Abstract
Worldwide, groundwater resources have been considered as the main sources of drinking, domestic uses, industrial and agriculture water demands, especially in arid and semiarid regions. Accordingly, the monitoring of the groundwater quality based on different tools and methods becomes a necessity. The aim of this study was to apply several approaches to assess the water quality and to define the main hydrochemical process which affect groundwater of the Maritime Djeffara shallow aquifer. In addition to the hydrochemical approach, two multivariate statistical analyses, hierarchical clusters analysis (HCA) and principal component analysis (PCA), were carried out to identify the natural and the anthropogenic processes affecting groundwater chemistry. Hydrochemical approach, based on 47 analyzed groundwater samples, shows that most of samples present a sulfate to mixed chloride, with sodi-potassic tendency facies. According to their chemically composition, the HCA revealed three different groups (C1, C2 and C3) according to their electrical conductivity (EC) values: C1 (average EC = 4500 µS/cm), C2 (average EC = 7040 µS/cm) and C3 (average EC = 9767 µS/cm). Furthermore, PCA results show two principal factors account 84.05% of the total variance: (1) F1 represents the natural component, and (2) F2 symbolizes the anthropic component. Moreover, the groundwater quality map of the Maritime Djeffara shows three categories: suitable, doubtful and unsuitable water for irrigation. These different results should be taken to protect water resources in arid and semiarid regions, especially at the alluvial coastal regions. Also, they help to make a suitable planning to manage and protect the groundwater resources.




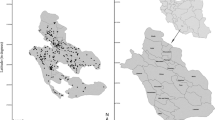
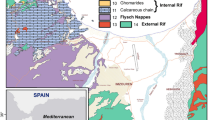
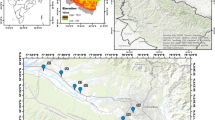
Reproduced with permission from Ayed et al. (2017)









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghazadeh N, Mogaddam AA (2010) Assessment of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural uses in the Oshnavieh area, Northwest of Iran. J Environ Prot 1(01):30
Agoubi B (2012) Caractérisation hydrogéologique et géochimique du système aquifère de la Jeffara maritime: Apport des approches géostatistiques (Hydrogeological and geochemistry characterization of the Maritime Jeffara aquifer system). Faculty of sciences of Sfax
Agoubi B, Kharroubi A, Abichou T, Abida H (2013) Hydrochemical and geoelectrical investigation of Marine Jeffara Aquifer, southeastern Tunisia. Appl Water Sci 3(2):415–429
Agoubi B, Kharroubi A, Abida H (2014) Geochemical assessment of environmental impact on groundwater quality in coastal arid area, south eastern Tunisia. J Environ Sci Eng Technol 2:35–46
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2005) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, 2nd edn. A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam
Ayed B, Jmal I, Sahal S, Bouri S (2017) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability using a specific vulnerability method: case of Maritime Djeffara shallow aquifer (Southeastern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 10:262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3035-8
Ayers RS, Westcot DW (1985) Water quality for agriculture FAO irrigation and drain, no. 29
Baig JA, Kazi TG, Shah AQ, Kandhro GA, Afridi HI, Arain MB et al (2010) Speciation and evaluation of arsenic in surface water and groundwater samples: a multivariate case study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:914–923
Bayo J, López-Castellanos J (2016) Principal factor and hierarchical cluster analyses for the performance assessment of an urban wastewater treatment plant in the Southeast of Spain. Chemosphere 155:152–162
Bencer S, Boudoukha A, Mouni L (2016) Multivariate statistical analysis of the groundwater of Ain Djacer area (Eastern of Algeria). Arab J Geosci 9(4):1–10
Bhattacharya P, Sracek O, Eldvall B, Asklund R, Barmen G, Jacks G, Koku J, Gustafsson JE, Singh N, Brokking Balfors B (2012) Hydrogeochemical study on the contamination of water resources in a part of Tarkwa mining area, Western Ghana. J Afr Earth Sci 66:72–84
Bošnjak MU, Capak K, Jazbec A, Casiot C, Sipos L, Poljak V, Dadić Ž (2012) Hydrochemical characterization of arsenic contaminated alluvial aquifers in Eastern Croatia using multivariate statistical techniques and arsenic risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 420:100–110
Bouaziz S (1995) Etude de la tectonique cassante dans la plate-forme et l’Atlas Sahariens (Tunisie méridionale): evolution des paléochamps de contraintes et implications géodynamiques. Unpublished thesis ès-Sciences, Université Tunis II
Bouaziz S, Jedoui Y, Barrier É, Angelier J (2003) Néotectonique affectant les dépôts marins tyrrhéniens du littoral sud-est tunisien: implications pour les variations du niveau marin. Comptes Rendus Geosci 335(2):247–254
Cloutier V, Lefebvre R, Therrien R, Savard MM (2008) Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J Hydrol 353:294–313
Colombani N, Cuoco E, Mastrocicco M (2017) Origin and pattern of salinization in the Holocene aquifer of the southern Po Delta (NE Italy). J Geochem Explor 175:130–137
Conover WJ (1999) Practical nonparametric statistics, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 428–433 (6.1)
Costa JL, Aparicio VC (2015) Quality assessment of irrigation water under a combination of rain and irrigation. Agric Water Manag 159:299–306
Dagnellie P (1992) Statistique théorique et appliquée, vol 1. Presses agronomiques de Gembloux, Gembloux
Delgado C, Pacheco J, Cabrera A, Batllori E, Orellana R, Bautista F (2010) Quality of groundwater for irrigation in tropical karst environment: the case of Yucatan, Mexico. Agric Water Manag 97(10):1423–1433
Doneen LD (1964) Notes on water quality in agriculture. Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California, Davis
Eaton FM (1950) Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci 69(2):123–134
Fetter CW (1990) Applied hydrogeology. CBS Publishers & Distributors, New Delhi
Güler C, Kurt MA, Alpaslan M, Akbulut C (2012) Assessment of the impact of anthropogenic activities on the groundwater hydrology and chemistry in Tarsus coastal plain (Mersin, SE Turkey) using fuzzy clustering, multivariate statistics and GIS techniques. J Hydrol 414–415:435–451
Helena B, Pardo R, Vega M, Barrado E, Fernández JM, Fernández L (2000) Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res 34:807–816
Huang G, Sun J, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Liu F (2013) Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area. South China Sci Total Environ 463–464:209–221
Jedoui Y (2000) Sédimentologie et géochronologie des dépôts littoraux quaternaires: reconstitution des variations des paléoclimats et du niveau marin dans le Sud-Est tunisien. These de doctorat es-sciences géologiques, université de Tunis II
Katz BG, Eberts SM, Kauffman LJ (2011) Using Cl/Br ratios and other indicators to assess potential impacts on groundwater quality from septic systems: a review and examples from principal aquifers in the United States. J Hydrol 397(3):151–166
Kharroubi A, Tlahigue F, Agoubi B, Azri C, Bouri S (2012) Hydrochemical and statistical studies of the groundwater salinization in Mediterranean arid zones: case of the Jerba coastal aquifer in southeast Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 67(7):2089–2100
Kolsi SH, Bouri S, Hachicha W, Dhia HB (2013) Implementation and evaluation of multivariate analysis for groundwater hydrochemistry assessment in arid environments: a case study of Hajeb Elyoun-Jelma, Central Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 70(5):2215–2224
Mamou A (1990) Caractéristiques, évaluation et gestion des ressources en eau du Sud-Tunisien. Doctoral dissertation, Paris 11
Monjerezi M, Vogt RD, Aagaard P, Saka JDK (2011) Hydro-geochemical processes in an area with saline groundwater in lower Shire River valley, Malawi: an integrated application of hierarchical cluster and principal component analysis. Appl Geochem 26:1399–1413
Moya CE, Raiber M, Taulis M, Cox ME (2015) Hydrochemical evolution and groundwater flow processes in the Galilee and Eromanga basins, Great Artesian Basin, Australia: a multivariate statistical approach. Sci Total Environ 508:411–426
Narasimha G, Sridevi A, Buddolla V, Subhosh CM, Rajasekhar RB (2006) Nutrient effects on production of cellulolytic enzymes by Aspergillus niger. Afr J Biotechnol 5(5):472–476
Ncibi K, Gaaloul N, Gasmi A (2016) Contribution de l’analyse multivariée et des SIG pour la caractérisation hydrochimique de la nappe phréatique de la plaine de Sidi Bouzid (Tunisie centrale)/[Contribution of the multivariate analysis and the GIS for Hydrochemical characterization of phreatic aquifer to the plain of Sidi Bouzid (Central Tunisia)]. Int J Innov Appl Stud 15(3):667
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (2013) Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3-A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations, U.S. geological survey techniques and methods
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water‐analyses. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928
Raghunath HM (1987) Ground water. New Age International, Seborga
Ramesh K, Elango L (2011) Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. J Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2231-3
Razali NM, Wah YB (2011) Power comparisons of Shapiro–Wilk, Kolmogorov–Smirnov, Lilliefors and Anderson–Darling tests. J Stat Model Anal 2(1):21–33
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett R, Dutter R (2008) Statistical data analysis explained: applied environmental statistics with R. Wiley, Chichester
Richards LA (1954) (US Salinity Laboratory) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkaline soils, US Department of Agriculture hand book
Simler R (2009) Diagrammes. Laboratoire d’Hydrogéologie d’Avignon, Avignon
Szabolcs I, Darab C (1964) The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils. In: Proceedings of 8th international congress of ISSS, Trans, II (pp 803–812)
Thorne DW, Peterson HB (1954) Irrigated soils: their fertility and management. Blakiston, New York
Voutsis N, Kelepertzis E, Tziritis E, Kelepertsis A (2015) Assessing the hydrogeochemistry of groundwaters in ophiolite areas of Euboea Island, Greece, using multivariate statistical methods. J Geochem Explor 159:79–92
Wanda E, Monjerezi M, Mwatseteza JF, Kazembe LN (2011) Hydro-geochemical appraisal of groundwater quality from weathered basement aquifers in Northern Malawi. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 36(14):1197–1207
Ward JH (1963) Hierarchical grou** to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc 58:236–244
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters, vol 969. USDA Circular, Washington, DC, USA
Williams B, Onsman A, Brown T (2010) Exploratory factor analysis: a five-step guide for novices. J Emerg Primary Health Care (JEPHC) 8(3):990399-1–990399-13
Zabala ME, Martínez S, Manzano M, Vives L (2016) Groundwater chemical baseline values to assess the recovery plan in the Matanza-Riachuelo River basin, Argentina. Sci Total Environ 541:1516–1530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayed, B., Jmal, I., Sahal, S. et al. Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater using multivariate statistical analysis: the Maritime Djeffara shallow aquifer (Southeastern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 76, 821 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7168-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7168-6