Abstract
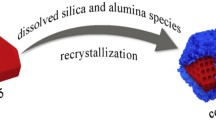
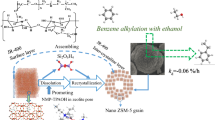
Develo** efficient and stable zeolites for vapor-phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime is still a great challenge to realize ε-caprolactam (CPL) green production. In this work, the hierarchical porous silicalite-1 zeolites with multiple hollow structure (S-1-M) are explored by in-situ desilication—recrystallization post-treatment of spongy highway-like zeolites (S-1-S), which are synthesized through silanization synthesis of conventional bulky silicalite-1 (S-1). Compared to S-1, S-1-M achieves superior catalytic performance, with improving the CPL selectivity from 85.7% to 94.1% and prolonging the catalyst lifetime from 74 to 126 h at a weight hourly space velocity (WHSV) of 6 h−1. Comprehensive physiochemical studies demonstrate that the highly dispersed intracrystalline cavities within S-1-M endow greater mass diffusion and better quasi acidity inducing by the enhanced H-bonds among abundant H-bonded silanols, which is cooperatively responsible for its superior catalytic performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, R.; Shah, S.; Das, P. P.; Bhagavanbhai, G. G. K.; Fatesh, A. A.; Chowdhury, B. An overview of caprolactam synthesis. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2019, 61, 516–594.
Kumar, R.; Chowdhury, B. Comprehensive study for vapor phase beckmann rearrangement reaction over zeolite systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 16587–16599.
Wang, Z. C.; Ling, H. J.; Shi, J.; Stampfl, C.; Yu, A. B.; Hunger, M.; Huang, J. Acidity enhanced [Al]MCM-41 via ultrasonic irradiation for the Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime to ε-caprolactam. J. Catal. 2018, 358, 71–79.
Bucko, T.; Hafner, J.; Benco, L. Active sites for the vapor phase beckmann rearrangement over mordenite: An ab initio study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 11388–11397.
Maronna, M. M.; Kruissink, E. C.; Parton, R. F.; Soulimani, F.; Weckhuysen, B. M.; Hoelderich, W. F. Spectroscopic study on the active site of a SiO2 supported niobia catalyst used for the gas-phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime to ε-caprolactam. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 22636–22646.
Sun, S. Q.; Liu, S. W.; Yu, F. L.; Zhang, J.; **ng, W. G.; Yu, S. T. High-yield and high-efficiency conversion of cyclohexanone oxime to ε-caprolactam in a green and facile reaction process over deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 253, 117519.
Heitmann, G. P.; Dahlhoff, G.; Niederer, J. P. M.; Hölderich, W. F. Active sites of a [B]-ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst for the beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime to caprolactam. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 122–129.
Heitmann, G. P.; Dahlhoff, G.; Hölderich, W. F. Catalytically active sites for the beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime to ε-caprolactam. J. Catal. 1999, 186, 12–19.
Vaschetto, E. G.; Casuscelli, S. G.; Eimer, G. A. Improvements in the Beckmann rearrangement process by using highly selective mesoporous catalysts. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2016, 221, 175–181.
Potter, M. E.; Kezina, J.; Bounds, R.; Carravetta, M.; Mezza, T. M.; Raja, R. Investigating the role of framework topology and accessible active sites in silicoaluminophosphates for modulating acid-catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5155–5164.
Kumar, R.; Shah, S.; Bahadur, J.; Melnichenko, Y. B.; Sen, D.; Mazumder, S.; Vinod, C. P.; Chowdhury, B. Highly stable In-SBA-15 catalyst for vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement reaction. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 234, 293–302.
Fernández, A. B.; Boronat, M.; Blasco, T.; Corma, A. Establishing a molecular mechanism for the Beckmann rearrangement of oximes over microporous molecular sieves. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2370–2373.
Marthala, V. R. R.; Jiang, Y. J.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Gläser, R.; Hunger, M. Beckmann rearrangement of 15N-cyclohexanone oxime on zeolites silicalite-1, H-ZSM-5, and H-[B]ZSM-5 studied by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14812–14813.
Yashima, T.; Oka, N.; Komatsu, T. Vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime on the zeolite catalysts. Catal. Today 1997, 38, 249–253.
Zong, B. N.; Sun, B.; Cheng, S. B.; Mu, X. H.; Yang, K. Y.; Zhao, J. Q.; Zhang, X. X.; Wu, W. Green production technology of the monomer of nylon-6: Caprolactam. Engineering 2017, 3, 379–384.
Du, C. C.; Zhang, J. S.; Li, L. T.; Wang, K.; Luo, G. S. A modified mixed-acid catalytic system for Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. AIChE J. 2019, 65, e16603.
Komatsu, T.; Maeda, T.; Yashima, T. Kinetic study on the effect of solvent in “vappr-phase” Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime on silicalite-1. Micropor. Mesopor. 2000, 35-36, 173–180.
Zhang, Y. F.; Xu, L. J.; Zhang, J.; Li, P. D.; Yuan, Y. Y.; Guo, H. C.; Zhang, X. M.; Xu, L. Insight into the dissolution-crystallization strategy towards macro/meso/microporous silicalite-1 zeolites and their performance in the Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 4526–4536.
Ge, C.; Sun, X. J.; Lian, D. D.; Li, Z. K.; Wu, J. B. Controllable synthesis and structure—performance relationship of silicalite-1 nanosheets in vapor phase beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. Catal. Lett. 2020, 151, 1488–1498.
Curtin, T.; Mcmonagle, J. B.; Ruwet, M.; Hodnett, B. K. Deactivation and regeneration of alumina catalysts for the rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime into caprolactam. J. Catal. 1993, 142, 172–181.
Heitmann, G. P.; Dahlhoff, G.; Hölderich, W. F. Modified Beta zeolites as catalysts for the Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1999, 185, 99–108.
Mao, D. S.; Lu, G. Z.; Chen, Q. L. Deactivation and regeneration of the B2O3/TiO2-ZrO2 catalyst in the vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2005, 240, 164–171.
Wei, H. J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y. Q.; Li, G. H.; Wang, X. Y.; Li, B. J. Synthesis of TS-1 submicrocrystals from inorganic reactants by a seed method for the vapor Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 20811–20815.
Newland, S. H.; Sinkler, W.; Mezza, T.; Bare, S. R.; Carravetta, M.; Haies, I. M.; Levy, A.; Keenan, S.; Raja, R. Expanding beyond the micropore: Active-site engineering in hierarchical architectures for beckmann rearrangement. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6587–6593.
Chang, A.; Hsiao, H. M.; Chen, T. H.; Chu, M. W.; Yang, C. M. Hierarchical silicalite-1 octahedra comprising highly-branched orthogonally-stacked nanoplates as efficient catalysts for vapor-phase Beckmann rearrangement. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11939–11942.
Abate, S.; Barbera, K.; Centi, G.; Lanzafame, P.; Perathoner, S. Disruptive catalysis by zeolites. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2485–2501.
Forni, L.; Fornasari, G.; Trifirò, F.; Aloise, A.; Katovic, A.; Giordano, G.; Nagy, J. B. Calcination and deboronation of B-MFI applied to the vapour phase Beckmann rearrangement. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2007, 101, 161–168.
Kim, J.; Park, W.; Ryoo, R. Surfactant-directed zeolite nanosheets: A high-performance catalyst for gas-phase beckmann rearrangement. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 337–341.
Forni, L.; Fornasari, G.; Giordano, G.; Lucarelli, C.; Katovic, A.; Trifirò, F.; Perri, C.; Nagy, J. B. Vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement using high silica zeolite catalyst. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 1842–1847.
**a, C. J.; Lin, M.; Zheng, A. G.; **ang, Y. J.; Zhu, B.; Xu, G. T.; Shu, X. T. Irreversible deactivation of hollow TS-1 zeolite caused by the formation of acidic amorphous TiO2-SiO2 nanoparticles in a commercial cyclohexanone ammoximation process. J. Catal. 2016, 338, 340–348.
Wang, Y. R.; Lin, M.; Tuel, A. Hollow TS-1 crystals formed via a dissolution—recrystallization process. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2007, 102, 80–85.
Pagis, C.; Prates, A. R. M.; Farrusseng, D.; Bats, N.; Tuel, A. Hollow zeolite structures: An overview of synthesis methods. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 5205–5223.
Tuel, A.; Farrusseng, D. Hollow zeolite single crystals: Synthesis routes and functionalization methods. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800197.
Ge, C.; Li, Z. K.; Chen, G.; Qin, Z. F.; Li, X. F.; Dou, T.; Dong, M.; Chen, J. G.; Wang, J. G.; Fan, W. B. Kinetic study of vapor-phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime over silicalite-1. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 153, 246–254.
Hufton, J. R.; Ruthven, D. M. Diffusion of light alkanes in silicalite studied by the zero length column method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 2379–2386.
Han, M. H.; Yin, X. Y.; **, Y.; Chen, S. Diffusion of aromatic hydrocarbon in ZSM-5 studied by the improved zero length column method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 3172–3175.
Lin, M.; Zhou, S. L.; Zhang, C. X.; Li, Y. X.; Wang, C. Q.; Shu, X. T. An efficient preparation method of Y zeolite-based catalyst for Isobutane-butene alkylation. Fuel 2022, 328, 125371.
Zhang, Y.; **a, C. J.; Lin, M.; Duan, Q. H.; Zhu, B.; Peng, X. X.; Wang, B. R.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Y. N.; Shu, X. T. Sponge-structured titanosilicate zeolite with high catalytic activity in epoxidation of fatty acid methyl ester. Catal. Commun. 2017, 101, 1–4.
Yin, C. Y.; He, J.; Liu, S. Synthesis of mesoporous silicalite-1 zeolite for the vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2020, 307, 110517.
Lezcano-González, I.; Boronat, M.; Blasco, T. Investigation on the Beckmann rearrangement reaction catalyzed by porous solids: MAS NMR and theoretical calculations. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2009, 35, 120–129.
Ronchin, L.; Bortoluzzi, M.; Vavasori, A. A DFT study on secondary reaction pathways in the acid-catalysed Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime in aprotic solvent. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2008, 858, 46–51.
Forni, L.; Tosi, C.; Fornasari, G.; Trifirò, F.; Vaccari, A.; Nagy, J. B. Vapour-phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone-oxime over Al-MCM-41 type mesostructured catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2004, 221, 97–103.
Dalstein, L.; Potapova, E.; Tyrode, E. The elusive silica/water interface: Isolated silanols under water as revealed by vibrational sum frequency spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 10343–10349.
Dib, E.; Costa, I. M.; Vayssilov, G. N.; Aleksandrov, H. A.; Mintova, S. Complex H-bonded silanol network in zeolites revealed by IR and NMR spectroscopy combined with DFT calculations. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 27347–27352.
Marthala, V. R. R.; Rabl, S.; Huang, J.; Rezai, S. A. S.; Thomas, B.; Hunger, M. In situ solid-state NMR investigations of the vapor-phase Beckmann rearrangement of 15N-cyclohexanone oxime on MFI-type zeolites and mesoporous SBA-15 materials in the absence and presence of the additive 13C-methanol. J. Catal. 2008, 257, 134–141.
Rimola, A.; Costa, D.; Sodupe, M.; Lambert, J. F.; Ugliengo, P. Silica surface features and their role in the adsorption of biomolecules: Computational modeling and experiments. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4216–4313.
Sirijaraensre, J.; Limtrakul, J. Effect of the acidic strength on the vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime over the MFI zeolite: An embedded ONIOM study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 578–585.
Ichihashi, H.; Kitamura, M. Some aspects of the vapor phase Beckmann rearrangement for the production of ε-caprolactam over high silica MFI zeolites. Catal. Today 2002, 73, 23–28.
**, X.; Peng, R. S.; Tong, W.; Yin, J. P.; Xu, H.; Wu, P. Investigation of the active centers and structural modifications for TS-1 in catalyzing the Beckmann rearrangement. Catal. Today 2022, 405-406, 193–202.
Munakata, H.; Koyama, T. R.; Yashima, T.; Asakawa, N.; O-Nuki, T.; Motokura, K.; Miyaji, A.; Baba, T. Temperature effect on 1H chemical shift of hydroxyl groups in zeolites and their catalytic activities as solid acids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 14551–14560.
Dubray, F.; Dib, E.; Medeiros-Costa, I.; Aquino, C.; Minoux, D.; van Daele, S.; Nesterenko, N.; Gilson, J. P.; Mintova, S. The challenge of silanol species characterization in zeolites. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1125–1133.
Schroeder, C.; Siozios, V.; Hunger, M.; Hansen, M. R.; Koller, H. Disentangling brønsted acid sites and hydrogen-bonded silanol groups in high-silica zeolite H-ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 23380–23386.
Yi, X. F.; **ao, Y.; Li, G. C.; Liu, Z. Q.; Chen, W.; Liu, S. B.; Zheng, A. M. From one to two: Acidic proton spatial networks in porous zeolite materials. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 1332–1342.
Chen, X.; Fu, Y. Y.; Yue, B.; He, H. Y. Acidity and basicity of solid acid catalysts studied by solid-state NMR. Chin. J. Magn. Reson 2021, 38, 491–502.
Shi, K. M.; Pedersen, C. M.; Chang, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y. X.; Qiao, Y. Characterization of the acidity and basicity of green solvents by NMR techniques. Magnetic Resonance Letters 2021, 1, 81–88.
Peng, Y. K.; Tsang, S. C. E. Probe-assisted NMR: Recent progress on the surface study of crystalline metal oxides with various terminated facets. Magnetic Resonance Letters 2022, 2, 9–16.
Liu, Y. J.; **ao, Y.; **a, C. J.; Yi, X. F.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, J. M.; Huang, K. M.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, A. M.; Lin, M. et al. Insight into the effects of acid characteristics on the catalytic performance of Sn-MFI zeolites in the transformation of dihydroxyacetone to methyl lactate. J. Catal. 2020, 391, 386–396.
Yi, X. F.; Ko, H. H.; Deng, F.; Liu, S. B.; Zheng, A. M. Solid-state 31P NMR map** of active centers and relevant spatial correlations in solid acid catalysts. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3527–3555.
Yi, F. J.; Chen, Y. L.; Tao, Z. C.; Hu, C. X.; Yi, X. F.; Zheng, A. M.; Wen, X. D.; Yun, Y. F.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. W. Origin of weak Lewis acids on silanol nests in dealuminated zeolite Beta. J. Catal. 2019, 380, 204–214.
Medeiros-Costa, I. C.; Dib, E.; Nesterenko, N.; Dath, J. P.; Gilson, J. P.; Mintova, S. Silanol defect engineering and healing in zeolites: Opportunities to fine-tune their properties and performances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11156–11179.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Development Plan “973” Project (No. 2006CB202508), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFA1502600), State Key Laboratory of Catalytic Materials and Reaction Engineering (RIPP, SINOPEC) (No. 33600000-20-ZC0607-0024), the SINOPEC Project (Nos. 411058 and 413025), and the National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 21808244, 22178347, and 22072182).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_5305_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Rational construction of multiple hollow silicalite-1 zeolite with enhanced quasi acidity for robust vapor-phase Beckmann rearrangement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Yi, X., **a, C. et al. Rational construction of multiple hollow silicalite-1 zeolite with enhanced quasi acidity for robust vapor-phase Beckmann rearrangement. Nano Res. 16, 7958–7966 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5305-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5305-3