Abstract
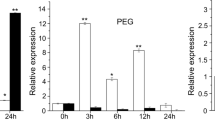
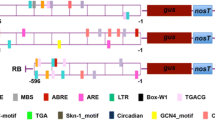
The clade A members of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2Cs (PP2Cs) play crucial roles in plant growth, development, and stress response via the ABA signaling pathway. But little is known about other PP2C clades in plants. Our previous study showed that maize the ZmPP2C26, a clade B member of ZmPP2Cs, negatively regulated drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. However, the upstream regulatory mechanism of ZmPP2C26 remains unclear. In the present study, the expression of ZmPP2C26 gene in maize was analyzed by quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR). The results showed that the expression of ZmPP2C26 in shoot and root was both significantly inhibited by drought stress. Subsequently, a 2175 bp promoter of ZmPP2C26 was isolated from maize genome (P2175). To validate whether the promoter possess some key cis-element and negatively drive ZmPP2C26 expression in drought stress, three 5´-deletion fragments of 1505, 1084 and 215 bp was amplified from P2175 and were fused to β-glucuronidase (GUS) and luciferase gene (LUC) to produce promoter::GUS and promoter::LUC constructs, and transformed into tobacco, respectively. Transient expression assays indicated that all promoters could drive GUS and LUC expression. The GUS and LUC activity were both significantly inhibited by PEG-6000 treatment. Notably, the − 1084 to − 215 bp promoter possess one MBS element and inhibits the expression of GUS and LUC under drought stress. Meanwhile, we found that the 215 bp length is enough to drive ZmPP2C26 expression. These findings will provide insights into understanding the transcription-regulatory mechanism of ZmPP2C26 negatively regulating drought tolerance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoni R, Gonzalezguzman M, Rodriguez L, Rodrigues A, Pizzio GA, Rodrigues P (2012) Selective inhibition of clade a phosphatases type 2c by PYR/PYL/RCAR abscisic acid receptors. Plant Physiol 158(2):970–980
Bhaskara GB, Nguyen TT, Verslues PE (2012) Unique drought resistance functions of the highly ABA-induced clade A protein phosphatase 2Cs. Plant Physiol 160(1):379–395
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Brock AK, Willmann R, Kolb D, Grefen L, Lajunen HM, Bethke G, Lee J, Nurnberger T, Gust AA (2010) The Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase PP2C5 affects seed germination, stomatal aperture, and abscisic acid-inducible gene expression. Plant Physiol 153(3):1098–1111
Cheng AY, Ross KE, Kaldis P, Solomon MJ (1999) Dephosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases by type 2C protein phosphatases. Genes Dev 13(22):2946–2957
Connors BJ, Miller M, Maynard CA, Powell WA (2002) Cloning and characterization of promoters from American chestnut capable of directing reporter gene expression in transgenicArabidopsis plants. Plant Sci 163(4):781
Han L, Li JL, ** M, Su YH (2018) Functional analysis of a type 2C protein phosphatase gene from Ammopiptanthus mongolicus. Gene 653:29–42
He ZH, Wu JF, Sun XP, Dai MQ (2019) The maize clade A PP2C phosphatases play critical roles in multiple abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 20(14):3573
Hou JJ, Jiang PP, Qi SM, Zhang K, He QX, Xu CZ, Ding ZH, Zhang KW, Li KP (2016) Isolation and functional validation of salinity and osmotic stress inducible promoter from the maize type-II H+-pyrophosphatase gene by deletion analysis in transgenic tobacco plants. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0154041
Hu X, Liu L, **ao B, Li D, **ng X, Kong X, Li D (2010) Enhanced tolerance to low temperature in tobacco by over-expression of a new maize protein phosphatase 2C, ZmPP2C2. J Plant Physiol 167(15):1307–1315
Jefferson RA, KavanaghTA BMWA (1987) GUS fusion: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6(13):3901–3907
Julijia U, Alois S, Vaiva K, Zoltan M, Zahra A, Verena U, Chonnanit C, Justyna B, James AHM, Laszlo B, Irute M (2010) MAPK phosphatase AP2C3 induces ectopic proliferation of epidermal cells leading to stomata development in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 5(12):1–18
Komatsu K, Suzuki N, Kuwamura M, Nishikawa Y, Nakatani M, Ohtawa H, Takezawa D, Seki M, Tanaka M, Taji T, Hayashi T, Sakata Y (2013) Group A PP2Cs evolved in land plants as key regulators of intrinsic desiccation tolerance. Nat Commun 4(2219):375–381
Lee SC, Lan W, Buchanan BB, Luan S (2009) A protein kinase phosphatase pair interacts with an iron channel to regulate ABA signaling in plant guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(50):21419–21424
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van dPY, Rouzé P, Rombauts S, (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):325–327
Luan S (2003) Protein phosphatases in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54(54):63–92
Lu X, **ong Q, Cheng T, Li QT, Liu XL, Bi YD, Li W, Zhang WK, Ma B, Lai YC, Du WG, Man WQ, Chen SY, Zhang JS (2017) A PP2C-1 allele underlying a quantitative trait locus enhances soybean 100-seed weight. Mol Plant 10(5):670–684
Ma Y, Szostkiewicz I, Korte A, Moes D, Yang Y, Christmann A, Grill E (2009) Regulators of PP2C phosphatase activity function as abscisic acid sensors. Science 324(5930):1064–1068
Meskiene I, Bogre L, Glaser W, Balog J, Brandstotter M, Zwerger K, Ammerer G, Hirt H (1998) MP2C, a plant protein phosphatase 2C, functions as a negative regulator of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in yeast and plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(4):1938–1943
Née G, Kramer K, Nakabayashi K, Yuan BJ, **ang Y, Miatton E, Finkemeier I, Soppe WJJ (2017) DELAY OF GERMINATION1 requires PP2C phosphatases of the ABA signaling pathway to control seed dormancy. Nat Commun 8(1):72
Nishimura N, Tsuchiya W, Moresco JJ, Hayashi Y, Satoh K, Kaiwa N, Irisa T, Kinoshita T, Schroeder JI, Yates JR, Hirayama T, Yamazaki T (2018) Control of seed dormancy and germination by DOG1-AHG1 PP2C phosphatase complex via binding to heme. Nat Commun 9(1):2132
Park SY, Fung P, Nishimura N, Jensen DR, Fujii H, Zhao Y, Lumba S, Santiago J, Rodrigues A, Chow TF, Alfred SE, Bonetta D, Finkelstein R, Provart NJ, Desveaux D, Rodriguez PL, McCourt P, Zhu JK, Schroeder JI, Volkman BF (2009) Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins. Science 324(5930):1068–1071
Rodriguez PL (1998) Protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) function in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 38(6):919–927
Schweighofer A, Hirt H, Meskiene I (2004) Plant PP2C phosphatases: emerging functions in stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci 9(5):236–243
Schweighofer A, Kazanaviciute V, Scheikl E, Teige M, Doczi R, Hirt H, Schwanninger M, Merijn KM, Schuurink R, Mauch F, Buchala A, Cardinale F, Meskiene I (2007) The PP2C-type phosphatase AP2C1, which negatively regulates MPK4 and MPK6, modulates innate immunity, jasmonic acid, and ethylene levels in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19(7):2213–2224
Shan H, Chen SM, Jiang JF, Chen FD, Chen Y, Gu CS, Li PL, Song AP, Zhu XR, Gao HS, Zhou GQ, Li T, Yang X (2012) Heterologous expression of the Chrysanthemum R2R3-MYB transcription factor CmMYB2 enhances drought and salinity tolerance, increases hypersensitivity to ABA and delays flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biotechnol 51(2):160–173
Sharma V, Goel P, Kumar S, Singh AK (2019) An apple transcription factor, MdDREB76, confers salt and drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco by activating the expression of stress-responsive genes. Plant Cell Rep 38(2):221–241
Shubchynskyy V, Boniecka J, Schweighofer A, Simulis J, Kvederaviciute K, Stumpe M, Mauch F, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B, Boutrot F, Zipfel C, Meskiene I (2017) Protein phosphatase AP2C1 negatively regulates basal resistance and defense responses to Pseudomonas syringae. J Exp Bot 68(5):1169–1183
Sidonskaya E, Schweighofer A, Shubchynskyy V, Kammerhofer N, Hofmann J, Wieczorek K, Meskiene I (2016) Plant resistance against the parasitic nematode Heterodera schachtii is mediated by MPK3 and MPK6 kinases, which are controlled by the MAPK phosphatase AP2C1 in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 67(1):107–118
Singh A, Yadav AK, Kaur K, Sanyal SK, Jha SK, Fernandes JL, Sharma P, Tokas I, Pandey A, Luan S, Pandey GK (2018) A protein phosphatase 2C, AP2C1, interacts with and negatively regulates the function of CIPK9 under potassium-deficient conditions in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 69(16):4003–4015
Sun FA, Yu HQ, Qu JT, Cao Y, Ding L, Feng WQ, Muhammad HBK, Li WC, Fu FL (2020) Maize ZmBES1/BZR1-5 decreases aba sensitivity and confers tolerance to osmotic stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):996
Takuya Y, Fujita Y, Sayama H, Satoshi K, Kyonoshin M, Junya M, Kazuo S, Kazuko YS (2010) AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J 61(4):672–685
Umbrasaite J, Schweighofer A, Kazanaviciute V, Magyar Z, Ayatollahi Z, Unterwurzacher V, Choopayak C, Boniecka J, Murray JA, Bogre L, Meskiene I (2010) MAPK Phosphatase AP2C3 Induces Ectopic Proliferation of Epidermal Cells Leading to Stomata Development in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 5(12):e15357
Wang YG, Fu FL, Yu HQ, Hu T, Zhang YY, Tao Y, Zhu JK, Zhao Y, Li WC (2018) Interaction network of core ABA signaling components in maize. Plant Mol Biol 96(3):245–263
Wu J, Jiang Y, Liang Y, Chen L, Chen W, Cheng B (2019) Expression of the maize MYB transcription factor ZmMYB3R enhances drought and salt stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 137:179–188
**ang YL, Sun XP, Gao S, Qin F, Dai MQ (2017) Deletion of an endoplasmic reticulum stress response element in a ZmPP2C-A gene facilitates drought tolerance of maize seedlings. Mol Plant 10(3):456–469
Yang K, Jeonghoe DH, Jang S (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a rice PP2C, OsPP2C4. J Plant Biol 44(1):1–6
Yoshihiro N, Kazuo N, Zatba KS, Yoh S, Takashi F, Hiroshi A, Mari N, Kazuo S, Kazuko YS (2003) Interaction between two cis-acting elements, ABRE and DRE, in ABA-dependent expression of Arabidopsis rd29A gene in response to dehydration and high-salinity stresses. Plant J 34(2):137–148
Yu HQ, Muhammad HBK, Lu FZ, Sun FA, Qu JT, Liu BL, Li WC, Fu FL (2019) Isolation and identification of a vegetative organ-specific promoter from maize. Physiol Mol Biol Plant 25(1):277–287
Zhang PW, Zhang XW, Yu HQ, Lx P, Fu FL, Li WC (2018) Function of two alternative splice variants of protein phosphatase type 2C gene ZmPP2C26 of maize. J Northwest A&F Univ 46(7):23–31
Zhao P, Hou S, Guo X, Jia J, Cheng L (2019) A MYB-related transcription factor from sheep grass, LcMYB2, promotes seed germination and root growth under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 19:564
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2018JY0470 and 2020YJ0353) and Key Laboratory of Dry-hot Valley Characteristic Bio-Resources Development at university of Sichuan Province (GR-2019-E-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, F., Wang, K., Yan, L. et al. Isolation and characterization of maize ZmPP2C26 gene promoter in drought-response. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 2189–2197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00910-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00910-2