Abstract
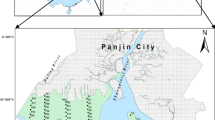
Twenty-eight polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) congeners were measured in surface sediments from Chaohu Lake to assess their characteristics, potential risk, and the correlation with lake trophic status. PCB levels ranged from 11.074 to 42.712 ng g−1 dry weight (d.w.) in the western lake and 2.017 to 20.189 ng g−1 d.w. in the eastern lake. The highest concentrations were found at the sites near the inlets of western lake tributary rivers where big cities and industrial centers are located. Congeners concentrations showed decreasing order of tetra-CB > tri-CB > deca-CB (PCB-209 detected) > penta-CB > hexa-CB > di-CB > hepta-CB > Octa-CB. It indicated that light and heavy Aroclor mixtures were simultaneously used surrounding the lake basin. PCB levels in the western lake are potentially dangerous to humans and the local fauna. There was a significant positive relationship between tetra-CB (one abundant PCB congener) concentration distribution and sediment grain size in the 16–64 μm fraction, whereas a negative correlation was found in the 4–8 μm fraction. Furthermore, PCB distributions were positively correlated with the total organic carbon of sediments and lake trophic status, especially in the more seriously polluted western lake zone. However, the correlation completely disappeared in eastern lake zone. It suggested that PCB contamination might be attributed to industrial wastewaters and domestic sewages from western lake basin, reaching the lake through rivers, rains and floods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berglund O, Larsson P, Ewald G, Okla L (2001) Influence of trophic status on PCB distribution in lake sediments and biota. Environ Pollut 113(2):199–210
Borja J, Taleon DM, Auresenia J, Gallardo S (2005) Polychlorinated biphenyls and their biodegradation. Process Biochem 40(6):1999–2013
Breivik K, Sweetman A, Pacyna JM, Jones KC (2002) Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners-a mass balance approach. 1. Global production and consumption. Sci Total Environ 290(1–3):181–198
Carlson RE (1977) A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 22(2):361–369
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment) (1999) Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). In: Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, Winnipeg, Manitoba
Chen Y, Fan C, Teubner K, Dokulil M (2003) Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: an 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 506–509(15):273–279
China State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) (2003) Building the Capacity of the People’s Republic of China to Implement the Stockholm Convention on POPs and Develop a National Implementation Plan, GEF Project Brief (GF/CPR/02/010). http://www.gefweb.org
Choi H, Al-Abed SR (2009) PCB congener sorption to carbonaceous sediment components: Macroscopic comparison and characterization of sorption kinetics and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 165(1):860–866
Dachs J, Eisenreich SJ, Hoff RM (2000) Influence of eutrophication on air–water exchange, vertical fluxes, and phytoplankton concentrations of persistent organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 34(6):1095–1102
Dachs J, Lohmann R, Ockenden WA, Mejanelle L, Eisenreich SJ, Jones KC (2002) Oceanic biogeochemical controls on global dynamics of persistent organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 36(20):4229–4237
Dai GH, Liu XH, Liang G, Han X, Liu S, Cheng DM, Gong WM (2011) Distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in surface water and sediments from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. J Environ Sci 23(10):1640–1649
Environment Canada (1997) Report of Environmental Protection Series Regulations/Guidelines/Codes of Reference methods (Report EPS 1/RM/31)
Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2008) Microbial transformation and degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ Pollut 155(1):1–12
Frame GM, Cochran JW, Bowadt SS (1996) Complete PCB congener distributions for 17 Aroclor mixtures determined by 3 HRGC systems optimized for comprehensive, quantitative, congener specific analysis. J High Resolut Chrom 19(12):657–668
He W, Qin N, Wang Y, He QS, Kong XZ, Ouyang HL, Xu FL (2011) Residues, source identification, and risk assessment of DDTs in surface water from Lake Chaohu. J Lake Sci 23(3):325–333 (in Chinese)
Hurme S, Puhakka JA (2007) Characterization and fate of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminants in Kernaalanjärvi sediments. Boreal Environ Res 4:331–342
Jeong GH, Kim HJ, Joo YJ, Kim YB, So HY (2001) Distribution characteristics of PCBs in the sediments of the lower Nakdong River, Korea. Chemosphere 44(6):1403–1411
Jiang K, Li LJ, Chen YD, ** J (1997) Determination of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in Chinese commercial PCBs and emissions from a testing PCB incinerator. Chemosphere 34(5):941–950
** X, Tu Q (eds) (1990) The standard methods for observation and analysis in Lake eutrophication, 2nd (edn) Chinese Environmental Science Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Li ZH, Zlabek V, Turek J, Velisek J, Pulkrabova J, Kolarova J, Sudova E, Berankova P, Hradkova P, Hajslova J, Randak T (2011) Evaluating environmental impact of STPs situated on streams in the Czech Republic: An integrated approach to biomonitoring the aquatic environment. Water Res 45(3):1403–1413
Long ER, MacDonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuary sediments. Environ Manage 19(1):81–97
Lorenzen CJ (1967) Determination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol Oceanogr 12(2):343–346
Marvin CH, Painter S, Charlton MN, Fox ME, Thiessen PAL (2004) Trends in spatial and temporal levels of persistent organic pollutants in Lake Erie sediments. Chemosphere 54(1):33–40
Miller S (1982) The Persistent PCB Problem. Environ Sci Technol 16(2):98A–99A
Newman JW, Becker JS, Blondina G, Tjeerdema RS (1998) Quantitation of Aroclors using congener-specific results. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(11):2159–2167
Nizzetto L, Macleod M, Borgå K, Cabrerizo A, Dachs J, Di Guardo A, Ghirardello D, Hansen KM, Jarvis A, Lindroth A, Ludwig B, Monteith D, Perlinger JA, Scheringer M, Schwendenmann L, Semple KT, Wick LY, Zhang G, Jones KC (2010) Past, present, and future controls on levels of persistent organic pollutants in the global environment. Environ Sci Technol 44(17):6526–6531
OSPAR Commission (2000) Quality Status Report 2000. OSPAR Commission, London
Pozo K, Urrutia R, Barra R, Mariottini M, Treutler HC, Araneda A, Focardi S (2007) Records of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments of four remote Chilean Andean Lakes. Chemosphere 66(10):1911–1921
Rawn DFK, Lockhart WL, Wilkinson P, Savoie DA, Rosenberg GB, Muir DCG (2001) Historical contamination of Yukon Lake sediments by PCBs and organochlorine pesticides: influence of local sources and watershed characteristics. Sci Total Environ 280(1–3):17–37
Rowe AA, Totten LA, **e M, Fikslin TJ, Eisenreich SJ (2007) Air–water exchange of polychlorinated biphenyls in the Delaware River. Environ Sci Technol 41(4):1152–1158
Rushneck DR, Beliveau A, Fowler B, Hamilton C, Hoover D, Kaye K, Berg M, Smith T, Telliard WA, Roman H, Ruder E, Ryan L (2004) Concentrations of dioxin-like PCB congeners in unweathered Aroclors by HRGC/HRMS using EPA Method 1668A. Chemosphere 54(1):79–87
Shang GP, Shang JC (2005) Causes and control countermeasures of eutrophication in Chaohu Lake, China. Chinese Geogr Sci 15(4):348–354
Shi YX (2006) Sedimentary and Geochemical Records of Climate and Environmental Change for the Chaohu-Hangpu River Catchment in Anhui Province. Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Doctoral Dissertation
Sivey JD, Lee CM (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyl contamination trends in Lake Hartwell, South Carolina (USA): sediment recovery profiles spanning two decades. Chemosphere 66(10):1821–1828
Van Bavel B, Abad E (2008) Long-term worldwide QA/QC of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs in environmental samples. Anal Chem 80(11):3956–3964
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld AT, Brunström B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy SW, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, Van Leeuwen FX, Liem AK, Nolt C, Peterson RE, Poellinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillitt D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Waern F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106(12):775–792
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93(2):223–241
Vives I, Canuti E, Castro-Jiménez J, Christoph EH, Eisenreich SJ, Hanke G, Huber T, Mariani G, Mueller A, Skejo H, Umlauf G, Wollgast J (2007) Occurrence of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Lake Maggiore (Italy and Switzerland). J Environ Monit 9(6):589–598
Vogelsang C, Grung M, Jantsch TG, Tollefsen KE, Liltved H (2006) Occurrence and removal of selected organic micropollutants at mechanical, chemical and advanced wastewater treatment plants in Norway. Water Res 40(19):3559–3570
Wan X, Pan XJ, Wang B, Zhao SM, Hu P, Li F, Boulanger B (2011) Distributions, historical trends, and source investigation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Dianchi Lake, China. Chemosphere 85(3):361–367
Wang MC, Liu XQ, Zhang JH (2002) Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication. Environ Monit China 18(5):47–49 (in Chinese)
Wang YW, Li XM, Li A, Wang T, Zhang QH, Wang P, Fu JJ, Jiang GB (2007) Effect of municipal sewage treatment plant effluent on bioaccumulation of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the recipient water. Environ Sci Technol 41(17):6026–6032
Wang JZ, Zhang K, Liang B, Zeng EY (2011) Occurrence, source apportionment and toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of Chaohu, one of the most polluted lakes in China. J Environ Monit 13(11):3336–3342
Wiegel J, Wu QZ (2000) Microbial reductive dehalogenation of polychlorinated biphenyls. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 32(1):1–15
**ng Y, Lu Y, Dawson RW, Shi Y, Zhang H, Wang T, Liu W, Ren H (2005) A spatial temporal assessment of pollution from PCBs in China. Chemosphere 60(6):731–739
Xu K, Liu F, An Z, Gao Y, Han X, Sun Q (2011) Spatial and temporal variations of phosphorus forms in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake. Environ Sci 32(11):3255–3263 (in Chinese)
Yang ZF, Shen ZF, Gao F, Tang ZW, Niu JF, He Y (2009a) Polychlorinated biphenyls in urban lake sediments from wuhan, central China: occurrence, composition, and sedimentary record. J Environ Qual 38(4):1441–1448
Yang ZF, Shen ZF, Gao F, Tang ZW, Niu JF (2009b) Occurrence and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments from the Wuhan reach of the Yangtze River, China. Chemosphere 74(11):1522–1530
Yang HY, Xue B, ** LX, Zhou SS, Liu WP (2011) Polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yueqing Bay, **angshan Bay, and Sanmen Bay in East China Sea. Chemosphere 83(2):137–143
Yu HB, ** BD, Jiang JY, Heaphy MJ, Wang HL, Li DL (2011) Environmental heterogeneity analysis, assessment of trophic state and source identification in Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(8):1333–1342
Zan FY, Huo SL, ** BD, Li QQ, Liao HQ, Zhang JT (2011a) Phosphorus distribution in the sediments of a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. Environ Earth Sci 62(8):1643–1653
Zan FY, Huo SL, ** BD, Su J, Li X, Zhang JT, Yeager KM (2011b) A 100 year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. J Environ Monit 13:2788–2797
Zan FY, Huo SL, ** BD, Liao HQ, Zhang JT, Yeage KM (2012) A 100-year sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic impacts on a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. J Environ Monit 14(3):804–816
Zhang QH, Jiang GB (2005) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments and aquatic organisms from the Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 61(3):314–322
Zhang S, Li CM, Huang SM, Zheng J (2008) Trophic states and nutrient storage of reservoirs in Chongqing, China. J Geochem 27(3):310–316
Zhao XR, Zheng BH, Qin YW, Jiao LX, Zhang L (2010) Grain size effect on PBDE and PCB concentrations in sediments from the intertidal zone of Bohai Bay, China. Chemosphere 81:1022–1026
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Mega-projects of Science Research for Water Environment Improvement (Program No. 2009ZX07106-001; 2012ZX07101-002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40901248) and the China Environmental Public Welfare Program (2010009032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., **, B., Huo, S. et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls residues in surface sediments of the eutrophic Chaohu Lake (China): characteristics, risk, and correlation with trophic status. Environ Earth Sci 71, 849–861 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2487-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2487-8