Abstract
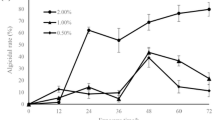
A bacterial strain named AB-4 showing algicidal activity against Chattonella marina was isolated from coastal water of UL**, Republic of Korea. The isolated strain was identified as Bacillus sp. by culture morphology, biochemical reactions, and homology research based on 16S rDNA. The bacterial culture led to the lysis of algal cells, suggesting that the isolated strain produced a latent algal-lytic compound. Amongst changes in algicidal activity by different culture filtrate volumes, the 10% (100 μl/ml) concentration showed the biggest change in algicidal activity; there, estimated algicidal activity was 95%. The swimming movements of Chattonella marina cells were inhibited because of treatment of the bacterial culture; subsequently, Chattonella marina cells became swollen and rounded. With longer exposure time, algal cells were disrupted and cellular components lost their integrity and decomposed. The released algicide(s) were heat-tolerant and stable in pH variations, except pH 3, 4, and 5. Culture filtrate of Bacillus sp. AB-4 was toxic against harmful algae bloom (HAB) species and nontoxic against livefood organisms. Bacillus sp. AB-4 showed comparatively strong activity against Akashiwo sanguinea, Fibriocapsa japonica, Heterosigma akashiwo, and Scrippsiella trochoidea. These results suggest that the algicidal activity of Bacillus sp. AB-4 is potentially useful for controlling outbreaks of Chattonella marina.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, C.Y., S.H. Joung, J.W. Jeon, H.S Kim, B.D. Yoon, and H.M. Oh. 2003. Selective control of cyanobacteria by surfactin-containing culture broth of Bacillus subtilis C1. Biotechnol. Lett. 25, 1137–1142.
Amaro, A.M., M.S. Fuentes, S.R. Ogalde, J.A. Venegas, and B.A. Suarez-Isla. 2005. Identification and characterization of potentially algal-lytic marine bacteria strongly associated with the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 52, 191–200.
Baker, K.H. and D.S. Herson. 1978. Interactions between the diatom Thallasiosira pseudonana and an associated pseudomonad in a mariculture system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 35, 791–796.
Bricelj, V.M. and R.E. Malouf. 1984. Influence of algal and suspended sediment concentrations on the feeding physiology of the hard clam Mercenaria mercenaria. Mar. Biol. 84, 155–165.
Choi, H.G., P.J. Kim, W.C. Lee, S.J. Yun, H.G. Kim, and H.J. Lee. 1998. Removal efficiency of Cochlodinium polykrikoides by yellow loess. J. Kor. Fish. Soc. 31, 109–113. (Written in Korean with English abstract)
Dakhama, A., J.D.L. Noűe, and M.C. Lavoie. 1993. Isolation and identification of antialgal substances produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Phycol. 5, 297–306.
Doucette, G.J. 1995. Interactions between bacteria and harmful algae: a review. Nat. Toxins 3, 65–74.
Doucette, G.J. and C.L. Powell. 1998. Algal-bacterial interactions: can they determine the PSP-related toxicity of dinoflagellates?, p. 406–409. In B. Reguera, J. Blanco, M.L. Fernandez, and T. Wyatt (eds.), Harmful algae. Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
Dunbar, J., L.O. Ticknor, and C.R. Kuske. 2000. Assessment of microbial diversity in four Southwestern United States soils by 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 2943–2950.
Fukuyo, Y., I. Imai, M. Kodama, and K. Tamai. 2002. Red tides and other harmful algal blooms in Japan, p. 7–20. In F.J.R.M. Taylor and V.L. Trainer (eds.), Harmful algal blooms in the PICES region of the North Pacific. PICES Scientific report No. 23. North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES), Sidney, Canada.
Garry, R.T., P. Hearing, and E.M. Cosper. 1998. Characterization of a lytic virus infectious to the bloom-forming microalga Aureococcus anophagefferens (Pelagophyceae). J. Phycol. 34, 616–621.
Guillard, R.R.L. and J.H. Ryther. 1962. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve). Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–235.
Hare, C.E., E. Demir, K.J. Coyne, S.C. Cary, D.L. Kirchman, and D.A. Hutchins. 2005. A bacterium that inhibits the growth of Pfiesteria piscicida and other dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 4, 221–234.
Hold, G.L., E.A. Smith, M.S. Rappé, E.W. Maas, E.R.B. Moore, C. Stroempl, J.R. Stephen, J.I. Prosser, T.H. Birkbeck, and S. Gallacher. 2001. Characterisation of bacterial communities associated with toxic and non-toxic dinoflagellates: Alexandrium spp. and Scrippsiella rochoidea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 37, 161–173.
Holmström, C. and S. Kjelleberg. 1999. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 30, 285–293.
Imai, I., Y. Ishida, and T. Hata. 1993. Killing of marine phytoplankton by a gliding bacterium Cytophaga sp., isolated from the coastal Sea of Japan. Mar. Biol. 116, 527–532.
Imai, I., Y. Ishida, K. Sakaguchi, and Y. Hata. 1995. Algicidal marine-bacteria isolated from northern Hiroshima Bay, Japan. Fish. Sci. 61, 628–636.
Imai, I., T. Sunahara, T. Nishikawa, Y. Hori, R. Kondo, and S. Hiroishi. 2001. Fluctuation of the red tide flagellates Chattonella sp., (Raphidophyceae) and the algicidal bacterium Cytophaga sp., in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Mar. Biol. 138, 1043–1049.
Imamura, N., I. Motoike, M. Noda, K. Adachi, A. Konno, and H. Fukami. 2000. Argimicin A, a novel anti-cyanobacterial compound produced by an algae-lysing bacterium. J. Antibiot. 53, 1317–1319.
Jeong, S.Y., K. Ishida, Y. Ito, S. Okada, and M. Murakami. 2003. Bacillamide, a novel algicide from the marine bacterium, Bacillus sp. SY-1, against the harmful dinoflagellate, Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Tet. Lett. 44, 8005–8007.
Jeong, J.H., H.J. **, C.H. Sohn, K.H. Suh, and Y.K. Hong. 2000. Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 12, 37–43.
Jeong, H., J.H. Yim, C. Lee, S.H. Choi, Y.K. Park, S.H. Yoon, C.G. Hur, H.Y. Kang, D. Kim, H.H. Lee, K.H. Park, S.H. Park, H.S. Park, H.K. Lee, T.K. Oh, and J.F. Kim. 2005. Genomic blueprint of Hahella chejuensis, a marine microbe producing an algicidal agent. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 7066–7073.
Kahn, S., O. Arakawa, and Y. Onoue. 1998 Physiological investigations of a neurotoxin-producing phytoflagellate, Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae). Aquacult. Res. 29, 9–17.
Kim, J.D., B. Kim, and C.G. Lee. 2007. Alga-lytic of Pseudomonas fluorescens against the red tide causing marine alga Heterosigma akshiwo (Raphidophyceae). Biol. Control 41, 296–303.
Kim, M.C., H.S. Yu, M.S. Ok, D.H. Kim, and D.S. Chang. 1999. The activities and characteristics of algicidal bacteria in Chindong Bay. J. Kor. Fish. Soc. 32, 359–367.
Kirchman, D.L. 2002. The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 39, 91–100.
Kopp, M., G.J. Doucette, M. Kodama, G. Gerdts, C. Schutt, and L.K. Medlin. 1997. Phylogenetic analysis of selected toxic and non-toxic bacterial strains isolated from the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 24, 251–257.
Lee, S.O., J. Kato, K. Nakashima, A. Kuroda, T. Ikeda, N. Takiguchi, and H. Ohtake. 2002. Cloning and characterization of extracellular metal protease gene of the algicidal marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain A28. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66, 1366–1369.
Lewin, R.A. 1997. Saprospira grandis: a flexibacterium that can catch bacterial prey by “ixotrophy.” Microb. Ecol. 34, 232–236.
Lewitus, A.J. and A.F. Holland. 2003. Initial results from a multi-institutional collaboration to monitor harmful algal blooms in South Carolina. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 81, 361–371.
Lewitus, A.J., L.B. Schmidt, L.J Mason, J.W. Kempton, S.B. Wilde, J.L. Wolny, B.J. Williams, K.C. Hayes, S.N. Hymel, C.J. Keppler, and A.H. Ringwood. 2003. Harmful algal blooms in South Carolina residential and golf course ponds. Popul. Environ. 24, 387–413.
Li, L.N., C. Kato, and K. Horikoshi. 1999. Bacterial diversity in deep-sea sediments from different depths. Biodiv. Conserv. 8, 659–677.
Liu, J., A.J. Lewitus, J.W. Kempton, and S.B. Wilde. 2008. The association of algicidal bacteria and raphidophyte blooms in South Carolina brackish detention ponds. Harmful Algae 7, 184–193.
Lovejoy, C., J.P. Bowman, and G.M. Hallegraeff. 1998. Algicidal effects of a novel marine Pseudoalteromonas isolate (class Proteobacteria, gamma subdivision) on harmful algal bloom species of the genera Chattonella, Gymnodinium, and Heterosigma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 2806–2813.
Mayali, X. and F. Azam. 2004. Algicidal bacteria in the sea and their impact on algal blooms. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 51, 139–144.
Mu, R.M., Z.Q. Fan, H.Y. Pei, X.L. Yuan, S.X. Liu, and X.R. Wang. 2007. Isolation and algae-lysing characteristics of the algicidal bacterium B5. J. Environ. Sci. 19, 1336–1340.
Na, G.H., W.J. Choi, and Y.Y. Chun. 1996. A study on red tide control with loess suspension. Kor. J. Aquacult. 9, 239–245. (Written in Korean with English abstract)
Nagayama, K., T. Shibata, K. Fujimoto, T. Honjo, and T. Nakamura. 2003. Algicidal effect of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome on red tide microalgae. Aquacult. 218, 601–611.
Nakashima, T., Y. Miyazaki, Y. Matsuyama, W. Muraoka, K. Yamaguchi, and T. Oda. 2006. Producing mechanism of an algicidal compound against red tide phytoplankton in a marine bacterium γ-Proteobacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 73, 684–690.
Park, Y.T., J.B. Park, S.Y. Chung, B.C. Song, W.A. Lim, C.H. Kim, and W.J. Lee. 1998. Isolation and algicidal properties of Micrococcus sp. LG-1 possessing killing activity for harmful Dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. J. Kor. Fish. Soc. 31, 767–773. (Written in Korean with English abstract)
Rhoads, D.C. and D.K. Young. 1970. The influence of deposit- feeding organisms on sediment stability and community trophic structure. J. Mar. Res. 28, 150–178.
Roth, P.B., M.J. Twiner, C.M. Mikulski, A.B. Barnhorst, and G.J. Doucette. 2008. Comparative analysis of two algicidal bacteria active against the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. Harmful Algae 7, 682–691.
Ryu, H.Y., J.M. Shim, J.D. Bang, and C. Lee. 1998. Experimental chemical treatments for the control of dinoflagellate, Cochlodinium polykrikoides in the land-based culture of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Kor. J. Aquacult. 11, 285–294. (Written in Korean with English abstract)
Sakata, T. 1990. Occurrence of marine Saprospira sp. possessing algicidal activity for diatoms. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 56, 1165.
Sangkhobol, V. and V.B.D. Skerman. 1981. Saprospira species-natural predators. Curr. Microbiol. 5, 169–174.
Schoemann, V., S. Becquevort, J. Stefels, W. Rousseau, and C. Lancelot. 2005. Phaeocystis blooms in the global ocean and their controlling mechanisms: a review. J. Sea Res. 53, 43–66.
Sigee, D.C., R. Glenn, M.J. Andrews, E.G. Bellinger, R.D. Butler, H.A.S. Epton, and R.D. Hendry. 1999. Biological control of cyanobacteria: principles and possibilities. Hydrobiologia 396, 161–172.
Skerratt, J.H., J.P. Bowman, G.M. Hallegraeff, S. James, and P.D. Nichols. 2002. Algicidal bacteria associated with blooms of a toxic dinoflagellate in a temperate Australian estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 244, 1–15.
Smibert, R.M. and N.R. Krieg. 1994. Phenotypic characterization. In Methods for general and molecular bacteriology, p. 607–654. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., USA.
Steidinger, K.A. 1983. A re-evaluation of toxic dinoflagellate biology and ecology. Prog. Phycol. Res. 2, 147–188.
Su, J., X. Yang, T. Zheng, Y. Tian, N. Jiao, L. Cai, and H. Hong. 2007. Isolation and characterization of marine algicidal bacterium against the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 6, 799–810.
Sun, X.X., J.K. Choi, and E.K. Kim. 2004. A preliminary study on the mechanism of harmful algal bloom mitigation by use of sophorolipid treatment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 304, 35–49.
Taga, N. 1968. Some ecological aspects of marine bacteria in the Kuroshio current. Bull. Misaki Mar. Biol. 12, 65–76.
Van Rijssel, M., I. Janse, D.J.B. Noordkamp, and W.W.C. Gieskes. 2000. An inventory of factors that affect polysaccharide production by Phaeocystis globosa. J. Sea Res. 43, 297–306.
Wang, X.L., L.Y. Gong, S.K. Liang, X.R. Han, C.J. Zhu, and Y.B. Li. 2005. Algicidal activity of rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 4, 433–443.
Yoshinaga, I., T. Kawai, and Y. Ishida. 1997. Analysis of algicidal ranges of the bacteria killing the marine dinoflagellate Gymnodinium mikimotoi isolated from Tanabe Bay, (Wakayama Pref., Japan). Fish. Sci. 63, 94–98.
Yoshinaga, I., T. Kawai, T. Takeuchi, and Y. Ishida. 1995. Distribution and fluctuation of bacteria inhibiting the growth of a marine red tide phytoplankton Gymnodinium mikimotoi in Tanabe Bay (Wakayama Pref., Japan). Fish. Sci. 61, 780–786.
Yoshinaga, I., M.C. Kim, N. Katanozaka, I. Imai, A. Uchida, and Y. Ishida. 1998. Population structure of algicidal marine bacteria targeting the red tide forming alga Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae), determined by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA genes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 170, 33–44.
Zingone, A. and H.O. Enevoldsen. 2000. The diversity of harmful algal blooms: a challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 43, 725–748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.S., Lee, DS., Jeong, SY. et al. Isolation and characterization of a marine algicidal bacterium against the harmful raphidophyceae Chattonella marina . J Microbiol. 47, 9–18 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0141-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0141-z