, R.; Pushpam, A.C.; Chelvan, Y.; Vanitha, M.C.: Efficacy of probiotic and nitrifier bacterial consortium for the enhancement of Litopenaeus Vannamei aquaculture. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Res. 1(1), 29–34 (2015)
Basavarajappa, S.H.; Raju, N.S.; Supreeth, M.; Hosmani, S.P.: Isolation and identification of heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria from sewage sludge biotechnology. Indian J. Appl. Res. 5(8), 228–229 (2015)
Li, Y.; Chapman, S.J.; Nicol, G.W.; Yao, H.: Nitrification and nitrifiers in acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 116, 290–301 (2018)
Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, B.: Immobilization of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria by polyvinyl alcohol and sodium alginate. Braz. J. Microbiol. 48(3), 515–521 (2017)
Fumasoli, A.; Burgmann, H.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Wells, G.F.; Beck, K.; Mohn, J.; Morgenroth, E.; Udert, K.M.: Growth of Nitrosococcus-related ammonia oxidizing bacteria coincides with extremely low ph values in wastewater with high ammonia content. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(12), 6857–6866 (2017)
Shan, H.; Obbard, P.: Ammonia removal from freshwater using nitrifying bacteria enriched from seawater aquaculture pond. Biotech. Lett. 25(17), 1469–1471 (2003)
Erna, N.M.; Banerjee, S.; Khatoon, H.; Shariff, M.; Yusoff, F.M.D.: Immobilized nitrifying bacterial consortium for improving water quality, survival and growth of Penaeus monodon Fabricius 1798 postlarvae in hatchery system. Asian Fish. Sci. 26, 212–221 (2013)
Manju, N.J.; Deepesh, V.; Achuthan, C.; Philip, R.; Singh, I.S.B.: Immobilization of nitrifying bacterial consortia on wood particles for bioaugmenting nitrification in shrimp culture systems. Aquaculture 294(1–2), 65–75 (2009)
Sahaya, S.D.; Akila, V.; Ashok, S.; Manikandan, A.; Santhanam, P.; Rajakumar, S.: Enrichment and isolation of nitrifying bacteria and molecular characterization of optimized nitrifiers from mangrove soil. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinf. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 5(1), 712–724 (2019)
Bollmann, A.; French, E.; Laanbroek, H.J.: Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of ammonia oxidizing bacteria and archaea adapted to low ammonium concentrations. Methods Enzymol. 486, 55–88 (2011)
Wood, T.M.; Saddler, J.N.: Increasing the availability of cellulose in biomass materials. Methods Enzymol. Acad. Press 160, 3–11 (1988)
APHA: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC (2005)
Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J.: The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–270 (1951)
Carrol, N.V.; Longley, W.W.; Roe, J.H.: Glycogen determination in liver and muscle by use of anthrone reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 220, 583–593 (1956)
Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanles, G.H.: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 226(1), 497–509 (1957)
Hesser, E.F.: Methods for routine fish hematology. Progress. Fish-Cultur. 22(4), 164–171 (1960)
Blaxhall, P.C.; Daisley, K.W.: Routine haematological methods for use with fish blood. J. Fish Biol. 5, 771–781 (1973)
Culling, C.F.A.; Allison, R.T.; Barr, W.T.: Cellular Pathology Techniques, 4th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2014)
Uemoto, H.; Saiki, H.: Distribution of Nitrosomonas europaea and Paracoccus denitrificans immobilized in tubular polymeric gel for nitrogen removal. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66(2), 816–819 (2000)
Shan, H.; Obbard, J.P.: Ammonia removal from prawn aquaculture water using immobilized nitrifying bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57, 791–798 (2001)
Muter, O.; Mihailova, A.; Berzins, A.; Svirksts, K.; Patmalnieks, A.; Strikauska, S.; Grube, M.: Optimization of nitrification process by a bacterial consortium in the submerged biofiltration system with ceramic bead carrier. J. Microbial. Biochem. Technol. 6, 148–153 (2014)
Lu, S.; Liao, M.; **e, C.; He, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.: Removing ammonium from aquaculture ponds using suspended biocarrier-immobilized ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. Ann. Microbiol. 65(4), 2041–2046 (2015)
Dzionek, A.; Wojcieszynska, D.; Guzik, U.: Natural carriers in bioremediation: a review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 19(5), 28–36 (2016)
Zhang, W.W.; Andong, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.N.; Wei, Y.Q.; Chen, L.X.: Isolation and characterization of a heterotrophic nitrifier Proteus mirabilis strain V7 and its potential application in NH4 +–N removal. Ann. Microbiol. 10, 1–8 (2014)
Pakhira, C.; Nagesh, T.S.; Abraham, T.J.; Dash, G.; Behera, S.: Stress responses in Labeo rohita transported at different densities. Aquac. Rep. 2, 39–45 (2015)
Shin, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, S.D.; Kang, J.C.: Toxic effects of ammonia exposure on growth performance, hematological parameters, and plasma components in rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, during thermal stress. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 19(1), 44–48 (2016)
Naidu, N.G.; Kumar, V.; Shameem, U.: Acute and sub acute toxic effect of ammonia on behavioural and haematological responses of Indian major carp Labeo rohita Ham, 1822. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 5(2), 332–335 (2017)
Li, Y.; Boyd, C.E.: Laboratory tests of bacterial amendments for accelerating oxidation rates of ammonia, nitrite and organic matter in aquaculture pond water. Aquaculture 460, 45–48 (2016)
Maheswaran, R.; Devapaul, A.; Muralidharan, S.; Velmurugan, B.; Ignacimuthu, S.: Haematological studies of fresh water fish, Clarias batrachus (L.) exposed to mercuric chloride. Int. J. Integr. Biol. 2(1), 49–54 (2008)
Yoon, G.; Al-Saadi, N.; Ambuali, A.: Gill histology of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus following chronic and acute exposure to ammonia. J. Agric. Mar. Sci. 20, 66–72 (2015)
Gobinath, J.; Ramanibai, R.: Histopathological studies in the gill, liver and kidney of the freshwater fish Labeo rohita fingerlings. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3(3), 10296–10301 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahaya Sukeetha, D., Dinesh Kumar, S., Manikandan, A. et al. Effect of Immobilized Nitrifying Bacterial Consortium on Ammonia Biodegradation in Aquaculture Pond and Enhanced Growth of Labeo rohita: An In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04073-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04073-5