Abstract
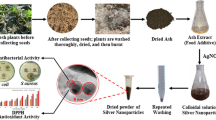
Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by an eco-friendly and sustainable process is an important target to be developed in nanotechnology area. In the present work, two different commercial brands of yerba mate from Argentina and their wastes (PYM and TYM samples) were used for the preparation of aqueous extracts, in order to synthesize silver nanoparticles at room temperature (25 °C). The silver nanoparticles obtained were spherical, hexagonal and, triangular in shape with the average particle size of 50 nm and, shows a surface plasmon peak around 460 nm. The antimicrobial activity of the silver nanoparticles obtained with the extracts from yerba mate wastes was evaluated against E. coli and S. aureus. The minimum inhibitory concentrations required for E. coli were 7.66 and 17.66 µg ml−1 using the treatment T2YE and P2YE, respectively and, for S. aureus were 23.25 and 50.60 µg ml−1 for the treatment T2YE and P2YE, respectively. The study suggests that polyphenols present in I. paraguariensis leaf extract act as reducing agent and stabilizer of the nanoparticles.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grigioni, G., Carduza, F., Irurueta, M., Pensel, N.: Flavour characteristics of Ilex paraguariensis infusion, a typical Argentine product, assessed by sensory evaluation and electronic nose. J. Sci. Food Agric. 84, 427–432 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.1670
Bracesco, N., Sanchez, A.G., Contreras, V., Menini, T., Gugliucci, A.: Recent advances on Ilex paraguariensis research: minireview. J. Ethnopharmacol. 136, 378–384 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.06.032
Heck, C.I., De Mejia, E.G.: Yerba mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis): a comprehensive review on chemistry, health implications, and technological considerations. J. Food Sci. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00535.x
Filip, R., Sebastian, T., Ferraro, G., Anesini, C.: Effect of Ilex extracts and isolated compounds on peroxidase secretion of rat submandibulary glands. Food Chem. Toxicol. 45, 649–655 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.10.014
Conforti, A.S., Gallo, M.E., Saraví, F.D.: Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) consumption is associated with higher bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Bone. 50, 9–13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2011.08.029
Instituto Nacional de la Yerba Mate, Instituto Nacional de la Yerba Mate (2016). http://yerbamateargentina.org.ar/.
Burris, K.P., Harte, F.M., Davidson, P.M., Neal Stewart, C. Jr., Zivanovic, S.: Composition and bioactive properties of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.): a review. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 72, 268–275 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392012000200016
Filip, R., López, P., Giberti, G., Coussio, J., Ferraro, G.: Phenolic compounds in seven South American Ilex species. Fitoterapia. 72, 774–778 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0367-326X(01)00331-8
Bragança, V.L.C., Melnikov, P., Zanoni, L.Z.: Trace elements in different brands of yerba mate tea. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 144, 1197–1204 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9056-3
Niraimathi, K.L., Sudha, V., Lavanya, R., Brindha, P.: Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alternanthera sessilis (Linn.) extract and their antimicrobial, antioxidant activities. Colloids Surf. B 102, 288–291 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.08.041
Bindhu, M.R., Umadevi, M.: Synthesis of monodispersed silver nanoparticles using Hibiscus cannabinus leaf extract and its antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim Acta A 101, 184–190 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.09.031
Mittal, A.K., Chisti, Y., Banerjee, U.C.: Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 31, 346–356 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.01.003
Hebbalalu, D., Lalley, J., Nadagouda, M.N., Varma, R.S.: Greener techniques for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts, enzymes, bacteria, biodegradable polymers, and microwaves. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1, 703–712 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/sc4000362
Kharissova, O.V., Dias, H.V.R., Kharisov, B.I., Pérez, B.O., Pérez, V.M.J.: The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 31, 240–248 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.01.003
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B.L., Ikram, S.: A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 7, 17–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Patel, A.C., Li, S., Wang, C., Zhang, W., Wei, Y.: Electrospinning of porous silica nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Chem. Mater. 19, 1231–1238 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm061331z
Abou El-Nour, K.M.M., Eftaiha, A., Al-Warthan, A., Ammar, R.A.A.: Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 3, 135–140 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.04.008
Rauwel, E., Simón-Gracia, L., Guha, M., Rauwel, P., Kuunal, S., Wragg, D.: Silver metal nanoparticles study for biomedical and green house applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 175, 11001 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/755/1/011001
Kim, J.S., Kuk, E., Yu, K.N., Kim, J.H., Park, S.J., Lee, H.J., Kim, S.H., Park, Y.K., Park, Y.H., Hwang, C.Y., Kim, Y.K., Lee, Y.S., Jeong, D.H., Cho, M.H.: Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 3, 95–101 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2006.12.001
Chou, W.-L., Yu, D.-G., Yang, M.-C.: The preparation and characterization of silver-loading cellulose acetate hollow fiber membrane for water treatment. Polym. Adv. Technol. 16, 600–607 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.630
Windler, L., Height, M., Nowack, B.: Comparative evaluation of antimicrobials for textile applications. Environ. Int. 53, 62–73 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.12.010
Arreche, R., Bellotti, N., Deyá, C., Vázquez, P.: Assessment of waterborne coatings formulated with sol-gel/Ag related to fungal growth resistance. Prog. Org. Coat. 108, 36–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2017.04.007
Panacek, A., Kvıtek, L., Prucek, R., Kolar, M., Vecerova, R., Pizurova, N., Sharma, V.K., Nevecna, T., Zboril, R., Kvı, L., Vec, R.: Silver colloid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 16248–16253 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp063826h
Alvarado, R., Solera, F., Vega-Baudrit, J.: Síntesis Sonoquímica de nanopartículas de óxido de cinc y de plata estabilizadas con quitosano. Evaluación de su actividad antimicrobiana. Revista Iberoamericana 15, 134–148 (2014)
Brause, R., Möltgen, H., Kleinermanns, K.: Characterization of laser-ablated and chemically reduced silver colloids in aqueous solution by UV/VIS spectroscopy and STM/SEM microscopy. Appl. Phys. B 75, 711–716 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-1024-3
Mulvaney, P.: Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 12, 788–800 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/la9502711
Sosa, I.O., Noguez, C., Barrera, R.G.: Optical properties of metal nanoparticles with arbitrary shapes. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 6269–6275 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0274076
Zhao, Y., Jiang, Y., Fang, Y.: Spectroscopy property of Ag nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A 65, 1003–1006 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2006.01.010
El Badawy, A.M., Luxton, T.P., Silva, R.G., Scheckel, K.G., Suidan, M.T., Tolaymat, T.M.: Impact of environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1260–1266 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/es902240k
Cosgrove, T.: Colloid Science: Principles, Methods and Applications. Wiley, New York (2005). https://doi.org/10.1097/00000433-198206000-00020
El-Zahry, M.R., Mahmoud, A., Refaat, I.H., Mohamed, H.A., Bohlmann, H., Lendl, B.: Antibacterial effect of various shapes of silver nanoparticles monitored by SERS. Talanta. 138, 183–189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.02.022
Bastos, D.H.M., Ishimoto, E.Y., Ortiz, M., Marques, M., Fernando Ferri, A., Torres, E.A.F.S.: Essential oil and antioxidant activity of green mate and mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) infusions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 19, 538–543 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2005.03.002
Berte, K.A., Beux, M.R., Spada, P.K., Salvador, M., Hoffmann-Ribani, R.: Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of yerba-mate (Ilex paraguariensis A.St.-Hil., Aquifoliaceae) extract as obtained by spray drying. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 5523–5527 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2008343
Bastos, D.H.M., Saldanha, L.A., Catharino, R.R., Sawaya, A.C.H.F., Cunha, I.B.S., Carvalho, P.O., Eberlin, M.N.: Phenolic antioxidants identified by ESI-MS from yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) and green tea (Camellia sinensis) extracts. Molecules 12, 423–432 (2007)
Isolabella, S., Cogoi, L., López, P., Anesini, C., Ferraro, G., Filip, R.: Study of the bioactive compounds variation during yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) processing. Food Chem. 122, 695–699 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.039
Anbinder, P.S., Deladino, L., Navarro, A.S., Amalvy, J.I., Martino, M.N.: Yerba mate extract encapsulation with alginate and chitosan systems: interactions between active compound encapsulation polymers. J Encapsul. Adsorpt. Sci. 2011, 80–87 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4236/jeas.2011.14011
Taylor, P., Marcelo, M.C.A., Pozebon, D., Ferrão, M.F.: Authentication of yerba mate according to the country of origin by using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) associated with chemometrics. Food Addit. Contam. A (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2015.1050702
Shamaila, S., Sajjad, A.K.L., Ryma, N.A., Farooqi, S.A., Jabeen, N., Majeed, S., Farooq, I.: Advancements in nanoparticle fabrication by hazard free eco-friendly green routes. Appl. Mater. Today. 5, 150–199 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2016.09.009
Castro, L., Blazquez, M.L., Munoz, J.A., Gonzalez, F., Garcıa-Balboa, C., Ballester, A.: Biosynthesis of gold nanowires using sugar beet pulp. Process Biochem. 46, 1076–1082 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.01.025
Buszewski, B., Railean-plugaru, V., Szultka-mlynska, M., Golinska, P.: Antimicrobial activity of biosilver nanoparticles produced by a novel Streptacidiphilus durhamensis strain. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2016.03.002
Dhand, V., Soumya, L., Bharadwaj, S., Chakra, S., Bhatt, D., Sreedhar, B.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.08.018
Rasulov, B., Rustamova, N., Yili, A., Zhao, H.: Synthesis of silver nanoparticles on the basis of low and high molar mass exopolysaccharides of Bradyrhizobium japonicum 36 and its antimicrobial activity against some pathogens. Folia Microbiol. 61, 283–293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0436-5
Agnihotri, S., Mukherji, S., Mukherji, S.: Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 4, 3974–3983 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra44507k
Ibrahim, H.M.M.: Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 8, 265–275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.01.007
Krishnaraj, C., Jagan, E.G., Rajasekar, S., Selvakumar, P., Kalaichelvan, P.T., Mohan, N.: Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf. B 76, 50–56 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.10.008
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their thanks for the financial support provided by Laboratorio Nacional de Nanotecnología (LANOTEC), Centro Nacional de Alta Tecnología (CeNAT-CONARE), POLIUNA-UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL de Costa Rica, National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) and National University of La Plata (UNLP). They also thank to Reynaldo Pereira for TEM micrographs, Universidad Nacional for the Dynamic light scattering (DLS) and Zeta potential analysis, and Yendry Corrales Ureña for AFM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arreche, R.A., Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G., Vega-Baudrit, J.R. et al. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Extracts from Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Wastes. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 245–253 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0394-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0394-7