Abstract
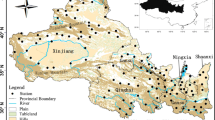
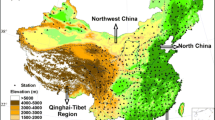
Daily precipitation data from 153 meteorological stations over Northwest China during summer from 1963 to 2012 were selected to analyze the spatiotemporal distribution of extreme summer precipitation frequency. The results show that the extreme precipitation frequency was regional dependent. Southern Gansu, northern Qinghai, and southern Shaanxi provinces exhibited a high extreme precipitation frequency and were prone to abrupt changes in the frequency. Northwest China was further divided into three sub-regions (northern, central, and southern) based on cluster analysis of the 50-yr extreme precipitation frequency series for each meteorological station. The extreme precipitation frequency changes were manifested in the northern region during the late 1970s and in the central region from the end of the 1980s to the 1990s. The southern region fluctuated on a timescale of quasi-10 yr. This study also explored the mechanism of changes in extreme precipitation frequency. The results demonstrate that stratification stability, atmospheric water vapor content, and upward motion all affected the changes in extreme precipitation frequency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, J. L., L. C. Sloan, and M. A. Snyder, 2004: Regional changes in extreme climatic events: A future climate scenario. J. Climate, 17, 81–87.
Chen Huopo, Sun Jianqi, and Fan Ke, 2012: Decadal features of heavy rainfall events in eastern China. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 26, 289–303.
Chen Zhikun, Zhang Shuyu, Luo Jiali, et al., 2013: A climatic analysis on the precipitation features and anomaly in Northwest China. J. Desert Res., 33, 1874–1883. (in Chinese)
Cheng Qiansheng, Zhou **aobo, and Zhu Yingshan, 1998: Cluster analysis of climate jump. Chinese J. Geophy., 41, 308–314. (in Chinese)
—, —, and Sun **chen, 2001: Discontinuous wavelet analysis and mixed cluster analysis. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 25, 552–558. (in Chinese)
Cheng Shenglong and Wang Naiang, 2004: Study on air temperature change in Lanzhou City in recent 70 years. Arid Land Geogr., 27, 558–563. (in Chinese)
Fu Congbin, Yan **aodong, and Guo Weidong, 2006: Aridification in the northern China and human adaptation. Prog. Natural Sci., 16, 1216–1223. (in Chinese)
Huang Wei, Wu **an, Chen Jianhui, et al., 2012: Tropospheric biennial oscillations and abrupt changes of precipitation in the arid central Asia. Prog. Inquis. Mutat. Climate, 8, 448–455. (in Chinese)
Iwashima, T., and R. Yamamoto, 1993: A statistical analysis of the extreme events: Long-term trend of heavy daily precipitation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 71, 637–640.
Jiang **aoyan, Liu Shuhua, Ma Mingmin, et al., 2009: A wavelet analysis of the precipitation time series in Northeast China during the last 100 years. Geogr. Res., 28, 354–362. (in Chinese)
Johanna, H., and S. Jenny, 2002: Climate variations in relation to local scale land use and farmer’s perception of climate in Danangou watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Earth Sciences Centre, Göteborg University, B355.
Milly, P. C. D., R. T. Wetherald, K. A. Dunne, et al., 2002: Increasing risk of great floods in a changing climate. Nature, 415, 514–516.
Min Shen and Qian Yongfu, 2008: Regionality and persistence of extreme precipitation events in China. Adv. Water Sci., 19, 763–771. (in Chinese)
Niu Cunwen, Zhang Li**, and **a Jun, 2004: Wavelet analysis on the precipitation in North China. Arid Land Geogr., 27, 66–70. (in Chinese)
Pal, J. S., F. Giorgi, and X. Q. Bi, 2004: Consistency of recent European summer precipitation trends and extremes with future regional climate projections. Geophy. Res. Lett., 31, L13202.
Shao **aomei, Xu Yueqing, and Yan Changrong, 2006: Wavelet analysis of rainfall variation in the Yellow River basin. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin., 42, 503–509. (in Chinese)
Shi Yafeng, Shen Yong**, and Hu Ruji, 2002: Preliminary study on signal, impact and foreground of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humid in Northwest China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol., 24, 219–226. (in Chinese)
Tosnis, A. A., 1996: Widespread increases in low-frequency variability of precipitation over the past century. Nature, 382, 700–702.
Wang **aojun, Gong Zhiqiang, Ren Fumin, et al., 2012: Changes in climate system spatial-temporal characteristics of regional extreme low temperature events in China during 1960–2009. Adv. Climatic Change Res., 4, 186–194.
Yang **hu, Jiang Zhihong, Yang Qiguo, et al., 2007: Analysis on extreme precipitation events over Northwest China in flood season. J. Desert Res., 27, 320–325. (in Chinese)
Zhai, P. M., X. B. Zhang, H. Wan, et al., 2005: Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J. Climate, 18, 1096–1108.
Zhang Naisheng and Dai Yuheng, 2012: Characteristics of extreme precipitation events and their circulations in Northwest China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 40, 14876–14878. (in Chinese)
Zhang **akun, Guo Pinwen, Zhang Shuyu, et al., 2012: Variations of extreme precipitation days during the main flood season in southern Gansu Province and its possible causes. Meteor. Mon., 38, 490–494. (in Chinese)
Zou Yongchang, Yang **uqun, Liao Yufang, et al., 2009: Seasonal difference of the spatiotemporal variation of the number of extreme precipitation processes in China. J. Nan**g Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 45, 98–109. (in Chinese)
Zwiers, F. W., and V. V. Kharin, 1998: Changes in the extremes of the climate simulated by CCC GCM2 under CO2 doubling. J. Climate, 11, 2200–2222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China Meteorological Administration Special Public Welfare Research Fund (GYHY201006017), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41375121 and 41305079), and Scientific Research and Innovation Plan for College Graduates of Jiangsu Province of China (CXZZ13-0500 and CXZZ13-0521).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, P., Zhang, X., Zhang, S. et al. Decadal variability of extreme precipitation days over Northwest China from 1963 to 2012. J Meteorol Res 28, 1099–1113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4022-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4022-6