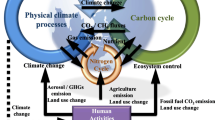
Abstract
The development of coupled earth/climate system models in China over the past 20 years is reviewed, including a comparison with other international models that participated in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) from phase 1 (CMIP1) to phase 4 (CMIP4). The Chinese contribution to CMIP is summarized, and the major achievements from CMIP1 to CMIP3 are listed as a reference for assessing the strengths and weaknesses of Chinese models. After a description of CMIP5 experiments, the five Chinese models that participated in CMIP5 are then introduced. Furthermore, following a review of the current status of international model development, both the challenges and opportunities for the Chinese climate modeling community are discussed. The development of high-resolution climate models, earth system models, and improvements in atmospheric and oceanic general circulation models, which are core components of earth/climate system models, are highlighted. To guarantee the sustainable development of climate system models in China, the need for national-level coordination is discussed, along with a list of the main components and supporting elements identified by the US National Strategy for Advancing Climate Modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anav, A., P. Friedlingstein, M. Kidston, et al., 2013: Evaluating the land and ocean components of the global carbon cycle in the CMIP5 Earth System Models. J. Climate, 26, 6801–6843.
Arora, V. K., J. F. Scinocca, G. J. Boer, et al., 2011: Carbon emission limits required to satisfy future representative concentration pathways of greenhouse gases. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L05805, doi:10.1029/2010GL046270.
Bao, Q., P. Lin, T. Zhou, et al., 2013: The Flexible Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System Model, Spectral Version 2: FGOALS-s2. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 561–576.
Bellenger, H, E. Guilyardi, J. Leloup, et al., 2013: ENSO representation in climate models: From CMIP3 to CMIP5. Climate Dyn., 42, 1999–2018, doi: 10.1007/s00382-013-1783-z.
Chen **aolong, Zhou Tianjun, and Guo Zhun, 2014: Climate sensitivities of two versions of FGOALS model to idealized radiative forcing. Sci. China Earth Sci., 57, 1363–1373, doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4692-4.
Collins, W. J., N. Bellouin, M. D. Boucher, et al., 2011: Development and evaluation of an Earth-System Model-HadGEM2. Geosci. Model Dev., 4, 997–1062, doi:10.5194/gmdd-4-997-2011.
Dong, L., T. J. Zhou, and B. Wu, 2014: Indian Ocean warming during 1958–2004 simulated by a climate system model and its mechanism. Climate. Dyn., 42, 203–217.
—, and —, 2014: The Indian Ocean sea surface temperature warming simulated by CMIP5 models during the 20th century: Competing forcing roles of GHGs and anthropogenic aerosols, J. Climate, 27, 3348–3362.
Dufresne, J. L., M. A. Foujols, S. Denvil, et al., 2013: Climate change projections using the IPSL-CM5 earth system model: From CMIP3 to CMIP5. Climate Dyn., 40, 2123–2165.
Dunne, J. P., J. G. John, A. J. Adcroft, et al., 2012: GFDL’s ESM2 global coupled climate-carbon earth system models. Part I: Physical formulation and baseline simulation characteristics. J. Climate, 25, 6646–6665.
Flato, G., J. Marotzke, B. Abiodun, et al., 2013. Evaluation of climate models. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Stocker, T. F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1522 pp.
Gates, W. L., P. R., Rowntree, and Q. C. Zeng, 1990: Validation of climate model. Climatic Change 1990: The IPCC Scientific Assessment. Houghton, J. T., G. J. Jenkins, and J. J. Rphraume, Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Great Britain, New York, NY, USA and Melbourne, Australia, 365 pp.
—, J. F. B. Mitchell, G. J. Boer, et al., 1992: Climate modelling, climate prediction and model validation. Climate Change 1992: The Supplementary Report to the IPCC Scientific Assessment. Houghton, J. T., B. A. Callander, and S. K. Varney, Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Great Britain, New York, NY, USA, and Victoria, Australia, 200 pp.
—, A. Henderson-Sellers, G. J. Boer, et al., 1995: Climate models evaluation. Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change. Houghton, J. T., L. G. Meira Filho, B. A. Callander, et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Great Britain, New York, NY, USA and Melbourne, Australia, 572 pp.
Giorgetta, M., J. Jungclaus, C. H. Reick, et al., 2013: Climate and carbon cycle changes from 1850 to 2100 in MPI-ESM simulations for the Coupled Model Inter-comparison Project phase 5. J. Adv. Model Earth Syst., 5, 572–597, doi:10.1002/jame.20038.
He, C., and T. J. Zhou, 2014: The two interannual variability modes of the western North Pacific subtropical high simulated by 28 CMIP5-AMIP models. Climate Dyn., doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2068-x. (in press)
Huang **, Wang Pengfei, Hu Kaiming, et al., 2014: An introduction to the Integrated Climate Model of the Center for Monsoon System Research and its simulated influence of El Niño on East Asianwestern North Pacific climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 31, 1136–1146, doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-3233-1.
Ilyina, T., K. D. Six, J. Segschneider, et al., 2013: Global ocean biogeochemistry model HAMOCC: Model architecture and performance as component of the MPI-Earth System Model in different CMIP5 experimental realizations. J. Adv. Model Earth Syst., 5, 287–315, doi:10.1029/2012MS000178.
Ji, D., L. Wang, J. Feng, et al., 2014: Description and basic evaluation of BNU-ESM version 1. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., 7, 1601–1647.
Jones, C. D., J. K. Hughes, N. Bellouin, et al., 2011: The HadGEM2-ES implementation of CMIP5 centennial simulations. Geosci. Model Dev., 4, 543–570, doi:10.5194/gmd-4-543-2011.
Li Lijuan, Lin Pengfei, Yu Yongqiang, et al., 2013: The Flexible Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System Model Grid-point Version 2: FGOALS-g2. Adv. At-mos. Sci., 30, 543–560.
Long, M. C., K. Lindsay, S. Peacock, et al., 2013: Twentieth-century oceanic carbon uptake and storage in CESM1 (BGC). J. Climate, 26, 6775–6800.
Man Wenmin and Zhou Tianjun, 2011: Forced response of atmospheric oscillations during the last millennium simulated by a climate system model. Chin. Sci. Bull., 56, 3042–3052.
— and —, 2014: Regional-scale surface air temperature and East Asian summer monsoon changes during the last millennium simulated by the FGOALS-gl climate system model. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 31, 765–778.
McAvaney, B. J., C. Covey, S. Joussaume, et al., 2001: Model evaluation. Climate Change 2001: The Science Basis. Houghton, J. T., Y. Ding, D. J. Griggs, et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 881 pp.
Meehl, G. A., J. Boer, C. Covey, et al., 1997: Intercomparison makes for a better climate model. Eos. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, 78, 445–451.
—, —, —, et al., 2000: The Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 81, 313–318.
—, C. Covey, B. McAvaney, et al., 2005: Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 86, 89–93.
—, C. Covey, T. Delworth, et al., 2007: The WCRP CMIP3 multimodel dataset: A new era in climate change research. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 88, 1383–1394, doi: 10.1175/BAMS-88-9-1383.
Qiao, F. L., Y. L. Yuan, Y. Z. Yang, et al., 2004: Waveinduced mixing in the upper ocean: Distribution and application in a global ocean circulation model. Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, L11303, doi:10.1029/2004GL019824.
—, Z. Y. Song, Y. Bao, et al., 2013: Development and evaluation of an Earth System Model with surface gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 118, 4514–4524.
Randall, D. A., R. A. Wood, S. Bony, et al., 2007: Climate models and their evaluation. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 996 pp.
Shao, P., X. B. Zeng, K. Sakaguchi, et al., 2013: Terrestrial carbon cycle: Climate relations in eight CMIP5 Earth System Models. J. Climate, 26, 8744–8764.
Shao Hui, Qian Yongfu, and Wang Qianqian, 1998: Impact of solar radiation diurnal cycle on the simulation results of R15L9. Plateau Meteor., 17, 158–168. (in Chinese)
Song, F. F., and T. Zhou, 2014: Interannual variability of East Asian summer monsoon simulated by CMIP3 and CMIP5 AGCMs: Skill dependence on Indian Ocean-western Pacific anticyclone teleconnection. J. Climate, 27, 1679–1697.
—, —, and Y. Qian, 2014: Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to natural and anthropogenic forcings in the 17 latest CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 596–603.
Song, Y., F. Qiao, and Z. Song, 2012: Improved simulation of the South Asian summer monsoon in a coupled GCM with a more realistic ocean mixed layer. J. Atmos. Sci., 69, 1681–1690.
Song Zhenya, Qiao Fangli, and Wang Chunzai, 2011: The correctness to the spuriously simulated semi-annual cycle of the sea surface temperature in the equatorial eastern Pacific. Sci. China Earth Sci., 54, 438–444, doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4176-3.
Sperber, K. R., H. Annamalai, I. S. Kang, et al., 2013: The Asian summer monsoon: An intercomparison of CMIP5 vs. CMIP3 simulations of the late 20th century. Climate Dyn., 41, 2711–2744.
Sun Hongchuan, Zhou Guangqing, and Zeng Qingcun, 2012: Assessments of the climate system model (CAS-ESM-C) using IAP AGCM4 as its atmospheric component. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 36, 215–233. (in Chinese)
Taylor, K. E., R. J. Stouffer, and G. A. Meehl, 2012: An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93, 485–498.
Tjiputra, J. F., C. Roelandt, M. Bentsen, et al., 2013: Evaluation of the carbon cycle components in the Norwegian Earth System Model (NorESM). Geosci. Model Dev., 2, 845–887.
Volodin, E. M., N. A. Dianskii, and A. V. Gusev, 2010: Simulating present day climate with the INMCM4.0 coupled model of the amospheric and oceanic general circulations. Izv. Atmos. Ocean Phys., 46, 448–466.
Wang Bin, Zhou Tianjun, Yu Yongqiang, et al., 2008: A perspective on earth system model development. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 66, 857–869. (in Chinese)
—, —, —, et al., 2009: A view of earth system model development. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 23, 1–17.
Wang Huijun, Zeng Qingcun, and Zhang Xuehong, 1993: The numerical simulation of the climatic change by CO2 doubling. Sci. China (Ser. B), 36, 451–462.
—, Xu Yongfu, Zhou Tianjun, et al., 2004: Atmospheric science: A vigorous frontier science. Adv. Earth Sci., 19, 525–532. (in Chinese)
Watanabe, S., T. Hajima, K. Sudo, et al., 2011: MIROC-ESM: Model description and basic results of CMIP5-20c3m experiments. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., 4, 1063–1128, doi:10.5194/gmdd-4-1063-2011.
Wu, T. W., R. C. Yu, F. Zhang, et al., 2010: The Bei**g Climate Center atmospheric general circulation model: Description and its performance for the present-day climate. Climate Dyn., 34, 123–147.
—, W. P. Li, J. J. Ji, et al., 2013a: Global carbon budgets simulated by the Bei**g Climate Center Climate System Model for the last century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 118, 4326–4347, doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50320.
Wu Bo and Zhou Tianjun, 2013: Relationships between East Asian-western North Pacific monsoon and ENSO simulated by FGOALS-s2. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 713–725, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2103-6.
Wu Guoxiong, Zhang Xuehong, Liu Hui, et al., 1997: Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land system of LASG (GOALS/LASG) and its performance in simulation study. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 8(Suppl.), 15–28. (in Chinese)
Wu Tongwen, Song Lianchun, Liu ** the short-range operational climate prediction system of China National Climate Center. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 24, 533–543. (in Chinese)
—, —, Li Wei**, et al., 2014: An overview of BCC climate system model development and application for climate change studies. J. Meteor. Res., 28, 34–56, doi: 10.1007/s13351-014-3041-7.
Wu Qizhong, Feng **ming, Dong Wenjie, et al., 2013: Introduction of the CMIP5 experiments carried out by BNU-ESM. Adv. Climate Change Res., 9, 291–294. (in Chinese)
**n **aoge, Wu Tongwen, and Zhang Jie, 2012: Introduction of CMIP5 experiments carried out by BCC Climate System Model. Adv. Climate Change Res., 8, 378–382. (in Chinese)
Yu Yongqiang and Zhang Xuehong, 1998: A modified air-sea flux anomaly coupling scheme. Chin. Sci. Bull., 43, 866–870.
—, Yu Rucong, Zhang Xuehong, et al., 2002: A flexible global coupled climate model. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 19, 169–190.
—, Zhang Xuehong, and Guo Yufu, 2004: Global coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation models in LASG/IAP. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 21, 444–455.
—, Zhi Hai, Wang Bing, et al., 2008: Coupled model simulations of climate changes in the 20th century and beyond. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25, 641–654.
Zhang Jie, Laurent Li, Zhou Tianjun, et al., 2013: Variation of surface temperature during the last millennium in a simulation with the FGOALS-g1 climate system model. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 699–712, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2178-0.
Zhang Lixia and Zhou Tianjun, 2014: An assessment of improvements in global monsoon precipitation simulation in FGOALS-s2. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 31, 165–178.
Zhang Xuehong, Guo Yufu, Yuan Chongguang, et al., 1999: The achievements of general circulation model (GCM) in Institute of Atmospheric Physics. The Greenhouse Effects and Climate Change Research: Advances of Joint Research on “Climate Changes Induced by CO 2 ” Between Chinese Academy of Sciences and U.S. Department of Energy. Tao Shiyan, M. R. Ricnes, Chen Banqin, et al., Eds. Ocean Press, Bei**g, 5–13. (in Chinese)
—, Shi Guangyu, Liu Hui, et al., 2000: IAP Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System Model. Science Press, Bei**g, 251 pp. (in Chinese)
Zhou Tianjun, Zhang Xuehong, Yu Yongqiang, et al., 2000: Response of IAP/LASG GOALS model to the coupling of air-sea freshwater exchange. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 473–486.
—, —, and Yu Yongqiang, 2001: The coupling procedure of air-sea freshwater exchange in climate system models. Chin. Sci. Bull., 46, 83–85.
—, Wang Zaizhi, Yu Rucong, et al., 2005a: The climate system model FGOALS_s using LASG/IAP spectral AGCM SAMIL as its atmospheric component. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 63, 702–715. (in Chinese)
—, Yu Rucong, Wang Zaizhi, et al., 2005b: The Atmospheric General System Model SAMIL and Its Associated Coupled Climate System Model FGOALS_s. China Meteorological Press, Bei**g, 288 pp. (in Chinese)
—, Yu Yongqiang, Liu Hailong, et al., 2007: Progress in the development and application of climate ocean models and ocean-atmosphere. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 1109–1120.
—, Wu Bo, Wen **nyu, et al., 2008: A fast version of LASG/IAP climate system model and its 1000-year control integration. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25, 655–672.
—, Li Bo, Man Wenmin, et al., 2011: A comparison of the Medieval Warm Period, Little Ice Age and 20th century warming simulated by the FGOALS climate system model. Chin. Sci. Bull., 56, 3028–3041.
—, Chen **aolong, Dong Lu, et al., 2014a: Chinese contribution to CMIP5: An overview of five Chinese models’ performances. J. Meteor. Res., 28, doi: 10.1007/s13351-014-4001-y.
—, Yu Yongqiang, Liu Yimin, et al., 2014b: Flexible Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System Model: A Modeling Tool for the Climate Change Research Community. Springer Press, ISBN 978-3-642-41800-6, ISBN 978-3-642-41801-3 (eBook), doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41801-3, Springer Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London, 483 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41125017 and 41330423) and LASG/IAP Funding for the Development of Climate System Model.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, T., Zou, L., Wu, B. et al. Development of earth/climate system models in China: A review from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project perspective. J Meteorol Res 28, 762–779 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4501-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4501-9