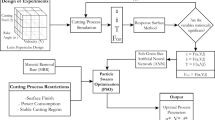
Abstract
7075 aluminum alloy has been widely applied in the field of aerospace and marine sheet metal because of its protruding mechanical and corrosion resistance. In this paper, the problem of selecting optimal process parameters to optimize multiple processing variables had been studied in precision manufacturing. Multi-objective particle swarm optimized neural networks system was put forward to determine the optimal cutting conditions with multi-objective particle swarm algorithm and multiple neural networks as prediction models of machining variables. Precision parts manufacturing of 7075 aluminum alloy would go through two operations of material removal and surface forming. Firstly, optimal cutting conditions were determined to minimize tool wear while maximizing metal removal rate in material removal stage. Secondly, it was significant and meaningful to select optimal cutting conditions corresponding to the best surface quality and minimum root mean square of tool vibration in surface forming stage. Orthogonal experiments had been carried out to observe the relationship between machining-related variables and cutting parameters in detail. Multiple neural networks were trained to establish predictive models of cutting process from orthogonal experimental and statistical data. Maximum deviation theory sorted the Pareto solutions searched by optimization process of neural networks driven by multi-objective particle swarm algorithm. The top ranking Pareto solutions had been determined as the optimal cutting parameters combination for material removal and surface forming stages, respectively. Finally, the proposed optimization system can also be used to optimize the processing of other difficult-to-machine materials.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rai, J. K., Brand, D., Slama, M., & **rouchakis, P. (2011). Optimal selection of cutting parameters in multi-tool milling operations using a genetic algorithm. International Journal of Production Research, 49(10), 3045–3068.
Yeganefar, A., Niknam, S. A., & Asadi, R. (2019). The use of support vector machine, neural network, and regression analysis to predict and optimize surface roughness and cutting forces in milling. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 105(1–4), 951–965.
Imani, L., Henzaki, A. R., Hamzeloo, R., & Davoodi, B. (2020). Modeling and optimizing of cutting force and surface roughness in milling process of Inconel 738 using hybrid ANN and GA. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B-Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 234(5), 920–932.
Jeyakumar, S., Marimuthu, K., & Ramachandran, T. (2015). Optimization of machining parameters of A16061 composite to minimize the surface roughness—modelling using RSM and ANN. Indian Journal of Engineering and Materials Sciences, 22(1), 29–37.
Chang, W. Y., Wu, S. J., & Hsu, J. W. (2020). Investigated iterative convergences of neural network for prediction turning tool wear. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 106(7–8), 2939–2948.
Twardowski, P., & Wiciak-Pikula, M. (2019). Prediction of Tool wear using artificial neural networks during turning of hardened steel. Materials, 12(19), 3091.
Wu, T. Y., & Lei, K. W. (2019). Prediction of surface roughness in milling process using vibration signal analysis and artificial neural network (vol. 102, p. 305, 2019). International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 102(1–4), 315–315.
Ramesh, K., Alwarsamy, T., & Jayabal, S. (2015). Prediction of cutting process parameters in boring operations using artificial neural networks. Journal of Vibration and Control, 21(6), 1043–1054.
Mundada, V., & Narala, K. R. S. (2018). Optimization of Milling operations using artificial neural networks (ANN) and simulated annealing algorithm (SAA). Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(2), 4971–4985.
Hu, L. K., Cai, W., Shu, L. J., Xu, K. K., Zheng, H., & Jia, S. (2020). Energy optimisation for end face turning with variable material removal rate considering the spindle speed changes. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology.
Pandey, R. K., & Panda, S. S. (2015). Optimization of bone drilling using Taguchi methodology coupled with fuzzy based desirability function approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26(6), 1121–1129.
Vukman, J., Lukic, D., Borojevic, S., Rodic, D., & Milosevic, M. (2020). Application of fuzzy logic in the analysis of surface roughness of thin-walled aluminum parts. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 21(1), 91–102.
Aamir, M., Tu, S. S., Tolouei-Rad, M., Giasin, K., & Vafadar, A. (2020). Optimization and modeling of process parameters in multi-hole simultaneous drilling using taguchi method and fuzzy logic approach. Materials, 13(3), 680.
Mia, M., Khan, M. A., & Dhar, N. R. (2017). Study of surface roughness and cutting forces using ANN, RSM, and ANOVA in turning of Ti–6Al–4V under cryogenic jets applied at flank and rake faces of coated WC tool. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 93(1–4), 975–991.
Cheng, D. J., Xu, F., Xu, S. H., Zhang, C. Y., Zhang, S. W., & Kim, S. J. (2020). Minimization of surface roughness and machining deformation in milling of Al alloy thin-walled parts. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing.
He, K., Xu, Q. S., & Jia, M. P. (2015). Modeling and predicting surface roughness in hard turning using a bayesian inference-based HMM–SVM model. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 12(3), 1092–1103.
Jurkovic, Z., Cukor, G., Brezocnik, M., & Brajkovic, T. (2018). A comparison of machine learning methods for cutting parameters prediction in high speed turning process. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(8), 1683–1693.
Yang, Y. F., Guo, Y. L., Huang, Z. P., Chen, N., Li, L., Jiang, Y. F., et al. (2019). Research on the milling tool wear and life prediction by establishing an integrated predictive model. Measurement, 145, 178–189.
Kim, D. H., Kim, T. J. Y., Wang, X. L., Kim, M., Quan, Y. J., Oh, J. W., et al. (2018). Smart machining process using machine learning: A review and perspective on machining industry. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 5(4), 555–568.
Blondet, G., Le Duigou, J., & Boudaoud, N. (2019). A knowledge-based system for numerical design of experiments processes in mechanical engineering. Expert Systems with Applications, 122, 289–302.
Deng, Z. H., Zhang, H., Fu, Y. H., Wan, L. L., & Lv, L. S. (2018). Research on intelligent expert system of green cutting process and its application. Journal of Cleaner Production, 185, 904–911.
**ao, Q. E., Li, C. B., Tang, Y., Li, L. L., & Li, L. (2019). A knowledge-driven method of adaptively optimizing process parameters for energy efficient turning. Energy, 166, 142–156.
Mohanty, C. P., Mahapatra, S. S., & Singh, M. R. (2016). A particle swarm approach for multi-objective optimization of electrical discharge machining process. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 27(6), 1171–1190.
Badiger, P. V., Desai, V., Ramesh, M. R., Prajwala, B. K., & Raveendra, K. (2019). Cutting forces, surface roughness and tool wear quality assessment using ANN and PSO approach during machining of MDN431 with TiN/AlN-coated cutting tool. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 44(9), 7465–7477.
Malghan, R. L., Rao, K. M. C., Shettigar, A. K., Rao, S. S., & D'Souza, R. J. (2017). Application of particle swarm optimization and response surface methodology for machining parameters optimization of aluminium matrix composites in milling operation. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 39(9), 3541–3553.
Kumar, S. P. L. (2019). Measurement and uncertainty analysis of surface roughness and material removal rate in micro turning operation and process parameters optimization. Measurement, 140, 538–547.
Laouissi, A., Yallese, M. A., Belbah, A., Belhadi, S., & Haddad, A. (2019). Investigation, modeling, and optimization of cutting parameters in turning of gray cast iron using coated and uncoated silicon nitride ceramic tools. Based on ANN, RSM, and GA optimization. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 101(1–4), 523–548.
Soepangkat, B. O. P., Pramujati, B., Effendi, M. K., Norcahyo, R., & Mufarrih, A. M. (2019). Multi-objective optimization in drilling kevlar fiber reinforced polymer using grey fuzzy analysis and backpropagation neural network-genetic algorithm (BPNN-GA) approaches. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 20(4), 593–607.
Klancnik, S., Hrelja, M., Balic, J., & Brezocnik, M. (2016). Multi-objective optimization of the turning process using a gravitational search algorithm (GSA) and NSGA-II approach. Advances in Production Engineering & Management, 11(4), 366–376.
Li, L., Liu, F., Chen, B., & Li, C. B. (2015). Multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters in sculptured parts machining based on neural network. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26(5), 891–898.
Younas, M., Jaffery, S. H. I., Khan, M., Khan, M. A., Ahmad, R., Mubashar, A., et al. (2019). Multi-objective optimization for sustainable turning Ti6Al4V alloy using grey relational analysis (GRA) based on analytic hierarchy process (AHP). International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 105(1–4), 1175–1188.
Muaz, M., & Choudhury, S. K. (2019). Experimental investigations and multi-objective optimization of MQL-assisted milling process for finishing of AISI 4340 steel. Measurement, 138, 557–569.
Quan, G. Z., Zhang, Z. H., Wang, X., Li, Y. L., Mao, A., & ** mold for high strength steel sheet based on MOPSO. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 90(1–4), 887–906.
Li, C. B., **ao, Q. G., Tang, Y., & Li, L. (2016). A method integrating Taguchi, RSM and MOPSO to CNC machining parameters optimization for energy saving. Journal of Cleaner Production, 135, 263–275.
Xu, G. D., Chen, J. H., Zhou, H. C., Yang, J. Z., Hu, P. C., & Dai, W. (2019). Multi-objective feedrate optimization method of end milling using the internal data of the CNC system. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 101(1–4), 715–731.
**e, Y. M., Tang, W., Zhang, F., Pan, B. B., Yue, Y. P., & Feng, M. Q. (2019). Optimization of variable blank holder force based on a sharing niching RBF neural network and an improved NSGA-II algorithm. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 20(2), 285–299.
Balan, A. V., Shivasankaran, N., & Magibalan, S. (2018). Optimization of cladding parameters for resisting corrosion on low carbon steels using simulated annealing algorithm. Materials Research Express, 5(4), 046527.
Rao, R. V., Rai, D. P., & Balic, J. (2018). Multi-objective optimization of machining and micro-machining processes using non-dominated sorting teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(8), 1715–1737.
Rao, K. V., & Murthy, P. B. G. S. N. (2018). Modeling and optimization of tool vibration and surface roughness in boring of steel using RSM, ANN and SVM. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(7), 1533–1543.
Sahin, R., & Liu, P. D. (2016). Maximizing deviation method for neutrosophic multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information. Neural Computing & Applications, 27(7), 2017–2029.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51575202, 51675204) and Science Challenge Project (Grant No. TZ2018006-0102-01). The authors sincerely thank the equipment and measuring devices provided by the Precision Measurement Laboratory of the School of Mechanical Science and Engineering for current research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Z., Shi, T., Xuan, J. et al. A Study on Multivariable Optimization in Precision Manufacturing Using MOPSONNS. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 21, 2011–2026 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00402-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00402-z