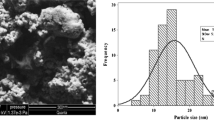
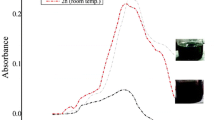
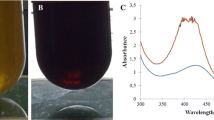
Abstract
In this study, toxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was compared using zebrafish as a model organism. At 96 h, LC50 of AgNPs and AuNPs was found to be 24.5 µg/L and 41 mg/L, respectively. Following the LC50 determination, half of the LC50 of AgNPs (12.25 µg/L) and AuNPs (20.5 mg/L) was exposed to adult zebrafishes for 14 days. Morphological changes, liver marker enzymes, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, genotoxic effects and mRNA expression levels of oxidative stress and innate immune response related genes were studied using nanoparticle treated gill, liver and blood cells. In this study, AgNP-treated gill and liver tissues showed a number of morphological changes such as cell membrane damage, irregular cell outlines, pyknotic nuclei and complete disruption of gill and liver cells; on the contrary, AuNPs treated liver tissues alone showed such changes. The levels of liver marker enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase were increased after AgNPs treatment when compared to AuNPs treatment. AgNP-treated liver cells showed higher levels of ROS generation than the control; on the other hand, AuNPs treatment exhibited lower levels of ROS generation than the control. Interestingly, AgNP-treated blood cells showed micronuclei formation and nuclear abnormalities, while AuNPs treatment did not show such effects. Based on these observations, it is clear that AgNPs may cause oxidative stress and immunotoxicity to adult zebrafish than the AuNPs. However, these results clearly reveal the significance of relatively safe and less toxic bionanomaterials for possible biomedical applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerle RV, Johnston BD, Lange A, Bastos ED, Moorhouse A, Booth T, Paszkiewicz K, Tyler CR, Ball K, Santos EM (2013) Molecular mechanisms of toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Environ Sci Technol 47:8005–8014
Asharani PV, Wu YL, Gong Z, Valiyaveettil S (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish models. Nanotechnology 19:255102
Asharani PV, Wu YL, Gong Z, Valiyaveettil S (2011) Comparison of the toxicity of silver, gold and platinum nanoparticles in develo** zebrafish embryos. Nanotoxicology 5:43–54
Ayllon FE, Garcia-Vazquez (2000) Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and mollie Poecilia latipinna: an assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutation Res 467:177–186
Balakumaran MD, Ramachandran R, Balashanmugam P, Mukeshkumar DJ, Kalaichelvan PT (2016) Mycosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles: optimization, characterization and antimicrobial activity against human pathogens. Microbiol Res 182:8–20
Bar-Ilan O, Albrecht RM, Fako VE, Furgeson DY (2009) Toxicity assessments of multisized gold and silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Small 5:1897–1910
Bilberg K, Hovgaard MB, Besenbacher F, Baatrup E (2012) In vivo toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Toxicol 2012:293784
Brasier AR (2006) The NF-κB regulatory network. Cardiovasc Toxicol 6:111–130
Buzea C, Pacheco II, Robbie K (2007) Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2:MR17–MR71
Choi JE, Kim S, Ahn JH, Youn P, Kang JS, Park K, Yi J, Ryu DY (2010) Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by silver nanoparticles in the liver of adult zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 100:151–159
Gilmore TD, Herscovitch M (2006) Inhibitors of NF-κB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene 25:6887–6899
Girilal M, Krishnakumar V, Poornima P, Fayaz AM, Kalaichelvan PT (2015) A comparative study on biologically and chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles induced heat shock proteins on fresh water fish Oreochromis niloticus. Chemosphere 139:461–468
Griffitt RJ, Hyndman K, Denslow ND, Barber DS (2009) Comparison of molecular and histological changes in zebrafish gills exposed to metallic nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 107:404–415
Gunes C, Heuchel R, Georgiev O, Muller KH, Lichtlen P, Bluthmann H, Marino S, Aguzzi A, Schaffner W (1998) Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the metal-responsive transcriptional activator MTF-1. Embo J 17:2846–2854
Haynes CL (2010) The emerging field of nanotoxicology. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:587–588
Hotchkiss RD (1948) A microchemical reaction resulting in the staining of polysaccharide structure in fixed tissue preparations. Arch Biochem 16:131–141
Hu YL, Qi W, Han F, Shao J, Gao J (2011) Toxicity evaluation of biodegradable chitosan nanoparticles using a zebrafish embryo model. Int J Nanomedicine 6:3351–3359
Impellitteri CA, Tolaymat TM, Scheckel KG (2009) The speciation of silver nanoparticles in antimicrobial fabric before and after exposure to a hypochlorite/detergent solution. J Environ Qual 38:1528–1530
Kiernan JA (1999) Histological and histochemical methods: theory and practice, 3rd edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Kim S, Choi JE, Choi J, Chung K-H, Park K, Yi J, Ryu D-Y (2009) Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23:1076–1084
Krishnaraj C, Ramachandran R, Mohan K, Kalaichelvan PT (2012) Optimization for rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 93:95–99
Krishnaraj C, Muthukumaran P, Ramachandran R, Balakumaran MD, Kalaichelvan PT (2014) Acalypha indica Linn: biogenic synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effects against MDA-MB-231, human breast cancer cells. Biotechnol Rep 4:42–49
Krishnaraj C, Harper SL, Yun S-I (2016) In vivo toxicological assessment of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Hazard Mater 301:480–491
Marcolin E, Miguel BS, Vallejo D, Tieppo J, Marroni N, Gallego JG, Tunon MJ (2012) Quercetin treatment ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis in mice with nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis 1–3. J Nutr 142:1821–1828
Massarsky A, Dupuis L, Taylor J, Eisa-Beygi S, Strek L, Trudeau VL, Moon TW (2013) Assessment of nanosilver toxicity during zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. Chemosphere 92:59–66
Nel A, **a T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150:5–22
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
OECD (1992) Test No. 203: fish, acute toxicity test. OECD Publishing, Paris
Olasagasti M, Gatti AM, Capitani F, Barranco A, Pardo MA, Escuredo K, Rainieri S (2014) Toxic effects of colloidal nanosilver in zebrafish embryos. J Appl Toxicol 34:562–575
Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies (2018) Consumer products inventory. http://www.nanotechproject.org/cpi/products/. Accessed 7 June 2018
Rajan R, Chandran K, Harper SL, Yun S-I, Kalaichelvan PT (2015) Plant extract synthesized silver nanoparticles: an ongoing source of novel biocompatible materials. Ind Crops Prod 70:356–373
Rajan R, Chandran K, Sivakumar AS, Prasannakumar P, Abhay Kumar VK, Shim KS, Song C-G, Yun S-I (2017) Anticancer activity of biologically synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles on mouse myoblast cancer cells and their toxicity against embryonic zebrafish. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 73:674–683
Saquib Q, Al-Khedhairy AA, Siddiqui MA, Abou-Tarboush FM, Azam A, Musarrat J (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in human amnion epithelial (WISH) cells. Toxicol In Vitro 26:351–361
Sarkar B, Netam SP, Mahanty A, Saha A, Bosu R, Krishnani KK (2014) Toxicity evaluation of chemically and plant derived silver nanoparticles on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 84:885–892
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C T method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Scown TM, Santos EM, Johnston BD, Gaiser B, Tyler CR (2010) Effects of aqueous exposure to silver nanoparticles of different sizes in Rainbow Trout. Toxicol Sci 115:521–534
Shah D, Savaliya R, Patel P, Kansara K, Pandya A, Dhawan A, Singh S (2018) Curcumin Ag nanoconjugates for improved therapeutic effects in cancer. Int J Nanomed 13:75–77
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2004a) Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core–Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:496–502
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ankamwar B, Singh A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2004b) Biological synthesis of triangular gold nanoprisms. Nat Mater 3:482–488
Singh S, D’Britto V, Prabhune AA, Ramana CV, Dhawan A, Prasad BLV (2010) Cytotoxic and genotoxic assessment of glycolipid-reduced and -capped gold and silver nanoparticles. New J Chem 34:294–301
Smirnova IV, Bittel DC, Ravindra R, Jiang H, Andrews GK (2000) Zinc and cadmium can promote the rapid nuclear translocation of MTF-1. J Biol Chem 275:9377–9384
Srivastava M, Singh S, Self WT (2012) Exposure to silver nanoparticles inhibits selenoprotein synthesis and the activity of thioredoxin reductase. Environ Health Perspect 120:56–61
Tsukada J, Yoshida Y, Kominato Y, Auron PE (2011) The CCAAT/enhancer binding (C/EBP) family of basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors is a multifaceted highly-regulated system for gene regulation. Cytokine 54:6–19
Williams JH, Farag AM, Stansbury MA, Young PA, Bergman HL, Petersen NS (1996) Accumulation of hsp70 in juvenile and adult rainbow trout gill exposed to metal-contaminated water and/or diet. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1324–1328
Zakin MM (1992) Regulation of transferrin gene expression. FASEB J 6:3253–3258x
Acknowledgements
RR sincerely acknowledges University Grants Commission (UGC), Government of India for awarding UGC-BSR Meritorious Fellowship in Sciences. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2013R1A1A2007953) and also funds from Chonbuk National University, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramachandran, R., Krishnaraj, C., Kumar, V.K.A. et al. In vivo toxicity evaluation of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles on adult zebrafish: a comparative study. 3 Biotech 8, 441 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1457-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1457-y