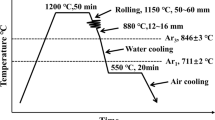
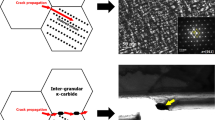
Abstract
The microstructural evolution and fire-resistant properties in the weld heat-affected zone (HAZ) of Mo and Mo + Nb-added fire-resistant steels were investigated. For this purpose, three Fe-0.1 wt%C-1.5 wt%Mn-0.1 wt%Si steels containing various Mo and Nb contents were prepared. HAZ samples were experimentally simulated using a Gleeble simulator at a welding heat input of 30 and 300 kJ/cm. The yield strength of the HAZ samples was higher than those of base steels at both room temperature and 600 ℃, whereas a greater decrease in the yield strength at 600 ℃ compared to that at room temperature occurred in the HAZ samples than in the base steels, indicating that the fire-resistance deteriorated in the HAZs as compared to the base steels. This is due to the formation of hard phases such as bainite and martensite in the HAZs, i.e., bainite and martensite phase have very high yield strength with high dislocation density at room temperature, while their strengths decrease rapidly at high temperature due to a great annihilation and recovery of dislocations at high temperature. In addition, the fire-resistance of the HAZ improved as the heat input was increased. The alloying of Mo and Nb improved the fire-resistance of both the base steels and the HAZs. Finally, the changes in the microstructures of the base steels and the HAZs upon alloying and the heat input and corresponding effects on the fire-resistance were carefully explored and discussed through transmission electron microscopy analyses, atom probe tomography analyses, and calculations of continuous cooling transformation diagrams.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
H.-H. Jo, C. Shin, J. Moon, J.H. Jang, H.-Y. Ha, S.-J. Park, T.-H. Lee, B.H. Lee, J.-H. Chung, J.G. Speer, K.O. Findley, T.R. Jacobs, C.-H. Lee, S.-D. Kim, Mater. Des. 194, 108882 (2020)
F.S. Kelly, W. Sha, J. Constr. Steel Res. 50, 223 (1999)
R. Wan, F. Sun, L. Zhang, A. Shan, Mater. Des. 35, 335 (2012)
R. Wan, F. Sun, L. Zhang, A. Shan, Mater. Des. 36, 227 (2012)
S. Yoshida, T. Okumura, H. Kita, J. Takahashi, K. Ushioda, Mater. Trans. 55, 899 (2014)
R. Uemori, H. Tamehiro, R. Chijiiwa, Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 69, 23 (1996)
W.-B. Lee, S.-G. Hong, C.-G. Park, S.-H. Park, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33, 1689 (2002)
B.R. Kirby, R.R. Preston, Fire Safety J. 13, 27 (1988)
D. Choi, H. Lee, S.-K. Cho, H.C. Kim, S.-K. Hyun, S.Y. Shin, Met. Mater. Int. 26, 867 (2020)
H.H. Wang, Z.P. Qin, X.L. Wan, R. Wei, K.M. Wu, D. Misra, Met. Mater. Int. 23, 848 (2017)
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, A. Giri, Met. Mater. Int. 23, 900 (2017)
J.S. Lee, K. Maruyama, Met. Mater. Int. 21, 639 (2015)
K. Easterling, Introduction to the Physical Metallurgy of Welding, 1st edn. (Butterworth, London, 1983), pp. 17–26
J. Moon, C.-H. Lee, T.-H. Lee, H.C. Kim, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46, 156 (2015)
ASTM A370-19e1, Standard test methods and definitions for mechanical testing of steel products, ASTM (2019)
S. Jeong, B. Kim, J. Moon, S.-J. Park, C. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 726, 223 (2018)
H. Mohrbacher, Mo and Nb alloying in plate steels for high-performance applications. in 2011 International Symposium on the Recent Developments in Plate Steels, Winter Park, Colorado, USA (2011), pp. 169–179
Acknowledgements
This study was supported financially by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea) (Grant No. 20010453).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM analyzed the results and wrote the manuscript. HHJ preformed the microstructure observations and the tensile tests. SDK contributed to the microstructure analyses using TEM. CHL, HUH, and JHC discussed the experimental results and commented on the manuscript. BHL carried out 3D-AP analyses.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The Authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, J., Lee, CH., Jo, HH. et al. Microstructure and High-Temperature Strength in the Weld Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of Fire-Resistant Steels and the Effects of Mo and Nb Additions. Met. Mater. Int. 28, 966–974 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00947-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00947-8