Abstract
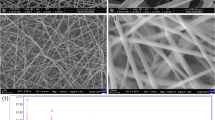
Ultrasmall γ-Fe2O3 nanodots (∼ 3.4 nm) were homogeneously encapsulated in interlinked porous N-doped carbon nanofibers (labeled as Fe2O3@C) at a considerable loading (∼ 51 wt.%) via an electrospinning technique. Moreover, the size and content of Fe2O3 could be controlled by adjusting the synthesis conditions. The obtained Fe2O3@C that functioned as a self-standing membrane was used directly as a binder- and current collector-free anode for sodium-ion batteries, displaying fascinating electrochemical performance in terms of the exceptional rate capability (529 mA·h·g–1 at 100 mA·g–1 compared with 215 mA·h·g–1 at 10,000 mA·g–1) and unprecedented cyclic stability (98.3% capacity retention over 1,000 cycles). Furthermore, the Na-ion full cell constructed with the Fe2O3@C anode and a P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2 cathode also exhibited notable durability with 97.2% capacity retention after 300 cycles. This outstanding performance is attributed to the distinctive three-dimensional network structure of the very-fine Fe2O3 nanoparticles uniformly embedded in the interconnected porous N-doped carbon nanofibers that effectively facilitated electronic/ionic transport and prevented active materials pulverization/aggregation caused by volume change upon prolonged cycling. The simple and scalable preparation route, as well as the excellent electrochemical performance, endows the Fe2O3@C nanofibers with great prospects as high-rate and long-life Na-storage anode materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slater, M. D.; Kim, D.; Lee, E.; Johnson, C. S. Sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 947–958.
Kundu, D.; Talaie, E.; Duffort, V.; Nazar, L. F. The emerging chemistry of sodium ion batteries for electrochemical energy storage. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3431–3448.
Pan, H. L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Chen, L. Q. Room-temperature stationary sodium-ion batteries for large-scale electric energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2338–2360.
Yabuuchi, N.; Kubota, K.; Dahbi, M.; Komaba, S. Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11636–11682.
Kim, S.-W.; Seo, D.-H.; Ma, X. H.; Ceder, G.; Kang, K. Electrode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries: Potential alternatives to current lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 710–721.
Palomares, V.; Serras, P.; Villaluenga, I.; Hueso, K. B.; Carretero-González, J.; Rojo, T. Na-ion batteries, recent advances and present challenges to become low cost energy storage systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5884–5901.
Cui, J.; Yao, S. S.; Kim, J.-K. Recent progress in rational design of anode materials for high-performance Na-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 7, 64–114.
Luo, W.; Shen, F.; Bommier, C.; Zhu, H. L.; Ji, X. L.; Hu, L. B. Na-ion battery anodes: Materials and electrochemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 231–240.
Wang, S. Q.; **a, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. H.; Lou, X. W. Free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber films: Integrated electrodes for sodium-ion batteries with ultralong cycle life and superior rate capability. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502217.
Ding, J.; Wang, H. L.; Li, Z.; Kohandehghan, A.; Cui, K.; Xu, Z. W.; Zahiri, B.; Tan, X. H.; Lotfabad, E. M.; Olsen, B. C. et al. Carbon nanosheet frameworks derived from peat moss as high performance sodium ion battery anodes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11004–11015.
Cao, Y. L.; **ao, L. F.; Sushko, M. L.; Wang, W.; Schwenzer, B.; **ao, J.; Nie, Z. M.; Saraf, L. V.; Yang, Z. G.; Liu, J. Sodium ion insertion in hollow carbon nanowires for battery applications. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3783–3787.
Wen, Y.; He, K.; Zhu, Y. J.; Han, F. D.; Xu, Y. H.; Matsuda, I.; Ishii, Y.; Cumings, J.; Wang, C. S. Expanded graphite as superior anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4033.
Yan, Y.; Yin, Y.-X.; Guo, Y.-G.; Wan, L.-J. A sandwichlike hierarchically porous carbon/graphene composite as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301584.
Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, N.; Jiao, L. F.; Tao, Z. L.; Chen, J. Ultrasmall Sn nanoparticles embedded in carbon as highperformance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 214–220.
Darwiche, A.; Marino, C.; Sougrati, M. T.; Fraisse, B.; Stievano, L.; Monconduit L. Better cycling performances of bulk Sb in Na-ion batteries compared to Li-ion systems: An unexpected electrochemical mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20805–20811.
Li, W. H.; Hu, S. H.; Luo, X. Y.; Li, Z. L.; Sun, X. Z.; Li, M. S.; Liu, F. F.; Yu, Y. Confined amorphous red phosphorus in MOF-derived N-doped microporous carbon as a superior anode for sodium-ion battery. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605820.
Li, L.; Seng, K. H.; Li, D.; **a, Y. Y.; Liu, H. K.; Guo, Z. P. SnSb@carbon nanocable anchored on graphene sheets for sodium ion batteries. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1466–1476.
Li, W. J.; Chou, S.-L.; Wang, J.-Z.; Kim, J. H.; Liu, H.-K.; Dou, S.-X. Sn4+xP3@amorphous Sn-P composites as anodes for sodium-ion batteries with low cost, high capacity, long life, and superior rate capability. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4037–4042.
Jiang, Y. Z.; Hu, M. J.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, T. Z.; Sun, W. P.; Xu, B.; Yan, M. Transition metal oxides for high performance sodium ion battery anodes. Nano Energy 2014, 5, 60–66.
Su, D. W.; Ahn, H.-J.; Wang, G. X. SnO2@graphene nanocomposites as anode materials for Na-ion batteries with superior electrochemical performance. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3131–3133.
Wang, L. J.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Z.; Duan, W. C.; Cheng, F. Y.; Chen, J. Porous CuO nanowires as the anode of rechargeable Na-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 199–208.
Zhu, C. B.; Mu, X. K.; van Aken, P. A.; Yu, Y.; Maier, J. Single-layered ultrasmall nanoplates of MoS2 embedded in carbon nanofibers with excellent electrochemical performance for lithium and sodium storage. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2152–2156.
Choi, S. H.; Kang, Y. C. Aerosol-assisted rapid synthesis of SnS-C composite microspheres as anode material for Na-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1595–1603.
Senguttuvan, P.; Rousse, G.; Seznec, V.; Tarascon, J.-M.; Palacín, M. R. Na2Ti3O7: Lowest voltage ever reported oxide insertion electrode for sodium ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 4109–4111.
Chen, C. J.; Wen, Y. W.; Hu, X. L.; Ji, X. L.; Yan, M. Y.; Mai, L. Q.; Hu, P.; Shan, B.; Huang, Y. H. Na+ intercalation pseudocapacitance in graphene-coupled titanium oxide enabling ultra-fast sodium storage and long-term cycling. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6929.
Xu, C.; Xu, Y. N.; Tang, C. J.; Wei, Q. L.; Meng, J. S.; Huang, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, G. B.; He, L.; Mai, L. Q. Carboncoated hierarchical NaTi2(PO4)3 mesoporous microflowers with superior sodium storage performance. Nano Energy 2016, 28, 224–231.
Zhao, Q.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J. Advanced organic electrode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601792.
Valvo, M.; Lindgren, F.; Lafont, U.; Björefors, F.; Edström, K. Towards more sustainable negative electrodes in Na-ion batteries via nanostructured iron oxide. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 967–978.
Jian, Z. L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, P.; Li, F. J.; Zheng, M. B.; Chen, M. W.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H. S. Fe2O3 nanocrystals anchored onto graphene nanosheets as the anode material for lowcost sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1215–1217.
Li, T.; Qin, A. Q.; Yang, L. L.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q. F.; Zhang, D. H.; Yang, H. X. In situ grown Fe2O3 single crystallites on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as high performance conversion anode for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9, 19900–19907.
Zhang, N.; Han, X. P.; Liu, Y. C.; Hu, X. F.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, J. 3D porous γ-Fe2O3@C nanocomposite as highperformance anode material of Na-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401123.
Li, M.; Ma, C.; Zhu, Q.-C.; Xu, S.-M.; Wei, X.; Wu, Y.-M.; Tang, W.-P.; Wang, K.-X.; Chen, J.-S. Well-ordered mesoporous Fe2O3/C composites as high performance anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 5025–5032.
Yang, J. Q.; Zhou, X. L.; Wu, D. H.; Zhao, X. D.; Zhou, Z. S-doped N-rich carbon nanosheets with expanded interlayer distance as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604108.
Hou, H. S.; Shao, L. D.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, G. Q.; Chen, J.; Ji, X. B. Large-area carbon nanosheets doped with phosphorus: A high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600243.
Xu, J. T.; Wang, M.; Wickramaratne, N. P.; Jaroniec, M.; Dou, S. X.; Dai, L.M. High-performance sodium ion batteriesbased on a 3D anode from nitrogen-doped graphene foams. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2042–2048.
Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, N.; Yu, C. M.; Jiao, L. F.; Chen, J. MnFe2O4@C nanofibers as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3321–3328.
Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, N.; Jiao, L. F.; Chen, J. Tin nanodots encapsulated in porous nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers as a free-standing anode for advanced sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6702–6707.
Zhu, Y. J.; Han, X. G.; Xu, Y. H.; Liu, Y. H.; Zheng, S. Y.; Xu, K.; Hu, L. B.; Wang, C. S. Electrospun Sb/C fibers for a stable and fast sodium-ion battery anode. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6378–6386.
Wang, H.-G.; Yuan, S.; Ma, D.-L.; Zhang, X.-B.; Yan, J.-M. Electrospun materials for lithium and sodium rechargeable batteries: From structure evolution to electrochemical performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1660–1681.
Wu, L.; Hu, X. H.; Qian, J. F.; Pei, F.; Wu, F. Y.; Mao, R. J.; Ai, X. P.; Yang, H. X.; Cao, Y. L. Sb–C nanofibers with long cycle life as an anode material for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 323–328.
**ong, X. Q.; Luo, W.; Hu, X. L.; Chen, C. J.; Qie, L.; Hou, D. F.; Huang, Y. H. Flexible membranes of MoS2/C nanofibers by electrospinning as binder-free anodes for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9254.
Li, Y.; Li, H. X.; Cao, K. Z.; **, T.; Wang, X. J.; Sun, H. M.; Ning, J. X.; Wang, Y. J.; Jiao, L. F. Electrospun three dimensional Co/CoP@nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers network for efficient hydrogen evolution. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 12, 44–53.
Zhu, J. D.; Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Ge, Y. Q.; Jiang, H.; Fu, K.; Zhang, X. W. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers derived from polyacrylonitrile for use as anode material in sodium-ion batteries. Carbon 2015, 94, 189–195.
Liu, Y. C.; Fan, L.-Z.; Jiao L. F. Graphene highly scattered in porous carbon nanofibers: A binder-free and highperformance anode for sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 1698–1705.
Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X. B.; Chen, C. C.; Fan, L.-Z.; Jiao, L. F. Red phosphorus nanoparticles embedded in porous N-doped carbon nanofibers as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 9, 170–178.
Cao, K. Z.; Jiao, L. F.; Liu, H. Q.; Liu, Y. C.; Wang, Y. J.; Guo, Z. P.; Yuan, H. T. 3D hierarchical porous a-Fe2O3 nanosheets for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401421.
Li, D.; Zhou, J. S.; Chen, X. H.; Song, H. H. Amorphous Fe2O3/graphene composite nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical performance for sodium-ion battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30899–30907.
Koo, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Shibata, T.; Prakapenka, V. B.; Johnson, C. S.; Raih, T.; Shevchenko, E. V. Intercalation of sodium ions into hollow iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 245–252.
Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z. X.; Xu, Z. J. Yolk–shell Fe2O3⊙C composites anchored on MWNTs with enhanced lithium and sodium storage. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9520–9525.
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 51532002), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2015CB932500), the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (No. BX201600014), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. FRF-TP-16-078A1), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M600042) are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2018_1985_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Self-standing Na-storage anode of Fe2O3 nanodots encapsulated in porous N-doped carbon nanofibers with ultra-high cyclic stability
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, F. & Fan, LZ. Self-standing Na-storage anode of Fe2O3 nanodots encapsulated in porous N-doped carbon nanofibers with ultra-high cyclic stability. Nano Res. 11, 4026–4037 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-1985-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-1985-0