Abstract
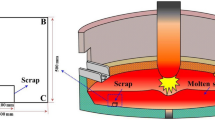
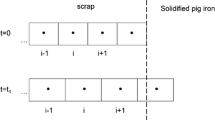
A 3D model applying temperature- and carbon concentration- dependent material properties was developed to describe the scrap melting behavior and carbon diffusion under natural convection. Simulated results agreed reasonably well with experimental ones. Scrap melting was subdivided into four stages: formation of a solidified layer, rapid melting of the solidified layer, carburization, and carburization + normal melting. The carburization stage could not be ignored at low temperature because the carburization time for the sample investigated was 214 s at 1573 K compared to 12 s at 1723 K. The thickness of the boundary layer with significant concentration difference at 1573 K increased from 130 µm at 5 s to 140 µm at 60 s. The maximum velocity caused by natural convection decreased from 0.029 m·s−1 at 5 s to 0.009 m·s−1 at 634 s because the differences in temperature and density between the molten metal and scrap decreased with time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Oeters and R.M. Ni, Metallurgy of Steelmaking, The Metallurgical Industry Press, Bei**g, 1997, p. 479.
R.D. Pehlke, P.D. Goodell, and R.W. Dunlap, Kinetics of steel dissolution in molten pig iron, Trans. Metall. Soc. ALME, 233(1965), p. 1420.
R.I.L. Guthrie and P. Stubbs, Kinetics of scrap melting in baths of molten pig iron, Can. Metall. Q., 12(1973), No. 4, p. 465.
K. Mori and H. Nomura, Study on the rate of scrap melting in the steelmaking process, Tetsu-to-Hagané, 55(1969), No. 5, p. 347.
E.M. Gol’dfarb and B.I. Sherstov, Heat and mass transfer when melting scrap in an oxygen converter, J. Eng. Phys., 18(1970), No. 3, p. 342.
D. Weisz-Patrault, Coupled heat conduction and multiphase change problem accounting for thermal contact resistance, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 104(2017), p. 595.
A.K. Shukla, B. Deo, and D.G.C. Robertson, Scrap dissolution in molten iron containing carbon for the case of coupled heat and mass transfer control, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 44(2013), No. 6, p. 1407.
Y.K. Wu and M. Lacroix, Numerical simulation of the melting of scrap metal in a circular furnace, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer, 22(1995), No. 4, p. 517.
K. Isobe, H. Maede, K. Ozawa, K. Umezawa, and C. Saito, Analysis of the scrap melting rate in high carbon molten iron, Tetsu-to-Hagané, 76(1990), No. 11, p. 2033.
A. Kruskopf and S. Louhenkilpi, 1-dimensional scrap melting model for steel converter (BOF), [in] Proceedings of the METEC & 2nd ESTAD, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2015, p. 15.
A. Kruskopf, Multiphysical Modeling Approach for Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Process [Dissertation], Aalto University, Finland, 2018, p. 12.
A. Kruskopf and V.V. Visuri, A gibbs energy minimization approach for modeling of chemical reactions in a basic oxygen furnace, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 48(2017), No. 6, p. 3281.
S. Deng, A.J. Xu, G. Yang, and H.B. Wang, Analyses and calculation of steel scrap melting in a multifunctional hot metal ladle, Steel Res. Int., 90(2018), No. 3, p. 1.
H.P. Sun, Y.C. Liu, C.C. Lin, and L.U. Muh-Jung, Experimental observation of spherical scrap melting in hot metal, [in] International Congress on the Science & Technology of Steelmaking, Bei**g, China, 2015, p. 136.
F.M. Penz, J. Schenk, R. Ammer, G. Klösch, K. Pastucha, and M. Reischl, Diffusive steel scrap melting in carbon-saturated hot metal-phenomenological investigation at the solid-liquid interface, Materials, 12(2019), No. 8, p. 1358.
M. Gao, S.F. Yang, and Y.L. Zhang, Experimental study on mass transfer during scrap melting in the steelmaking process, Ironmaking Steelmaking, (2019), p. 1.
H.L. Zhao, X. Zhao, L.Z. Mu, L.F. Zhang, and L.Q. Yang, Gas-liquid mass transfer and flow phenomena in a peirce-smith converter: a numerical model study, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 9, p. 1092.
J. Dongik, K. Yumkyum, S. Minsoo, and L. Joonho, Kinetics of carbon dissolution of coke in molten iron, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 43(2012), No. 6, p. 1308.
A. Fluent, ANSYS Fluent Theory Guide, Release 15.0 ed., ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg, PA, 2013. ANSYS Inc., USA, 15317, 724.
J.X. Chen, Metallurgy of Iron and Steel (Steelmaking), The Metallurgical Industry Press, Bei**g, 2012, p. 174.
J. Szekely, Y.K. Chuang, and J.W. Hlinka, The melting and dissolution of low-carbon steels in iron-carbon melts, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 3(1972), No. 11, p. 2825.
Y.U. Kim and R. Pehlke, Mass transfer during dissolution of a solid into liquid in the iron-carbon system, Metall. Trans., 5(1974), No. 12, p. 2527.
M. Kosaka and S. Minowa, Mass-transfer from solid metal cylinder into liquid metal, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 52(1966), No. 12, p. 1748.
M. Kosaka and S. Minowa, Mass-transfer from graphite cylinder into liquid Fe-C alloy, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 53(2010), No. 13, p. 1467.
K. Wu, Principle of Metallurgical Transmission, Peking University Press, Bei**g, 2016, p. 142.
J.K. Wright, Steel dissolution in quiescent and gas stirred Fe/C melts, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 20(1989), No. 3, p. 363.
Z.Y. Liu, Y.P. Bao, M. Wang, X. Li, and F.Z. Zeng, Austenite grain growth of medium carbon alloy steel with aluminum additions during heating process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 3, p. 282.
V. Dakre, D.R. Peshwe, S.U. Pathak, and A. Likhite, Effect of austenitization temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon equivalent carbidic austempered ductile iron, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 25(2018), No. 7, p. 770.
G.S. Wei, R. Zhu, T.P. Tang, and K. Dong, Study on the melting characteristics of steel scrap in molten steel, Ironmaking Steel-making, 46(2019), No. 7, p. 609.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2019YFC1905701), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51674022 and 51734003), and the Key projects of NSFC (No. U1960201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Gao, Jt., Zhang, Yl. et al. Simulation on scrap melting behavior and carbon diffusion under natural convection. Int J Miner Metall Mater 28, 380–389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1997-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1997-0