Abstract
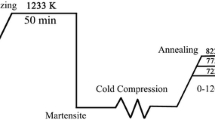
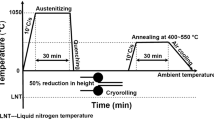
A simple process of 50% cold-rolled and annealed at different temperatures and times to obtain ultrafine-grained structured low-carbon steel with superior mechanical properties is utilized in this investigation. The microstructure evolves from bulky austenite to lathy martensite and then ultrafine ferrite grain with nanocarbide particles. Recovery occurs in the specimen annealed at about \(500\,{^{\circ }}\)C and 30 min, while recrystallization happens in the specimen annealed at \(550\,{^{\circ }}\)C and 30 min. The optimal balance between the tensile strength (867 MPa) and elongation (16.7%) is obtained in the specimen annealed at \(550\,{^{\circ }}\)C and 30 min, in which the mean size of ferrite grains and nanocarbides is 330 and 55 nm, respectively. Moreover, the distribution of ferrite grain conforms to the Gaussian distribution. The recrystallization activation energy of low-carbon steel with ultrafine grain is calculated to be \(320,682\,\hbox {J}\, \hbox {mol}^{-1}\) based on the Arrhenius equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song, R.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.: Overview of processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained bcc steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 441, 1–17 (2006)
Li, X.; **g, T.F.; Lu, M.M.; Zhang, J.W.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine lath-shaped low carbon steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 21, 1496–1499 (2012)
Sauvage, X.; Lefebvre, W.; Genevois, C.; Ohaakib, S.; Hono, K.: Complementary use of transmission electron microscopy and atom probe tomography for the investigation of steels nanostructured by severe plastic deformation. Scr. Mater. 60, 1056–1061 (2009)
Tsuji, N.; Ueji, R.; Minamino, Y.; Saito, Y.: A new and simple process to obtain nano-structured bulk low-carbon steel with superior mechanical property. Scr. Mater. 46, 305–310 (2002)
Tsuji, N.; Ito, Y.; Saito, Y.; Minamino, Y.: Strength and ductility of ultrafine grained aluminum and iron produced by ARB and annealing. Scr. Mater. 47, 893–899 (2002)
Tsuji, N.; Saito, Y.; Ito, Y.; Utsunomiya, H.; Sakai, T.: Ultra-fine grained ferrous and aluminum alloys produced by accumulative roll-bonding. In: Mishra, R.S. (ed.) The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS), pp. 207–218. Warrendale (2000)
Ito, Y.; Tsuji, N.; Saito, Y.; Utsunomiya, H.; Sakai, T.: Change in microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-fine grained aluminum during annealing. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 64, 429–437 (2002)
Tsuji, N.; Ueji, R.; Saito, Y.: Ultra-fine grains in ultra low carbon IF steel highly strained by ARB. Mater. Jpn. 39, 961 (2000). (in Japanese)
Wang, B.F.; Sun, J.Y.; Zou, J.D.; Vincent, S.; Li, Juan: Mechanical responses, texture and microstructural evolution of high purity aluminum deformed by equal channel angular pressing. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 3698–3704 (2015)
Valiev, R.Z.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Rauch, E.F.; Baudelet, B.: Microstructural evolution and the mechanical properties of an aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 7789–7795 (2012)
Matsybara, K.; Miyahara, Y.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G.: Develo** superplasticity in a magnesium alloy through a combination of extrusion and ECAP. Acta Mater. 51, 3073–3084 (2003)
Shin, D.H.; Kim, B.C.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.S.: Microstructure evolution in a commercial low carbon steel by equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 48, 2247–2255 (2000)
Sabbaghianrad, S.; Kawasaki, M.; Langdon, T.G.: Microstructural evolution and the mechanical properties of an aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 7789–7795 (2012)
Dobatkin, S.V.; Rybalchenko, O.V.; Enikeev, N.A.; Tokar, A.A.; Abramova, M.M.: Formation of fully austenitic ultrafine-grained high strength state in metastable Cr-Ni-Ti stainless steel by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Lett. 166, 276–279 (2016)
Takaki, S.; Kawasaki, K.; Kimura, Y.: Ultrafine grained materials. In: Mishra, R. S. (eds.) The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS), pp. 247–55. Warrendale (2000)
Belyakov, A.; Sakika, Y.; Hara, T.; Kimura, Y.; Tsuzaki, K.: Annealing behavior of submicrocrystalline oxide-bearing iron produced by mechanical alloying. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34, 131–138 (2003)
Okitsu, Y.; Takatab, N.; Tsuji, N.: A new route to fabricate ultrafine-grained structures in carbon steels without severe plastic deformation. Scr. Mater. 60, 76–79 (2009)
Sadeghpour, S.; Kermanpur, A.; Najafizadeh, A.: Influence of Ti microalloying on the formation of nanocrystalline structure in the 201L austenitic stainless steel during martensite thermomechanical treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 584, 177–183 (2013)
Ma, Y.Q.; **, J.E.; Lee, Y.K.: A repetitive thermomechanical process to produce nano-crystalline in a metastable austenitic steel. Scr. Mater. 52, 1311–1315 (2005)
Alizamini, A.; Militzer, M.; Poole, W.J.: A novel technique for develo** bimodal grain size distributions in low carbon steels. Scr. Mater. 57, 1065–1068 (2007)
Wang, T.S.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, M.; Lvb, B.: A novel process to obtain ultrafine-grained low carbon steel with bimodal grain size distribution for potentially improving ductility. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 485, 456–460 (2008)
Morrison, W.B.: The effects of grain size on the stress-strain relationship in low carbon steel. Trans. ASM 59, 824–846 (1966)
Ueji, R.; Tsuji, N.; Minamino, Y.; Koizumi, Y.: Ultragrain refinement of plain low carbon steel by coldrolling and annealing of martensite. Acta Mater. 50, 4177–4189 (2002)
Hosseini, S.M.; Alishahi, M.; Najafizadeh, A.; Kermanpur, A.: The improvement of ductility in nano/ultrafine grained low carbon steels via high temperature short time annealing. Mater. Lett. 74, 206–208 (2012)
Tsuji, N.; Maki, T.: Enhanced structural refinement by combining phase transformation and plastic deformation in steels. Scr. Mater. 60, 1044–1049 (2009)
Bao, Y.Z.; Adachi, Y.; Toomine, Y.; Xu, P.G.; Suzuki, T.; Tomota, Y.: Dynamic recrystallization by rapid heating followed by compression for a 17Ni–0.2C martensite steel. Scr. Mater. 53, 1471–1476 (2005)
Hazra, S.S.; Pereloma, E.V.; Gazder, A.A.: Microstructure and mechanical properties after annealing of equal-channel angular pressed interstitial-free steel. Acta Mater. 59, 4015–4029 (2011)
Nayaka, S.H.; Chaudhari, G.P.; Daniel, B.S.S.: Grain growth kinetics of accumulative roll bonded AZ61 alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 585, 387–391 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Q., Xu, G., Tian, Jy. et al. The Recrystallization Behavior in Ultrafine-Grained Structure Steel Fabricated by Cold Rolling and Annealing. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 4771–4777 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2633-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2633-9