Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the effects of protein enriched bread and drinking yoghurt, substituting regular products, on the total protein intake and the distribution of protein intake over the day in older adults.
Design
A single blind randomised controlled trial.
Setting
Rehabilitation centre.
Participants
Older adults (≥ 55 years) admitted to a rehabilitation centre after hospital discharge (n=34).
Intervention
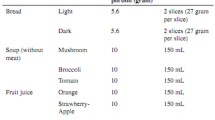
Participants received a high protein diet (protein enriched bread and protein enriched drinking yoghurt; n=17) or a regular diet (regular bread and regular drinking yoghurt; n=17) for three consecutive weeks.
Measurements
Total protein intake and protein intake per meal, measured twice weekly over a three weeks period (six measurements per participant).
Results
Compared with controls, patients who received the protein enriched products had a significantly higher protein intake (115.3 g/d vs 72.5 g/d, P<0.001; 1.6 g/kg/d vs 1.1 g/kg/d, P<0.001). The intervention group consumed quantities over the recommended level (25–30 g/meal) during each of the three meals (32.5 g, 30.0 g, 34.8 g/meal), where the control group consumed quantities below the recommended level during breakfast (17.7 g) and lunch (18.4 g).
Conclusions
The use of protein enriched products, replacing regular products, results in a significant increased daily protein intake in older adults. In addition, the daily consumption of protein enriched products improves protein distribution over the day.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ageing and Life Course. Interesting facts about ageing. World Health Organization (online). Available at: http://www.who.int/ageing/about/facts/en/. Accessed December 8, 2013.
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinková E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010;39(4):412–423. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afq034
Walrand S, Guillet C, Salles J, Cano N, Boirie Y. Physiopathological mechanism of sarcopenia. Clin Geriatr Med 2011;27(3):365–385. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2011.03.005.
Holloszy JO. The biology of aging. Mayo Clin Proc 2000;75:3–9.
Bauer J, Biolo G, Cederholm T, Cesari M, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Morley JE, Phillips S, Sieber C, Stehle P, Teta D, Visvanathan R, Volphi E, Boirie Y. Evidence-based Recommendations for Optimal Dietary Protein Intake in Older People: A Position Paper From the PROT-AGE Study Group. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2013;14(8):542–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.05.021
Burd AB, Gorissen SH, Loon van LJC. Anabolic resistance of muscle protein synthesis with aging. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2013;41(3):169–173. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e318292f3d5.
Pennings B, Groen B, de Lange A, Gijsen AP, Zorenc AH, Senden JM, van Loon LJ. Amino acid absorption and subsequent muscle protein accretion following graded intakes of whey protein in older adults men. Am J of Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2012;302(8):E992–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00517.2011.
Yang Y, Breen L, Burd NA, Hector AJ, Churchward-Venne TA, Josse AR, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM. Resistance exercise enhances myofibrillar protein synthesis with graded intakes of whey protein in older men. Br J Nutr 2012;108(10):1780–8. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511007422.
Koopman R, Walrand S, Beelen M, Gijsen AP, Kies AK, Boirie Y, Saris WH, van Loon LJ. Dietary protein digestion and absorption rates and the subsequent postprandial muscle protein synthetic response do not differ between young and older adults men. J Nutr 2009;139(9):1707–1713. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.109173.
Pennings B, Koopman R, Beelen M, Senden JM, Saris WH, van Loon LJ. Exercising before protein intake allows for greater use of dietary protein-derived amino acids for de novo muscle protein synthesis in both young and older adults men. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;93(2):322–31. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2010.29649.
Nieuwenhuizen WF, Weenen H, Rigby P, Hetherington MM. Older adults and patients in need of nutritional support: Review of current treatment options and factors influencing nutritional intake. Clin Nutr 2010;29(2):160–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2009.09.003.
Furman EF. Undernutrition in Older Adults across the Continuum of Care: Nutritional assessment, barriers, and interventions. J Gerontol Nurs 2006;32(1):22–7.
Costa AI, Jongen WM. Designing New Meals for an Ageing Population. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2010;50(6):489–502. doi: 10.1080/10408390802544553.
Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Lemmens SG, Westerterp KG. Dietary protein, its role in satiety, energetics, weight loss and health. Br J Nutr 2012;108(2);105–12. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512002589.
Tieland M, Borgonjen-Van den Berg KJ, van Loon LJ, de Groot LC. Dietary protein intake in community-dwelling, frail, and institutionalized older adults people: scope for improvement. Eur J Nutr 2012;51(2):173–9. doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0203-6.
Chumlea WC, Roche AF, Steinbaugh ML. Estimating stature from knee height for persons 60 to 90 years of age. J Am Geriatr Soc 1985;33(2):116–120.
Nederlands Voedingsstoffenbestand. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu (online). Available at: http://www.rivm.nl/Onderwerpen/N/Nederlands_Voedingsstoffenbestand. Accessed January 7, 2014.
Valenzuela RE, Ponce JA, Morales-Figueroa GG, Muro KA, Carreón VR, Alemán-Mateo H. Insufficient amounts and inadequate distribution of dietary protein intake in apparently healthy older adults in a develo** country: implications for dietary strategies to prevent sarcopenia. Clin Interv Aging 2013;8:1143–8. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S49810.
Paddon-Jones D, Rasmussen BB. Dietary protein recommendations and the prevention of sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2009;12(1):86–90. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32831cef8b.
Symons TB, Sheffield-Moore M, Wolfe RR, Paddon-Jones D. A moderate serving of high quality protein maximally stimulates skeletal muscle protein synthesis in young and older adults subjects. J Am Diet Assoc 2009;109(9):1582–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2009.06.369.
Bollwein J, Diekmann R, Kaiser MJ, Bauer JM, Uter W, Sieber CC, Volkert D. Distribution but not amount of protein intake is associated with frailty: a cross-sectional investigation in the region of Nürnberg. Nutr J 2013;12(1):109. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-109.
Van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren MA, Roosemalen MM, Weijs PJ, Langius JA. High waste contributes to low food intake in hospitalized patients. Nutr Clin Pract 2012;27(2):274–80. doi: 10.1177/0884533611433602.
Milne AC, Avenell, AJ Potter J. Oral protein and energy supplementation in older people: a systematic review of randomized trials. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Clin Perform Programme 2005;10:103–20.
Mucci E, Jackson SH. Nutritional supplementation in community-dwelling older adults people. Ann Nutr Metabol 2008;52(1):33–7. doi: 10.1159/000115346.
Joosten E, Vander Elst B. Does nutritional supplementation influence the voluntary dietary intake in an acute geriatric hospitalized population? Aging 2001;13(5):391–4.
Simmons SF, Patel AV. Nursing home staff delivery of oral liquid nutritional supplements to residents at risk for unintentional weight loss. J Am Geriatr Soc 2006;54(9):1372–6.
Gosney M. Are we wasting our money on food supplements in elder care wards? J Adv Nurs 2003;43(3):275–80.
McAlpine SJ, Harper J, McMurdo ME, Bolton-Smith C, Hetherington MM. Nutritional supplementation in older adults: pleasantness, preference and selection of sip-feeds. Br J Health Psychol 2003;8(1):57–66.
Stelten S, Dekker IM, Ronday EM, Thijs A, Boelsma E, Peppelenbos HW, de van der Schueren MA. Protein-enriched ‘regular products’ and their effects on protein intake in acute hospitalized older adults; a randomised controlled trial. Clin Nutr 2014;S0261–5614(14)00211-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.08.007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Til, A.J., Naumann, E., Cox-Claessens, I.J.H.M. et al. Effects of the daily consumption of protein enriched bread and protein enriched drinking yoghurt on the total protein intake in older adults in a rehabilitation centre: A single blind randomised controlled trial. J Nutr Health Aging 19, 525–530 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0471-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0471-6