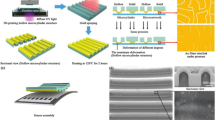
Abstract
Recently, 3D printing technology has taken the spotlight internationally with the recognition of the importance of the manufacturing industry. Currently, there are many mature 3D printing processes and materials. However, an absence of fabrication capability of smart structures such as sensors and actuators remains. In this research, we present a hybrid manufacturing process including directprint/cure (DPC) and projection-based stereolithography, along with printable materials for stretchable tactile sensors. The suggested DPC system consists of a robotically controlled micro-dispensing head, and a light curing module combined with projection stereolithography (PSL) retrofitted from a commercial projector. The materials developed in this research are based on a photocurable and stretchable liquid resin filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs); this polymer/nanocomposite exhibits the piezoresistive property used in tactile sensing. We also used another hybrid process to develop a tactile sensor using a commercial machine to build the sensor body while a dispensing system was used to create the sensing elements. We have characterized the fabricated sensors with several experiments to detect the locations where forces are applied to the surfaces of the sensors. It is concluded that the suggested processes and materials are promising in develo** accurate and reliable stretchable tactile sensors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipson, H, and Kurman, M., “Fabricated: The New World of 3D Printing,” John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
Wohlers, T. T., “Wohlers Report 2013: Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing State of the Industry: Annual Worldwide Progress Report,” 2013.
Lopes, A. J., MacDonald, E., and Wicker, R. B., “Integrating Stereolithography and Direct Print Technologies for 3D Structural Electronics Fabrication,” Rapid Prototy** Journal, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 129–143, 2012.
Wicker, R. B. and MacDonald, E. W., “Multi-Material, Multi-Technology Stereolithography: This Feature Article Covers a Decade of Research into Tackling One of the Major Challenges of the Stereolithography Technique, which is Including Multiple Materials in One Construct,” Virtual and Physical Prototy**, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 181–194, 2012.
Lu, Y., Vatani, M., and Choi, J. W., “Direct-Write/Cure Conductive Polymer Nanocomposites for 3D Structural Electronics,” Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, vol. 27, no. 10, pp. 2929–2934, 2013.
Kim, M. S., Chu, W. S., Kim, Y. M., Avila, A. P. G., and Ahn, S. H., “Direct Metal Printing of 3D Electrical Circuit Using Rapid Prototy**,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 147–150, 2009.
Aguilera, E., Ramos, J., Espalin, D., Cedillos, F., Muse, D., et al., 3D Printing of Electro Mechanical Systems, Proc. of 24th Annual Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, pp. 950–961, 2013.
Weiss, L., Merz, R., Prinz, F. B., Neplotnik, G., Padmanabhan, P., et al., “Shape Deposition Manufacturing of Heterogeneous Structures,” Journal of Manufacturing Systems, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 239–248, 1997.
Willis, K., Brockmeyer, E., Hudson, S., and Poupyrev, I., “Printed Optics: 3D Printing of Embedded Optical Elements for Interactive Devices,” Proc. of the 25th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pp. 589–598, 2012.
Ahn, B. Y., Duoss, E. B., Motala, M. J., Guo, X., Park, S. I., at al., “Omnidirectional Printing of Flexible, Stretchable, and Spanning Silver Microelectrodes,” Science, vol. 323, no. 5921, pp. 1590–1593, 2009.
Sun, K., Wei, T. S., Ahn, B. Y., Seo, J. Y., Dillon, S. J., and Lewis, J. A., “3D Printing of Interdigitated Li-Ion Microbattery Architectures,” Advanced Materials, vol. 25, no. 33, pp. 4539–4543, 2013.
Engeberg, E. D., Vatani, M., and Choi, J. W., “Detection of the Direction and Speed of Motion of Forces on the Surface of a Compliant Tactile Sensor,” Proc. of IEEE 13th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, pp. 158–163, 2013.
Engeberg, E. D., Vatani, M., and Choi, J. W., “Direction of Slip Detection For A Biomimetic Tactile Sensor,” Proc. of IEEE 12th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, pp. 1933–1937, 2012.
Choi, J. W., Vatani, M., and Engeberg, E. D., “Direct-Write of Multi-Layer Tactile Sensors,” Proc. of IEEE 13th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, pp. 164–168, 2013.
Vatani, M., Engeberg, E. D., and Choi, J. W., Force and Slip Detection with Direct-Write Compliant Tactile Sensors using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composites, Sensors and Actuators A: physical, vol. 195, pp. 90–97, 2013.
Arafat, M. T., Gibson, I., and Li, X., “State of the Art and Future Direction of Additive Manufactured Scaffolds-Based Bone Tissue Engineering,” Rapid Prototy** Journal, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 13–26, 2014.
Geng, L., Feng, W., Hutmacher, D. W., San-Wong, Y., Loh, H. T., and Fuh, J. Y., “Direct Writing of Chitosan Scaffolds using a Robotic System,” Rapid Prototy** Journal, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 90–97, 2005.
Jiang, C. P., Huang, J. R., and Hsieh, M. F., “Fabrication of Synthesized PCL-PEG-PCL Tissue Engineering Scaffolds using an Air Pressure-Aided Deposition System,” Rapid Prototy** Journal, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 288–297, 2011.
Khalil, S., Nam, J., and Sun, W., “Multi-Nozzle Deposition for Construction of 3D Biopolymer Tissue Scaffolds,” Rapid Prototy** Journal, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 9–17, 2005.
Phattanaphibul, T., Koomsap, P., Idram, I., and Nachaisit, S., “Development of SVM Rapid Prototy** for Scaffold Fabrication,” Rapid Prototy** Journal, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 90–104, 2014.
Cohen, D. L., Malone, E., Lipson, H., and Bonassar, L. J., “Direct Freeform Fabrication of Seeded Hydrogels in Arbitrary Geometries,” Tissue Engineering, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 1325–1335, 2006.
Mironov, V., Boland, T., Trusk, T., Forgacs, G., and Markwald, R. R., “Organ Printing: Computer-Aided Jet-based 3D Tissue Engineering,” Trends in Biotechnology, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 157–161, 2003.
Lewis, J. A. and Gratson, G. M., “Direct Writing in Three Dimensions,” Materials today, vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 32–39, 2004.
Guo, S. Z., Gosselin, F., Guerin, N., Lanouette, A. M., Heuzey, M. C., and Therriault, D., “3D Printing: SolventCast ThreeDimensional Printing of Multifunctional Microsystems (Small 24/2013),” Small, vol. 9, no. 24, pp. 4090–4090, 2013.
Ahn, B. Y., Shoji, D., Hansen, C. J., Hong, E., Dunand, D. C., and Lewis, J. A., “Printed Origami Structures,” Advanced Materials, vol. 22, no. 20, pp. 2251–2254, 2010.
Malone, E. and Lipson, H., “Multi-Material Freeform Fabrication of Active Systems,” Proc. of ASME 9th Biennial Conference on Engineering Systems Design and Analysis, vol. 1, pp. 345–353, 2008.
Vatani, M., Lu, Y., Lee, K.-S., Kim, H.-C., and Choi, J.-W., “Direct-Write Stretchable Sensors using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Matrix,” Journal of Electronic Packaging, vol. 135, no. 1, Paper No. 011009, 2013.
Ahn, B. Y., Lorang, D. J., Duoss, E. B., and Lewis, J. A., “Direct-Write Assembly of Microperiodic Planar and Spanning ITO Microelectrodes,” Chemical Communications, vol. 46, no. 38, pp. 7118–7120, 2010.
Castillo, S., Muse, D., Medina, F., MacDonald, E., and Wicker, R., “Electronics Integration in Conformal Substrates Fabricated with Additive Layered Manufacturing,” Proc. of the 20th Annual Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, pp. 730–737, 2009.
Adams, J. J., Duoss, E. B., Malkowski, T. F., Motala, M. J., Ahn, B. Y., et al., “Conformal Printing of Electrically Small Antennas on Three Dimensional Surfaces,” Advanced Materials, vol. 23, no. 11, pp. 1335–1340, 2011.
Vatani, M., Engeberg, E. D., and Choi, J. W., “Hybrid Additive Manufacturing of 3D Compliant Tactile Sensors,” Proc. of ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Vol. 2A, Paper No. V02AT02A004, 2013.
Farahani, R. D., Dalir, H., Le Borgne, V., Gautier, L. A., El Khakani, et al., “Direct-Write Fabrication of Freestanding Nanocomposite Strain Sensors,” Nanotechnology, vol. 23, no. 8, Paper No. 085502, 2012.
Lebel, L. L., Aissa, B., Khakani, M. A. E., and Therriault, D., “Ultraviolet Assisted Direct Write Fabrication of Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Nanocomposite Microcoils,” Advanced Materials, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 592–596, 2010.
Yousef, H., Boukallel, M., and Althoefer, K., “Tactile Sensing for Dexterous In-Hand Manipulation in Robotics-a Review,” Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, vol. 167, no. 2, pp. 171–187, 2011.
Tiwana, M. I., Redmond, S. J., and Lovell, N. H., “A Review of Tactile Sensing Technologies with Applications in Biomedical Engineering,” Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, vol. 179, pp. 17–31, 2012.p
Engeberg, E. D. and Meek, S. G., “Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Prosthetic Hands to Simultaneously Prevent Slip and Minimize Deformation of Grasped Objects,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 376–385, 2013.
Karnati, N., Kent, B. A., and Engeberg, E. D., “Bioinspired Sinusoidal Finger Joint Synergies for a Dexterous Robotic Hand to Screw and Unscrew Objects with Different Diameters,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 612–623, 2013.
Engeberg, E. D., Meek, S. G., and Minor, M. A., “Hybrid Force-Velocity Sliding Mode Control of a Prosthetic Hand,” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 1572–1581, 2008.
Wettels, N., Parnandi, A. R., Moon, J. H., Loeb, G. E., and Sukhatme, G., “Grip Control Using Biomimetic Tactile Sensing Systems,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 718–723, 2009.
Rocha, J. G., Santos, C., Cabral, J. M., and Lanceros-Mendez, S., “3 Axis Capacitive Tactile Sensor and Readout Electronics,” Proc. of IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, vol. 4, pp. 2767–2772, 2006.
Ohmura, Y., Kuniyoshi, Y., and Nagakubo, A., “Conformable and Scalable Tactile Sensor Skin for Curved Surfaces,” Prof. of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1348–1353, 2006.
Hammond, F. L., Kramer, R. K., Wan, Q., Howe, R. D., and Wood, R. J., “Soft Tactile Sensor Arrays for Micromanipulation,” Proc. of in IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 25–32, 2012.
Kim, M. S., Shin, H. J., and Park, Y. K., “Design Concept of High-Performance Flexible Tactile Sensors with a Robust Structure,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., vol. 13, no. 11, pp. 1941–1947, 2012.
Elango, N., Faudzi, A. A. M., Hassan, A., and Rusydi, M. R. M., “Experimental Investigations of Skin-Like Material and Computation of Its Material Properties,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 1909–1914, 2014.
Zhang, Y. F., Liu, Y. W., **, M. H., and Liu, H., “Design of a Finger-Tip Flexible Tactile Sensor for an Anthropomorphic Robot Hand,” Springer, pp. 762–773, 2010.
Yu, J., Grossiord, N., Koning, C. E., and Loos, J., “Controlling the Dispersion of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes in Aqueous Surfactant Solution,” Carbon, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 618–623, 2007.
Choi, J. W., MacDonald, E., and Wicker, R., “Multi-Material Microstereolithography,” The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 49, no. 5–8, pp. 543–551, 2010.
Vatani, M., Engeberg, E. D., and Choi, J. W., “Detection of the Position, Direction and Speed of Sliding Contact with a Multi-Layer Compliant Tactile Sensor Fabricated using Direct-Print Technology,” Smart Materials and Structures, vol. 23, no. 9, Paper No. 095008, 2014.
Johnson, K. O., Yoshioka, T., and Vega-Bermudez, F., “Tactile Functions of Mechanoreceptive Afferents Innervating the Hand,” Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 539–558, 2000.
Srinivasan, M. A., Whitehouse, J., and LaMotte, R. H., “Tactile Detection of Slip: Surface Microgeometry and Peripheral Neural Codes,” Journal of Neurophysiology, vol. 63, no. 6, pp. 1323–1332, 1990.
Johnson, K. O., “The Roles and Functions of Cutaneous Mechanoreceptors,” Current Opinion in Neurobiology, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 455–461, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vatani, M., Lu, Y., Engeberg, E.D. et al. Combined 3D printing technologies and material for fabrication of tactile sensors. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 1375–1383 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0181-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0181-3