Abstract
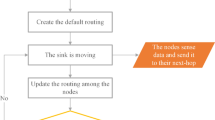
Realizing energy-efficient communication in the IoT-based large-scale systems has become a key challenge in the past few years. The need is to minimize the global energy usage of battery-operated objects so as to reduce data transmission cost and extend the network lifetime. In this paper, we propose SEES, a scalable and energy-efficient scheme for green IoT-based heterogeneous wireless nodes. We study the impact of energy-harvesting techniques by utilizing ambient energy-harvesting relay nodes in such a way that enables a higher energy conservation and guarantees a long-lived network. SEES includes: (1) a zone-based hybrid-placement scheme, (2) a Multi-Stage Weighted Election heuristic (MSWE), and (3) a Minimum Cost Cross-layer Transmission model (MCCT). Our aim is to ensure an even-random deployment of heterogeneous nodes, a scalable pre-deterministic placement of energy-harvesting nodes, a fair energy-load balancing among all the zones, and a minimum energy-cost for data transmission from the bottom layer to the topmost layer. SEES is a general scheme that supports up to n levels of heterogeneity, as well as m different election parameters (static and dynamic, associated with m generated weights), and can be used for any type of IoT-based deployment. Experimental results of extensive simulations indicate the superiority of SEES over the other traditional protocols proposed in literature. It can save up to \(62\%\) of the total energy, and, at least, it increases the network lifetime by 58, 68, 70, \(42\%\); the stability period by 192, 108, 424, \(150\%\); and the network throughput by 107, 111, 100, \(114\%\); over LEACH, SEP, ZSEP, and hetDEEC protocols respectively, for all the cases and scenarios tested.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas Z, Yoon W (2015) A survey on energy conserving mechanisms for the internet of things: wireless networking aspects. Sensors 15(10):24,818–24,847
Abbasi AA, Younis M (2007) A survey on clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks. Comput Commun 30(1415):2826–2841
Abdollahzadeh S, Navimipour NJ (2016) Deployment strategies in the wireless sensor network: a comprehensive review. Comput Commun 91–92:1–16
Abdul-Qawy ASH, Srinivasulu T (2017) EH-mulSEP: energy-harvesting enabled multi-level SEP protocol for IoT-based heterogeneous WSNs. In: 3rd International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Computing and Communication Technology (iCATccT) (Presented)
Agiwal M, Roy A, Saxena N (2016) Next generation 5g wireless networks: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun Surveys Tutori 18(3):1617–1655
Akyildiz I, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E (2002) Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Netw 38(4):393–422
Al-Fuqaha A, Guizani M, Mohammadi M, Aledhari M, Ayyash M (2015) Internet of things: a survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Commun Surveys Tutor 17(4):2347–2376
Anastasi G, Conti M, Francesco MD, Passarella A (2009) Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: a survey. Ad Hoc Netw 7(3):537–568
Augustin A, Yi J, Clausen T, Townsley WM (2016) A study of lora: long range and low power networks for the internet of things. Sensors 16(9)
Bauer M, Bui N, De Loof J, Magerkurth C, Nettsträter A, Stefa J, Walewski JW (2013) IoT Reference Model. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 113–162
Begishev V, Samuylov A, Moltchanov D, Samouylov K (2017) Modeling the process of dynamic resource sharing between lte and nb-iot services. In: Vishnevskiy VM, Samouylov KE, Kozyrev DV (eds) Distributed computer and communication networks. Springer, Cham, pp 1–12
Borgia E (2014) The internet of things vision: key features, applications and open issues. Comput Commun 54:1–31
Brar GS, Rani S, Chopra V, Malhotra R, Song H, Ahmed SH (2016) Energy efficient direction-based pdorp routing protocol for wsn. IEEE Access 4:3182–3194
Carbajales RJ, Zennaro M, Pietrosemoli E, Freitag F (2015) Energy-efficient internet of things monitoring with low-capacity devices. In: Internet of Things (WF-IoT), 2015 IEEE 2nd World Forum on, pp 305–310
de Carvalho Silva J, Rodrigues JJPC, Alberti AM, Solic P, Aquino ALL (2017) Lorawan—a low power wan protocol for internet of things: a review and opportunities. In: 2017 2nd International Multidisciplinary Conference on Computer and Energy Science (SpliTech), pp 1–6
Chen M, Miao Y, Hao Y, Hwang K (2017) Narrow band internet of things. IEEE Access 5:20557–20577
Chen RC, Hsieh CF, Chang WL (2016) Using ambient intelligence to extend network lifetime in wireless sensor networks. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 7(6):777–788
Cui X, Liu Z (2009) Bcee: A balanced-clustering, energy-efficient hierarchical routing protocol in wireless sensor networks. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Network Infrastructure and Digital Content, pp 26–30
DGAniello G, Gaeta M, Hong TP, (2018) Effective quality-aware sensor data management. IEEE Trans Emerg Topics Comput Intell 2(1):65–77
De Guglielmo D, Anastasi G, Seghetti A (2014) From IEEE 802.15.4 to IEEE 802.15.4e: a step towards the internet of things. Springer, Cham, pp 135–152
Decuir J (2010) Bluetooth 4.0: Lowenergy. Cambridge Silicon Radio SR PLC, UK
Djenouri D, Bagaa M (2015) Energy harvesting aware relay node addition for power-efficient coverage in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp 86–91
Faisal S, Javaid N, Javaid A, Khan MA, Bouk SH, Khan ZA (2013) Z-SEP: zonal-stable election protocol for wireless sensor networks. J Basic Appl Sci Res (JBASR) 3(5):132–139
Gaeta M, Loia V, Tomasiello S (2015) Multisignal 1-d compression by F-transform for wireless sensor networks applications. Appl Soft Comput 30:329–340
Gaeta M, Loia V, Tomasiello S (2016) Cubic bspline fuzzy transforms for an efficient and secure compression in wireless sensor networks. Inf Sci 339:19–30
Gandotra P, Jha RK (2017) A survey on green communication and security challenges in 5g wireless communication networks. J Netw Comput Appl 96:39–61
Gandotra P, Jha RK, Jain S (2017) Green communication in next generation cellular networks: A survey. IEEE Access 5:11727–11758
Gherbi C, Aliouat Z, Benmohammed M (2016) An adaptive clustering approach to dynamic load balancing and energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks. Energy 114:647–662
Gulia S, Nagendra SS, Khare M, Khanna I (2015) Urban air quality management—a review. Atmos Pollut Res 6(2):286–304
Gupta V, Pandey R (2016) An improved energy aware distributed unequal clustering protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19(2):1050–1058
Hari U, Ramachandran B, Johnson C (2013) An unequally clustered multihop routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), pp 1007–1011
Heinzelman WB, Chandrakasan AP, Balakrishnan H (2002) An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 1(4):660–670
Heinzelman WR, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H (2000) Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In: 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, pp 1–10
Huang J, Meng Y, Gong X, Liu Y, Duan Q (2014) A novel deployment scheme for green internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J 1(2):196–205
Jaffri ZUA, Cai Y (2014) Zet: Zone and energy threshold based clustering routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: 23rd International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), pp 1–6
Kamalinejad P, Mahapatra C, Sheng Z, Mirabbasi S, Leung VCM, Guan YL (2015) Wireless energy harvesting for the internet of things. IEEE Commun Mag 53(6):102–108
Kumar A, Kim H, Hancke GP (2013) Environmental monitoring systems: a review. IEEE Sens J 13(4):1329–1339
Kumar JS, Zaveri MA (2016) Hierarchical clustering for dynamic and heterogeneous internet of things. Proc Comput Sci 93:276 – 282, proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Computing and Communications
Kumaramangalam MV, Adiyapatham K, Kandasamy C (2014) Zone-based routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Int Scholar Res Not 2014:1–9
Liao Y, Qi H, Li W (2013) Load-balanced clustering algorithm with distributed self-organization for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens J 13(5):1498–1506
Lin TH, Liaw DC (2015) Development of an intelligent disaster information-integrated platform for radiation monitoring. Nat Hazards 76(3):1711–1725
Lindsey S, Raghavendra C, Sivalingam KM (2002) Data gathering algorithms in sensor networks using energy metrics. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 13(9):924–935
LoRa Alliance (2015) White paper: a technical overview of lora and lorawan. The LoRa Alliance, San Ramon
Lu X, Wang P, Niyato D, Kim DI, Han Z (2015) Wireless networks with rf energy harvesting: a contemporary survey. IEEE Commun Surveys Tutor 17(2):757–789
Mahdavinejad MS, Rezvan M, Barekatain M, Adibi P, Barnaghi P, Sheth AP (2017) Machine learning for internet of things data analysis: a survey. Digital Communications and Networks
Maksimovic M (2018) Greening the future: green internet of things (G-IoT) as a key technological enabler of sustainable development. Springer, Cham, pp 283–313
Mary SA, Gnanadurai JB (2016) Enhanced zone stable election protocol based on fuzzy logic for cluster head election in wireless sensor networks. Int J Fuzzy Syst, Springer pp 1–14
Mathna C, ODonnell T, Martinez-Catala RV, Rohan J, OFlynn B (2008) Energy scavenging for long-term deployable wireless sensor networks. Talanta 75(3):613–623
Mekki K, Bajic E, Chaxel F, Meyer F (2018) A comparative study of lpwan technologies for large-scale iot deployment. ICT Express
Meng J, Zhang X, Dong Y, Lin X (2012) Adaptive energy-harvesting aware clustering routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: 7th International ICST Conference on Communications and Networking (CHINACOM), pp 742–747
Minoli D (2011) Designing green networks and network operations: saving run-the-engine costs, 1st edn. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton
Minoli D (2013) Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: the evolving world of M2M communications, 1st edn. Wiley, USA
Minoli D, Sohraby K, Kouns J (2017a) IoT security (IoTSec) considerations, requirements, and architectures. In: 2017 14th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications Networking Conference (CCNC), pp 1006–1007
Minoli D, Sohraby K, Occhiogrosso B (2017b) IoT considerations, requirements, and architectures for smart buildings energy optimization and next generation building management systems. IEEE Internet Things J 4(1):269–283
Mondal P, Basu M (2009) Adoption of precision agriculture technologies in india and in some develo** countries: scope, present status and strategies. Prog Nat Sci 19(6):659–666
Muruganathan SD, Ma DCF, Bhasin RI, Fapojuwo AO (2005) A centralized energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun Mag 43(3):S8–13
Naznin M, Chowdhury AS (2015) Zdg: Energy efficient zone based data gathering in a wireless sensor network. In: International Conference on Networking Systems and Security (NSysS), pp 1–7
Peng S, Wang T, Low C (2015) Energy neutral clustering for energy harvesting wireless sensors networks. Ad Hoc Netw 28:1–16
Perera C, Liu CH, Jayawardena S (2015) The emerging internet of things marketplace from an industrial perspective: a survey. IEEE Trans Emerg Topics Comput 3(4):585–598
Pierpaoli E, Carli G, Pignatti E, Canavari M (2013) Drivers of precision agriculture technologies adoption: A literature review. Procedia Technology 8:61–69, 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment (HAICTA 2013)
Qin Y, Sheng QZ, Falkner NJ, Dustdar S, Wang H, Vasilakos AV (2016) When things matter: a survey on data-centric internet of things. J Netw Comput Appl 64:137–153
Rani S, Talwar R, Malhotra J, Ahmed S, Sarkar M, Song H (2015) A novel scheme for an energy efficient internet of things based on wireless sensor networks. Sensors 15(11):28603–28626
Rault T, Bouabdallah A, Challal Y (2014) Energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks: a top–down survey. Comput Netw 67:104–122
Samo D, Anka L (2009) Multi-attribute decision analysis in gis: weighted linear combination and ordered weighted averaging. Informatica 33:459474
SASA M, JB G (2015) A zone-based clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: 9th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, pp 151–161
Schellberg J, Hill MJ, Gerhards R, Rothmund M, Braun M (2008) Precision agriculture on grassland: applications, perspectives and constraints. Eur J Agron 29(2):59–71
Shah T, Javaid N, Qureshi TN (2012) Energy efficient sleep awake aware (eesaa) intelligent sensor network routing protocol. In: 2012 15th International Multitopic Conference (INMIC), pp 317–322
Shahraki A, KuchakiRafsanjani M, BorumandSaeid A (2017) Hierarchical distributed management clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. Telecommun Syst Springer 65(1):193–214
Shaikh FK, Zeadally S (2016) Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:1041–1054
Shaikh FK, Zeadally S, Exposito E (2017) Enabling technologies for green internet of things. IEEE Syst J 11(2):983–994
Shalli R, Jyoteesh M, Rajneesh T (2015) Energy efficient chain based cooperative routing protocol for {WSN}. Appl Soft Comput 35:386–397
Sheikh OM, Mahmoud SA (2012) Cross-layer design for smart routing in wireless sensor networks. In: Wireless Sensor Networks—Technology and Protocols., InTech, chap 09, pp 189–214
Singh S (2017) Energy efficient multilevel network model for heterogeneous WSNs. Eng Sci Technol Int J 20(1):105–115
Singh S, Malik A, Kumar R (2016) Energy efficient heterogeneous DEEC protocol for enhancing lifetime in WSNs. Eng Sci Technol Int J 20(1):345–353
Smaragdakis G, Matta I, Bestavros A (2004) Sep: a stable election protocol for clustered heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. In: International Workshop on SANPA, pp 251–261
Sohraby K, Minoli D, Znati T (2007) Wireless sensor networks: technology, protocols, and applications. Wiley
Soyata T, Copeland L, Heinzelman W (2016) Rf energy harvesting for embedded systems: a survey of tradeoffs and methodology. IEEE Circuits Syst Mag 16(1):22–57
Tocchi A, Roca V, Angrisani L, Bonavolont F, Moriello RSL (2017) First step towards an iot implementation of a wireless sensors network for environmental radiation monitoring. In: 2017 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), pp 1–6
Vangelista L, Zanella A, Zorzi M (2015) Long-range iot technologies: the dawn of lora™. In: Atanasovski V, Leon-Garcia A (eds) Future access enablers for ubiquitous and intelligent infrastructures. Springer, Cham, pp 51–58
Wang YPE, Lin X, Adhikary A, Grovlen A, Sui Y, Blankenship Y, Bergman J, Razaghi HS (2017) A primer on 3g pp narrowband internet of things. IEEE Commun Mag 55(3):117–123
Weyrich M, Ebert C (2016) Reference architectures for the internet of things. IEEE Softw 33(1):112–116
Wixted AJ, Kinnaird P, Larijani H, Tait A, Ahmadinia A, Strachan N (2016) Evaluation of lora and lorawan for wireless sensor networks. In: 2016 IEEE SENSORS, pp 1–3
Yetgin H, Cheung KTK, El-Hajjar M, Hanzo LH (2017) A survey of network lifetime maximization techniques in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun Surveys Tutor 19(2):828–854
Younis O, Fahmy S (2004) Heed: a hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 3(4)
Yu J, Qi Y, Wang G (2011) An energy-driven unequal clustering protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. J Control Theory Appl 9(1):133–139
Zhang P, **ao G, Tan HP (2013) Clustering algorithms for maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks with energy-harvesting sensors. Comput Netw 57(14):2689–2704
Zhang P, Tan HP, **ao G, Yu Y (2015) Maximizing lifetime in clustered wsns with energy harvesting relay: Profiling and modeling. In: IEEE Tenth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing (ISSNIP), pp 1–6
Zhu C, Leung VCM, Shu L, Ngai ECH (2015) Green internet of things for smart world. IEEE Access 3:2151–2162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul-Qawy, A.S.H., Srinivasulu, T. SEES: a scalable and energy-efficient scheme for green IoT-based heterogeneous wireless nodes. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10, 1571–1596 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0758-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0758-7