Abstract
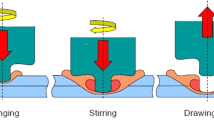
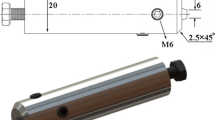
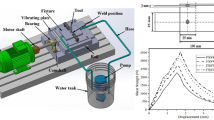
Friction stir spot welding (FSSW) is a solid state joining technique with a simple concept. A non-consumable rotating tool with a specially designed pin and shoulder are inserted into the sheets or plates to be joined. In this study, the effect of vibration on microstructure and thermal properties of Al5083 weldment made by FSSW using rotation speed of 1500 rpm and different dwelling times, namely 5 and 10 s, was investigated. This new method was entitled FSSVW (friction-stir-spot-vibration welding). The experimental and numerical results, obtained using Abaqus software, were compared. In this work, the Johnson–Cook hardening condition was used for modeling of deformable metals. The results showed good comparability between experimental and FEM data. Also, metallography analyses indicated that the grain size decreased and the temperature increased as FSSVW method was applied. The results showed that vibration during FSSW leads to grain size decrease of about 30–50% in the weld region.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FSSW:
-
Friction stir spot welding
- FSSVW:
-
Friction stir spot vibration welding
- S-FSSVW:
-
Simulation of friction stir spot vibration welding
- ALE:
-
Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian
- JCP:
-
Johnson–Cook Plasticity
- EDS:
-
Energy dispersive spectrometry
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Static yield stress (MPa)
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Equivalent plastic strain (%)
- HAZ:
-
Heat-affected zone
- TMAZ:
-
Thermo-mechanical affected zone
- WNZ:
-
Weld nugget zone
- SZ:
-
Stir zone
- Z:
-
Zener–Hollomon parameter
- R:
-
Gas constant
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- ω:
-
Rotation speed (rpm)
- υ:
-
Traverse speed (mm/min
References
Mishra, R. S., & Ma, Z. Y. (2005). Friction stir welding and processing. Materials Science and Engineering R, 50(1–2), 1–78.
Nandan, R., DebRoy, T., & Bhadeshia, H. (2008). Recent advances in friction stir welding process, weldment structure and properties. Progress in Materials Science, 53, 980–1023.
Lee, C. Y., Choi, D. H., Yeon, Y. M., & Jung, S. B. (2009). Dissimilar friction stir spot welding of low carbon steel and AlMg alloy by formation of IMCs. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 14(3), 216–220.
Coelho, R. S., Kostka, A., Sheikhi, S., Dos Santos, J., & Pyzalla, A. R. (2009). Microstructure and mechanical properties of an AA6181-T4 aluminium alloy to HC340LA high strength steel friction stir overlap weld. Advanced Engineering Materials, 10(10), 961–972.
Coelho, R. S., Kostka, A., Dos Santos, J., & Pyzalla, A. R. (2009). EBSD technique visualization of material flow in aluminum to steel friction-stir dissimilar welding. Advanced Engineering Materials, 10(12), 1127–1133.
Cavaliere, P., Cerri, E., Marzoli, L., & Dos Santos, J. (2004). Friction stir welding of ceramic particle reinforced aluminium based metal matrix composites. Applied Composite Materials, 11(4), 247–258.
Wert, J. A. (2003). Microstructures of friction stir weld joints between an aluminum-base metal matrix composite and a monolithic aluminum alloy. Scripta Materialia, 49(6), 607–612.
Mishra, R. S., & Mahoney, M. W. (2007). Friction stir welding and processing. Ohio: ASM International.
Ueji, R., Fujii, H., Cui, L., Nishioka, A., Kunishige, K., & Nogi, K. (2006). Friction stir welding of ultrafine grained plain low carbon steel formed by the martensite process. Materials Science and Engineering A, 423(1–2), 324–330.
Fujii, H., Cui, L., Maeda, M., & Nogi, K. (2006). Effect of tool shape on mechanical properties and microstructure of friction stir welded aluminum alloys. Materials Science and Engineering A, 419(1–2), 25–31.
Fujii, H., Cui, L., Tsuji, N., Maeda, M., Nakata, K., & Nogi, K. (2006). Friction stir welding of carbon steels. Materials Science and Engineering A, 429(1–2), 50–57.
Al-Shahrani, A., & Wynne, B. P. (2010). Effect of dwell time on friction stir spot welded dual phase steel. Advanced Materials Research, 83, 1143–1150.
Su, P., Gerlich, A., North, T. H., & Bendzsak, G. J. (2007). Intermixing in dissimilar friction stir spot welds. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 38(3), 584–595.
Guerra, M., Schmidt, C., McClure, J. C., Murr, L. E., & Nunes, A. C. (2002). Flow patterns during friction stir welding. Materials Characterization, 49(2), 95–101.
Yang, Q., Mironov, S., Sato, Y. S., & Okamoto, K. (2010). Material flow during friction stir spot welding. Materials Science and Engineering A, 527(16–17), 4389–4398.
Tuncel, O., Aydin, H., Tutar, M., & Bayram, A. (2016). Mechanical performance of friction stir spot welded AA6082-T6 sheets. International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering, 4(1), 114–118.
Dey, A., Saha, S. C., & Pandey, K. M. (2014). Study of mechanical properties change during friction stir spot welding of aluminum alloys. Current Trends in Technology & Sciences, 3(1), 26–33.
Baek, S. W., Choi, D. H., Lee, S. Y., Ahn, B. W., Yeon, Y. M., Song, K., et al. (2010). Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir spot welded galvanized steel. Materials Transactions, 51(5), 1044–1050.
Sheikhhasani, H., Sabet, H., & Abasi, M. (2016). Investigation of the effect of friction stir spot welding of BH galvanized steel plates on process parameters and weld mechanical properties. Engineering Technology & Applied Science Research, 6(5), 1149–1154.
Kulekci, M. K. (2014). Effects of process parameters on tensile shear strength of friction stir spot welded aluminiumalloy (EN AW 5005). Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 59(1), 221–224.
Jweeg, M., Tolephih, M., Muhammed, M., & Sadiq, G. (2016). Numerical and experimental analysis of transient temperature and residual thermal stresses in friction stir welding of aluminum alloy 7020-T53. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 11(19), 143–152.
Khuder, A. W. H., Muhammed, M. A., & Ibrahim, H. K. (2017). Numerical and experimental study of temperature distribution in friction stir spot welding of AA2024-T3 Aluminum Alloy. Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 6(5), 7281–7291.
Quazi, I. A., Shete, M. T., & Quazi, M. A. (2015). Thermo-mechanical characterization of friction stir spot welded HDPE sheets. Journal for Science Research and Development, 3(4), 746–769.
Campanelli, L. C., Antonialli, A. I. S., de Alcântara, N. G., Bolfarini, C., Suhuddin, U. F. H., & dos Santos, J. F. (2013). Lap shear test of a magnesium friction spot joint: numerical modeling. Tecnologia em Metalurgia, Materiais e Mineração, 10(2), 97–102.
ASTM-E112-13. (2013). Standard test methods for determining average grain size. West Con shohocken: ASTM International.
ABAQUS/6.14.2. (2016). Providence, RI, USA: Dassault Systems Simulia Corp.
Yalavarthy, H. (2009). Friction stir welding process and material microstructure evolution modeling in 2000 and 5000 series of aluminum alloys. All Thesis, Clemson University.
Getting Started with Abaqus/Explicit: Hibbit, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc., version 6.14 (2004).
Belytschko, T., Liu, W., & Moran, B. (2000). Nonlinear finite elements for continua and structures. Hoboken: Wiley.
Woo, W., Ungar, T., Feng, Z., Kenik, E., & Clausen, B. (2010). X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements of dislocation density and subgrain size in a friction-stir-welded aluminum alloy. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 41, 1210–1216.
Abbasi, M., Abdollahzadeh, A., Omidvar, H., & Bagheri, B. (2016). Rezaei M (2016) Incorporation of SiC particles in FS weldedzone of AZ31 Mg alloy to improve the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. International Journal of Materials Research. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.111369.
Etter, A. L., Baudin, T., Fredj, N., & Penelle, R. (2007). Recrystallization mechanisms in 5251-H14 and 5251-O aluminum friction stir welds. Materials Science and Engineering A, 445–446, 94–99.
Callister, W. D. (2007). Materials science and engineering: an introduction. Hoboken: Wiley.
Rahmi, M., & Abbasi, M. (2017). Friction stir vibration welding process: modifed version of friction stir welding process. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 90, 141–151.
Kalaki, A., Ketabchi, M., & Abbasi, M. (2014). The joining of D2 and M2 tool steels: analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties. International Journal of Materials Research, 105, 764–769.
Arbegast, W.J. & Hartley, P.J. (1998). Friction stir weld technology development at Lockheed Martin Michoud space systems- An overview. Proceedings of the Fifth In Con on Trends in Weld Research (pp. 541–554). Pine Mountain, GA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagheri, B., Abbasi, M. & Givi, M. Effects of Vibration on Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Friction Stir Spot Welded (FSSW) Aluminum Alloy (Al5083). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 20, 1219–1227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00134-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00134-9