Abstract
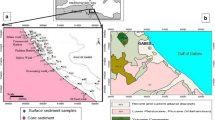
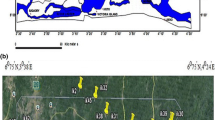
On July 2010, 26 surface sediments of the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia were sampled at depth ranging from 0.5 to 10 m. These specimens were analyzed to determine Al, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, F, P, and N concentrations and total organic carbon contents. The distribution map shows that the high amounts of pollutants are principally located between the commercial harbor and the fishing harbor of Gabes. Measurements of heavy metal contents were carried out using (absorption atomic spectrometer), where the enrichment factor (EF), the geoaccumulation index (I geo), and the contamination index (CI) are determined. The EF values of all metals were >1.5, corroborate anthropogenic impact on the metal levels in this studied area. However, the I geo and CI values of Cd and Zn elements indicated that sediments collected from sites at the vicinity of the commercial harbor are very contaminated, although for Pb, Cr, and Cu elements these indices indicated that the same sediments are uncontaminated. Statistical analyses (principal component analysis/factor analysis and matrix correlation) show that heavy metals, fluoride, and phosphorus are resulting from the same anthropogenic source.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Hilal A (1985) Phosphate pollution in the Jordan gulf of Aqaba. Mar Poll Bull 16(07):281–285
Ahdy H, Khaled A (2009) Heavy metals contamination in sediments of the western part of Egyptian Mediterranean Sea. Aust J Ba App Sci 3(4):3330–3336
Aloulou F (2010) Contamination des sédiments marins par les hydrocarbureset les métaux lourds et utilisation des foraminifères commebio-indicateurs de pollution. Dissertation, University of Sfax
Aloulou F, EllEuch B, Kallel M (2011) Benthic foraminiferal assemblages as pollution proxies in the northern coast of Gabes Gulf, Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2001-2
Amorri J, Geffroy-Rodier C, Boufahja F, Maghoudi E, Aïssa P, Ksibi M, Amblès A (2011) Organic matter compounds as source indicators and tracers for marine pollution in a western Mediterranean coastal zone. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1606–1616. doi:10.1007/s 11356-011-0522-4
Attia OEA, Abu Khadra AM, Nawwar AH, Radwan GE (2012) Impacts of human activities on the sedimentological and geochemical characteristics of mabahiss Bay, north hurghada, Red Sea. Egypt Arab J Geosci 5:481–499
Béjaoui B, Rais S, Koutitonsky VG (2004) Modélisation de la dispersion du phosphogypse dans le golfe de Gabès. Bull Inst Natn Scient Tech Océangr Pêche Salammbô 31:113–119
Bel Hassen M, Drira Z, Hamza A, Ayadi H, Akrout F, Messaoudi S, Issaoui H, Aleya L, Bouaîn A (2009) Phytoplancton dynamics related to water mass properties in the Gulf of Gabes: ecological implications. J Mar Syst 75(1–2):216–226
Ben Garali A, Ouakad M, Gueddari M (2010) Contamination of superficial sediments by heavy metals and iron in the Bizerte lagoon, northern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 3:295–306
Bradai MN, Ghorbel M, Bouain A (1995) Aperçu sur l’activité de pêche dans le gouvernorat de Sfax. Cah. CERES. Sér Géogr 1:211–236
Buccolieri A, Buccolieri G, Cardellicchio N, Dell’Atti A, Di Leo A, Maci A (2006) Heavy metals in marine sediments of Taranto Gulf (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Mar Chem 99:227–235
Centre d’Expertise en Analyse Environnementale du Québec (CEAEQ) (2006) Détermination du carbone organique total dans les solides : dosage par titrage. MA.405–C1.0, Ministère du développement durable, de l’Environnement et des Parcs du Québec, 9p
Chakravarty M, Patgiri A (2009) Metal Pollution Assessment in Sediments of the Dikrong River, N.E. India. J Hum Ecol 27(1):63–67
Choi K Y, Kim S H, Chon H T (2008) Distributions and accumulations of heavy metals in the sediments of harbors and coastal areas in Korea. Proceedings of the International Symposia on Geoscience Resources and Environments of Asian Terranes, 4th IGCP 516, and 5th APSEG, Thailand
Darmoul B, Hadj Ali Salem M, Vitiello P (1980) Effets des rejets industriels de la région de Gabès (Tunisie) sur le milieu marin récepteur. Bull Inst Natn Scient Tech Océangr PêcheSalammbô 7:5–61
El Gohary SS, Zaki HR, Elnaggar MF (2012) Geochemical study and distribution of some trace metals along coastal zone of Abu-Qir bay, Mediterranean Sea-Alexandria. Egypt Wld App Sci J 18(8):1011–1022
El Hatimi I, Achab M, El Moumni B (2002) Impact des émissaires et canalisations sur l’environnement de la baie de Tanger (Maroc): approche géochimique. Bull Inst Sci Rab 24:49–58
Emam A, Saad-Eldin M (2013) Distribution and environmental geochemistry of some heavy metals in stream sediments of Wadi Allaqi South Eastern Desert od Egypt. Arab J of Geosci 5:1325–1332
Erdoğan M (2009) Monitoring and statistical assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments along Izmir bay using ICP-MS. Dissertation. School of Engineering and Sciences of İzmir Institute of Technology, Turkey
Essersi R, Nechad B, Ruddick K, Zargouni F (2010) Optical remote sensing of the Gulf of Gabès—relation between turbidity, Secchi depth and total suspended matte. Ocean Sci Discuss 7:1767–1783
Fekri M, Kasmaei LS (2013) Fluoride pollution in soil and waters of koohbanan region, southeastern Iran. Arab J Geosci 6:157–161
Gabelle C (2006) Etude de la contamination des sédiments par les métaux dans les canaux et rivières du Nord de la France. Dissertation, University of Lille
Garcia EM, Cruz-Motta JJ, Farina O, Bastidas C (2008) Anthropogenic influences on heavy metals across marine habitats in the western coast of Venezuela. ContShelResea 28:2757–2766
Gargouri D, Azri CH, Serbaji MM, Jedoui Y, Montcer M (2011) Heavy metal concentrations in the surface marine sediments of Sfax Coast, Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 175:519–530. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1548-7
Garrett M, Wolny J, Truby E, Heil C, Kovach C (2011) Harmful algal bloom species and phosphate-processing effluent: field and laboratory studies. Mar Poll Bull 62:596–601
Gouidera M, Fekia M, Sayadi S (2009) Separative recovery with lime of phosphate and fluoride from an acidic effluent containing H3PO4, HF and/or H2SiF6. J Haz Mater 170:962–968
Guven DE, Akinci G (2008) Heavy metals partitioning in the sediments of Izmir Inner Bay. J Environ Sci 20:413–418
Hattour MJ, Sammari C, Ben Nassrallah S (2010) Hydrodynamique du golfe de Gabès déduite à partir des observations de courants et de niveaux. Rev Para 3:3.1–3.12
Institut National de l'Environnement Industriel et des Risques (INEIR) (2010) Qualité chimique des sediments marines en France: synthèse des bases de données disponibles. Rapport d’étude, 102 p
Matijević S, Bogner D, Morović M, Tičina V, Grbec B (2008) Characteristics of the sediment along the eastern Adriatic coast (Croatia). Fresenius Environ Bull 17(10b):1763–1772
Muller G (1979) Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine-Changes seity. Umsch Wiss Tech 79:778–783
Parizanganeh A, Lakhan C, Jalalian H (2007) A geochemical and statistical approach for assessing heavy metal pollution in sediments from the southern Caspian coast. Int J Environ Sci Tech 4(3):351–358
Paytan A, McLaughlin K (2007) The oceanic phosphorus cycle. Chem Rev 107(2):563–576
Pekey H (2006) The distribution and sources of heavy metals in Izmit Bay surface sediments affected by a polluted stream. Mar Poll Bull 52:1197–1208
Ramachandran M, Sabarathinam C, Ulaganthan K, Paluchamy A, Sivaji M, Hameed S (2012) Map** of fluoride ions in groundwater of Dindigul district, Tamilnadu, India—using GIS techniques. Arab J Geosci 5:433–439
Sammari C, Koutitonsky VG, Moussa M (2006) Sea level variability and tidal resonance in the Gulf of Gabes. Tunisia. Cont Shel Resea 26:338–350
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Haz Mater 195:355–364
Yu R, Yuan X, Zhao Y, Hu G, Tu X (2008) Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay. China. J Environ Sci 20:664–669
Zaouali J (1993) Les peuplements benthiques de la petite Syrte, golfe de Gabès - Tunisie. Résultats de la campagne de prospection du mois de juillet 1990. Etude préliminaire :biocoenoses et thanatocoenoses récentes. Mar Lif 3(1–2):47–60
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to knowledge NATO SfP project members at L3E-ENIS for the help in the analysis of metallic element by atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Authors also would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their critical revision, which greatly helped to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayadi, N., Aloulou, F. & Bouzid, J. Assessment of contaminated sediment by phosphate fertilizer industrial waste using pollution indices and statistical techniques in the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 8, 1755–1767 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1291-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1291-4