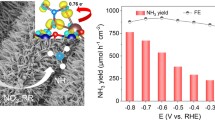
Abstract
The demand for high-performance non-precious-metal electrocatalysts to replace the noble metal-based catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is intensively increasing. Herein, single-atomic copper sites supported on N-doped three-dimensional hierarchically porous carbon catalyst (Cu1/NC) was prepared by coordination pyrolysis strategy. Remarkably, the Cu1/NC-900 catalyst not only exhibits excellent ORR performance with a half-wave potential of 0.894 V (vs. RHE) in alkaline media, outperforming those of commercial Pt/C (0.851 V) and Cu nanoparticles anchored on N-doped porous carbon (CuNPs/NC-900), but also demonstrates high stability and methanol tolerance. Moreover, the Cu1/NC-900 based Zn-air battery exhibits higher power density, rechargeability and cyclic stability than the one based on Pt/C. Both experimental and theoretical investigations demonstrated that the excellent performance of the as-obtained Cui/NC-900 could be attributed to the synergistic effect between copper coordinated by three N atoms active sites and the neighbouring carbon defect, resulting in elevated Cu d-band centers of Cu atoms and facilitating intermediate desorption for ORR process. This study may lead towards the development of highly efficient non-noble metal catalysts for applications in electrochemical energy conversion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand, M.; Tarascon, J. M. Building better batteries. Nature 2008, 451, 652–657.
Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303.
Mao, J. J.; Yang, L. F.; Yu, P.; Wei, X. W.; Mao, L. Q. Rlectrocatalytic four-electron reduction of oxygen with copper (II)-based metal-organic frameworks. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 19, 29–31.
Li, Y. G.; Dai, H. J. Recent advances in zinc-air batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5257–5275.
Shao, M. H.; Chang, Q. W.; Dodelet, J. P.; Chenitz, R. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3594–3657.
**a, B. Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, H. B.; Lou, X. W.; Wang, X. A metal-organic framework-derived bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 15006.
Yang, Z. K.; Chen, B. X.; Chen, W. X.; Qu, Y. T.; Zhou, F. Y.; Zhao, C. M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Q. H.; Duan, X. Z.; Wu, Y. E. Directly transforming copper(I) oxide bulk into isolated single-atom copper sites catalyst through gas-transport approach. Nat. Commun. 2019, 70, 3734.
Han, X. P.; Ling, X. F.; Yu, D. S.; **e, D. Y.; Li, L. L.; Peng, S. J.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, N. Q.; Deng, Y. D.; Hu, W. B. Atomically dispersed binary Co-Ni sites in nitrogen-doped hollow carbon nanocubes for reversible oxygen reduction and evolution. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1905622.
Zhang, N. Q.; Ye, C. L.; Yan, H.; Li, L. C.; He, H.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom site catalysts for environmental catalysis. Nana Res. 2020, 13, 3165–3182.
Sun, T. T.; Li, Y. L.; Cui, T. T.; Xu, L. B.; Wang, Y. G.; Chen, W. X.; Zhang, P. P.; Zheng, T. Y.; Fu, X. Z.; Zhang, S. L. et al. Engineering of coordination environment and multiscale structure in single-site copper catalyst for superior electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Nana Lett. 2020, 20, 6206–6214.
Mao, J. J.; Li, J.; Pei, J. J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Structure regulation of noble-metal-based nanomaterials at an atomic level. Nana Today 2019, 26, 164–175.
Li, K.; Li, X. X.; Huang, H. W.; Luo, L. H.; Li, X.; Yan, X. P.; Ma, C.; Si, R.; Yang, J. L.; Zeng, J. One-nanometer-thick PtNiRh trimetallic nanowires with enhanced oxygen reduction electrocatalysis in acid media: Integrating multiple advantages into one catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16159–16167.
Yin, P. Q.; Yao, T.; Wu, Y. E.; Zheng, L. R.; Lin, Y.; Liu, W.; Ju, H. X.; Zhu, J. F.; Hong, X.; Deng, Z. X. et al. Single cobalt atoms with precise N-coordination as superior oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10800–10805.
Mao, J. J.; Chen, Y. J.; Pei, J. J.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Pt-M (M = Cu, Fe, Zn, etc.) bimetallic nanomaterials with abundant surface defects and robust catalytic properties. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5985–5988.
Li, F.; Han, G. F.; Noh, H. J.; Kim, S. J.; Lu, Y. L.; Jeong, H. Y.; Fu, Z. P.; Baek, J. B. Boosting oxygen reduction catalysis with abundant copper single atom active sites. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2263–2269.
Wang, X. X.; Cullen, D. A.; Pan, Y T.; Hwang, S.; Wang, M. Y.; Feng, Z. X.; Wang, J. Y.; Engelhard, M. H.; Zhang, H. G.; He, Y. H. et al. Nitrogen-coordinated single cobalt atom catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706758.
Shang, H. S.; Sun, W. M.; Sui, R.; Pei, J. J.; Zheng, L. R.; Dong, J. C.; Jiang, Z. L.; Zhou, D. N.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Chen, W. X. et al. Engineering isolated Mn-N2C2 atomic interface sites for efficient bifunctional oxygen reduction and evolution reaction. Nana Lett. 2020, 20, 5443–5450.
Wu, H. H.; Li, H. B.; Zhao, X. F.; Liu, Q. F.; Wang, J.; **ao, J. P.; **e, S. H.; Si, R.; Yang, F.; Miao, S. et al. Highly doped and exposed Cu(I)-N active sites within graphene towards efficient oxygen reduction for zinc-air batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3736–3745.
Zhang, H. G.; Hwang, S.; Wang, M. Y.; Feng, Z. X.; Karakalos, S.; Luo, L. L.; Qiao, Z.; **e, X. H.; Wang, C. M.; Su, D. et al. Single atomic iron catalysts for oxygen reduction in acidic media: Particle size control and thermal activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14143–14149.
Sun, T. T.; Xu, L. B.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Metal organic frameworks derived single atom catalysts for electrocatalytic energy conversion. Nana Res. 2019, 12, 2067–2080.
Mao, J. J.; Yin, J. S.; Pei, J. J.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single atom alloy: An emerging atomic site material for catalytic applications. Nana Today 2020, 34, 100917.
Sun, J. Q.; Lowe, S. E.; Zhang, L. J.; Wang, Y. Z.; Pang, K. L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y. L.; Liu, P. R.; Zhao, K.; Tang, Z. Y. et al. Ultrathin nitrogen-doped holey carbon@graphene bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions in alkaline and acidic media. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16511–16515.
Shang, H. S.; Zhou, X. Y.; Dong, J. C.; Li, A.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q. H.; Lin, Y.; Pei, J. J.; Li, Z. et al. Engineering unsymmetrically coordinated Cu-S1N3 single atom sites with enhanced oxygen reduction activity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3049.
Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. M.; Zhu, J. W.; Kou, Z. K.; Hu, P.; Liu, L.; Li, S. Z.; Mu, S. C.; Huang, Y. H. Defect and pyridinic nitrogen engineering of carbon-based metal-free nanomaterial toward oxygen reduction. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 307–314.
Qiao, B. T.; Wang, A. Q.; Yang, X. F.; Allard, L. F.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, Y. Y.; Liu, J. Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 634–641.
Zhou, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, W. J.; Chen, W. X.; Yu, P.; Lin, Y. Q.; Mao, J. J.; Mao, L. Q. Single-atom Ni-N4 provides a robust cellular NO sensor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3188.
Tian, S. B.; Hu, M.; Xu, Q.; Gong, W. B.; Chen, W. X.; Yang, J. R.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Chen, C.; He, J.; Liu, Q. et al. Single-atom Fe with FeiN3 structure showing superior performances for both hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenation of nitrobenzene. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 10.1007/s40843-020-1443-8.
Mao, J. J.; He, C. T.; Pei, J. J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, W. X.; He, D. S.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Isolated Ni atoms dispersed on Ru nanosheets: High-performance electrocatalysts toward hydrogen oxidation reaction. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3442–3448.
Ma, W. J.; Mao. J. J.; Yang, X. T.; Pan, C.; Chen, W. X.; Wang, M.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. Q.; Li, Y. D. A single-atom Fe-N4 catalytic site mimicking bifunctional antioxidative enzymes for oxidative stress cytoprotection. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 159–162.
Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Y.; Zhang, M. L.; Qiu, Y. J.; Xu, Q.; Cheong, W. C.; Chen, W. X.; Zheng, L. R.; Gu, L.; Hu, Z. P. et al. Controlling N-do** type in carbon to boost single-atom site Cu catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of quinoline. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3082–3087.
Xu, Q.; Guo, C. X.; Tian, S. B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. X.; Cheong, W. C.; Gu, L.; Zheng, L. R.; **ao, J. P.; Liu, Q. et al. Coordination structure dominated performance of single-atomic Pt catalyst for anti-Markovnikov hydroboration of alkenes. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 65, 972–981.
Mao, J. J.; He, C. T.; Pei, J. J.; Chen, W. X.; He, D. S.; He, Y. Q.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Chen, C.; Peng, Q.; Wang, D. S. et al. Accelerating water dissociation kinetics by isolating cobalt atoms into ruthenium lattice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4958.
Yang, J.; Qiu, Z. Y.; Zhao, C. M.; Wei, W. C.; Chen, W. X.; Li, Z. J.; Qu, Y. T.; Dong, J. C.; Luo, J.; Li, Z. Y. et al. In situ thermal atomization to convert supported nickel nanoparticles into surface-bound nickel single-atom catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14095–14100.
**ao, M. L.; Zhu, J. B.; Li, G. R.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Cano, Z. P.; Ma, L.; Cui, P. X.; Xu, P.; Jiang, G. P. et al. A single-atom iridium heterogeneous catalyst in oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9640–9645.
Zhu, C. Z.; Fu, S. F.; Shi, Q. R.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. H. Single-atom electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13944–13960.
Li, J. Z.; Chen, M. J.; Cullen, D. A.; Hwang, S.; Wang, M. Y.; Li, B. Y.; Liu, K. X.; Karakalos, S.; Lucero, M.; Zhang, H. G. et al. Atomically dispersed manganese catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 935–945.
Li, X. Y.; Rong, H. P.; Zhang, J. T.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Modulating the local coordination environment of single-atom catalysts for enhanced catalytic performance. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1842–1855.
Qu, Y. T.; Li, Z. J; Chen, W. X.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, T. W.; Yang, Z. K.; Zhao, C. M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X. et al. Direct transformation of bulk copper into copper single sites via emitting and trap** of atoms. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 781–786.
Wang, A. Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 65–81.
Li, D. H.; Jia, Y.; Chang, G. J.; Chen, J.; Liu, H. W.; Wang, J. C.; Hu, Y. F.; **a, Y. Z.; Yang, D. J.; Yao, X. D. A defect-driven metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in acidic electrolyte. Chem 2018, 4, 2345–2356.
Hammer, B.; Norskov, J. K. Why gold is the noblest of all the metals. Nature 1995, 376, 238–240.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21804319 and 21971002), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui province (Nos. 1908085QB45 and 2008085QB81) and the Education Department of Anhui Province Foundation (No. KJ2019A0503). We thank the BL14W1 station in Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) and 1W1B station for XAFS measurement in Bei**g Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF). The calculations in this paper have been done on the supercomputing system of the National Supercomputing Center in Changsha.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2020_3141_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Single copper sites dispersed on hierarchically porous carbon for improving oxygen reduction reaction towards zinc-air battery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Liu, Y., Liu, D. et al. Single copper sites dispersed on hierarchically porous carbon for improving oxygen reduction reaction towards zinc-air battery. Nano Res. 14, 998–1003 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3141-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3141-x