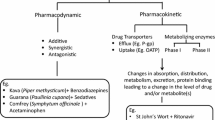
Abstract
As the use of herbal medicines increases, the public health consequences of drug-herb interactions are becoming more significant. Herbal medicines share the same drug metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters, including cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs), glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), and P-glycoprotein, with several clinically important drugs. Interactions of several commonly used herbal medicines, such as Ginko biloba, milk thistle, and St. John’s wort, with therapeutic drugs including warfarin, midazolam, alprazolam, indinavir, saquinavir, digoxin, nifedipine, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, irinotecan, and imatinib in humans have been reported. Many of these drugs have very narrow therapeutic indices. As the herb-drug interactions can significantly alter pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of administered drugs, the drugs interacting with herbal medicines should be identified by appropriate in vitro and in vivo methods. A good understanding of the mechanisms of herb-drug interactions is also essential for assessing and minimizing clinical risks. In vitro methods are useful for providing mechanistic information and evaluating multiple components in herbal medicines. This review describes major factors affecting the metabolism of herbal medicines, mechanisms of herb-drug interactions mediated by CYPs and UGTs, and several in vitro methods to assess the herb-drug interactions. Finally, drug interactions of Ginkgo biloba and St. John’s wort, as representative herbal medicines, are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, M. J., Bedoya, L. M., and Bermejo, P., An update on drug interactions with the herbal medicine Ginkgo biloba. Curr. Drug Metab., 11, 171–181 (2010).
Ang, C. Y., Hu, L., Heinze, T. M., Cui, Y., Freeman, J. P., Kozak, K., Luo, W., Liu, F. F., Mattia, A., and DiNovi, M., Instability of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.) and degradation of hyperforin in aqueous solutions and functional beverage. J. Agric. Food Chem., 52, 6156–6164 (2004).
Anthérieu, S., Chesné, C., Li, R., Camus, S., Lahoz, A., Picazo, L., Turpeinen, M., Tolonen, A., Uusitalo, J., Guguen-Guillouzo, C., and Guillouzo, A., Stable expression, activity, and inducibility of cytochromes P450 in differentiated HepaRG cells. Drug Metab. Dispos., 38, 516–525 (2010).
Bardia, A., Nisly, N. L., Zimmerman, M. B., Gryzlak, B. M., and Wallace, R. B., Use of herbs among adults based on evidence-based indications: findings from the National Health Interview Survey. Mayo Clin. Proc., 82, 561–566 (2007).
Barone, G. W., Gurley, B. J., Ketel, B. L., Lightfoot, M. L., and Abul-Ezz, S. R., Drug interaction between St. John’s wort and cyclosporine. Ann. Pharmacother., 34, 1013–1016 (2000).
Bent, S., Herbal medicine in the United States: review of efficacy, safety, and regulation: grand rounds at University of California, San Francisco Medical Center. J. Gen. Intern. Med., 23, 854–859 (2008).
Bjornsson, T. D., Callaghan, J. T., Einolf, H. J., Fischer, V., Gan, L., Grimm, S., Kao, J., King, S. P., Miwa, G., Ni, L., Kumar, G., McLeod, J., Obach, R. S., Roberts, S., Roe, A., Shah, A., Snikeris, F., Sullivan, J. T., Tweedie, D., Vega, J. M., Walsh, J., and Wrighton, S. A., The conduct of in vitro and in vivo drug-drug interaction studies: a Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) perspective. Drug Metab. Dispos., 31, 815–832 (2003).
Bolley, R., Zülke, C., Kammerl, M., Fischereder, M., and Krämer, B. K., Tacrolimus-induced nephrotoxicity unmasked by induction of the CYP3A4 system with St John’s wort. Transplantation, 73, 1009 (2002).
Bu, H. Z., Magis, L., Knuth, K., and Teitelbaum, P., Highthroughput cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition screening via a cassette probe-dosing strategy. VI. Simultaneous evaluation of inhibition potential of drugs on human hepatic isozymes CYP2A6, 3A4, 2C9, 2D6 and 2E1. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 15, 741–748 (2001).
Burchell, B., Lockley, D. J., Staines, A., Uesawa, Y., and Coughtrie, M. W., Substrate specificity of human hepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Methods Enzymol., 400, 46–57 (2005).
Chang, T. K., Chen, J., and Yeung, E. Y., Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on procarcinogen-bioactivating human CYP1 enzymes: identification of isorhamnetin, kaempferol, and quercetin as potent inhibitors of CYP1B1. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 213, 18–26 (2006).
Chen, G., Yang, M., Song, Y., Lu, Z., Zhang, J., Huang, H., Guan, S., Wu, L., and Guo, D. A., Comparative analysis on microbial and rat metabolism of ginsenoside Rb1 by highperformance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr., 22, 779–785 (2008).
Colalto, C., Herbal interactions on absorption of drugs: Mechanisms of action and clinical risk assessment. Pharmacol. Res., 62, 207–227 (2010).
Court, M. H., Isoform-selective probe substrates for in vitro studies of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Methods Enzymol., 400, 104–116 (2005).
Dierks, E. A., Stams, K. R., Lim, H. K., Cornelius, G., Zhang, H., and Ball, S. E., A method for the simultaneous evaluation of the activities of seven major human drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450s using an in vitro cocktail of probe substrates and fast gradient liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab. Dispos., 29, 23–29 (2001).
Donato, M. T., Montero, S., Castell, J. V., Gómez-Lechón, M. J., and Lahoz, A., Validated assay for studying activity profiles of human liver UGTs after drug exposure: inhibition and induction studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 396, 2251–2263 (2010).
Etheridge, A. S., Black, S. R., Patel, P. R., So, J., and Mathews, J. M., An in vitro evaluation of cytochrome P450 inhibition and P-glycoprotein interaction with goldenseal, Ginkgo biloba, grape seed, milk thistle, and ginseng extracts and their constituents. Planta Med., 73, 731–741 (2007).
Fan, L., Tao, G. Y., Wang, G., Chen, Y., Zhang, W., He, Y. J., Li, Q., Lei, H. P., Jiang, F., Hu, D. L., Huang, Y. F., and Zhou, H. H., Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract ingestion on the pharmacokinetics of talinolol in healthy Chinese volunteers. Ann. Pharmacother., 43, 944–949 (2009).
FDA, Guidance for Industry: Drug interaction studies-study design, data analysis and implications for dosing and labeling (2006). Available at: http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm.
Fujiwara, R., Nakajima, M., Yamanaka, H., Katoh, M., and Yokoi, T., Product inhibition of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes by UDP obfuscates the inhibitory effects of UGT substrates. Drug Metab. Dispos., 36, 361–367 (2008).
Gertz, H. J. and Kiefer, M., Review about Ginkgo biloba special extract EGb 761 (Ginkgo). Curr. Pharm. Des., 10, 261–264 (2004).
Grime, K., Ferguson, D. D., and Riley, R. J., The use of HepaRG and human hepatocyte data in predicting CYP induction drug-drug interactions via static equation and dynamic mechanistic modelling approaches. Curr. Drug Metab., 11, 870–885 (2010).
Grimm, S. W., Einolf, H. J., Hall, S. D., He, K., Lim, H. K., Ling, K. H., Lu, C., Nomeir, A. A., Seibert, E., Skordos, K. W., Tonn, G. R., Van Horn, R., Wang, R. W., Wong, Y. N., Yang, T. J., and Obach, R. S., The conduct of in vitro studies to address time-dependent inhibition of drugmetabolizing enzymes: a perspective of the pharmaceutical research and manufacturers of America. Drug Metab. Dispos., 37, 1355–1370 (2009).
Guengerich, F. P., Cytochrome P450s and other enzymes in drug metabolism and toxicity. AAPS J., 8, E101–E111 (2006).
Guillemette, C., Pharmacogenomics of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes. Pharmacogenomics J., 3, 136–158 (2003).
Guillemette, C., Lévesque, E., Harvey, M., Bellemare, J., and Menard, V., UGT genomic diversity: beyond gene duplication. Drug Metab. Rev., 42, 24–44 (2010).
Gurley, B. J., Gardner, S. F., Hubbard, M. A., Williams, D. K., Gentry, W. B., Cui, Y., and Ang, C. Y., Cytochrome P450 phenotypic ratios for predicting herb-drug interactions in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 72, 276–287 (2002).
Gutmann, H., Poller, B., Büter, K. B., Pfrunder, A., Schaffner, W., and Drewe, J., Hypericum perforatum: which constituents may induce intestinal MDR1 and CYP3A4 mRNA expression? Planta Med., 72, 685–690 (2006).
Hart, S. N., Li, Y., Nakamoto, K., Subileau, E. A., Steen, D., and Zhong, X. B., A comparison of whole genome gene expression profiles of HepaRG cells and HepG2 cells to primary human hepatocytes and human liver tissues. Drug Metab. Dispos., 38, 988–994 (2010).
He, F., Bi, H. C., **e, Z. Y., Zuo, Z., Li, J. K., Li, X., Zhao, L. Z., Chen, X., and Huang, M., Rapid determination of six metabolites from multiple cytochrome P450 probe substrates in human liver microsome by liquid chromatography/ mass spectrometry: application to high-throughput inhibition screening of terpenoids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 21, 635–643 (2007).
He, S. M., Li, C. G., Liu, J. P., Chan, E., Duan, W., and Zhou, S. F., Disposition pathways and pharmacokinetics of herbal medicines in humans. Curr. Med. Chem., 17, 4072–4113 (2010).
He, S. M., Chan, E., and Zhou, S. F., ADME properties of herbal medicines in humans: evidence, challenges and strategies. Curr. Pharm. Des., 17, 357–407 (2011).
Hellum, B. H. and Nilsen, O. G., In vitro inhibition of CYP3A4 metabolism and P-glycoprotein-mediated transport by trade herbal products. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 102, 466–475 (2008).
Hewitt, N. J., Lecluyse, E. L., and Ferguson, S. S., Induction of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes: methods, mechanisms, recommendations, and in vitro-in vivo correlations. Xenobiotica, 37, 1196–1224 (2007).
Hoehle, S. I., Pfeiffer, E., and Metzler, M., Glucuronidation of curcuminoids by human microsomal and recombinant UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 51, 932–938 (2007).
Huang, S. M., Temple, R., Throckmorton, D. C., and Lesko, L. J., Drug interaction studies: study design, data analysis, and implications for dosing and labeling. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 81, 298–304 (2007).
Huang, S. M., Strong, J. M., Zhang, L., Reynolds, K. S., Nallani, S., Temple, R., Abraham, S., Habet, S. A., Baweja, R. K., Burckart, G. J., Chung, S., Colangelo, P., Frucht, D., Green, M. D., Hepp, P., Karnaukhova, E., Ko, H. S., Lee, J. I., Marroum, P. J., Norden, J. M., Qiu, W., Rahman, A., Sobel, S., Stifano, T., Thummel, K., Wei, X. X., Yasuda, S., Zheng, J. H., Zhao, H., and Lesko, L. J., New era in drug interaction evaluation: US Food and Drug Administration update on CYP enzymes, transporters, and the guidance process. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 48, 662–670 (2008).
Ioannides, C., Pharmacokinetic interactions between herbal remedies and medicinal drugs. Xenobiotica, 32, 451–478 (2002).
Izukawa, T., Nakajima, M., Fujiwara, R., Yamanaka, H., Fukami, T., Takamiya, M., Aoki, Y., Ikushiro, S., Sakaki, T., and Yokoi, T., Quantitative analysis of UDP-glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) 1A and UGT2B expression levels in human livers. Drug Metab. Dispos., 37, 1759–1768 (2009).
Izzo, A. A. and Ernst, E., Interactions between herbal medicines and prescribed drugs: an updated systematic review. Drugs, 69, 1777–1798 (2009).
Kiang, T. K., Ensom, M. H., and Chang, T. K., UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and clinical drug-drug interactions. Pharmacol. Ther., 106, 97–132 (2005).
Kim, D. K., Liu, K. H., Jeong, J. H., Ji, H. Y., Oh, S. R., Lee, H. K., and Lee, H. S., In vitro metabolism of magnolin and characterization of cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for its metabolism in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica, 41, 358–371 (2011).
Kim, M. J., Kim, H., Cha, I. J., Park, J. S., Shon, J. H., Liu, K. H., and Shin, J, G., High-throughput screening of inhibitory potential of nine cytochrome P450 enzymes in vitro using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 19, 2651–2658 (2005).
Klieber, S., Hugla, S., Ngo, R., Arabeyre-Fabre, C., Meunier, V., Sadoun, F., Fedeli, O., Rival, M., Bourrie, M., Guillou, F., Maurel, P., and Fabre, G., Contribution of the N-glucuronidation pathway to the overall in vitro metabolic clearance of midazolam in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos., 36, 851–862 (2008).
Lee, H. S., Ji, H. Y., Park, E. J., and Kim, S. Y., In vitro metabolism of eupatilin by multiple cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes. Xenobiotica, 37, 803–817 (2007).
Li, L., Stanton, J. D., Tolson, A. H., Luo, Y., and Wang, H., Bioactive terpenoids and flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba extract induce the expression of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes through pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated pathways. Pharm. Res., 26, 872–882 (2009).
Lin, J. H. and Wong, B. K., Complexities of glucuronidation affecting in vitro in vivo extrapolation. Curr. Drug Metab., 3, 623–646 (2002).
Lin, J. H., CYP induction-mediated drug interactions: in vitro assessment and clinical implications. Pharm. Res., 23, 1089–1116 (2006).
Madabushi, R., Frank, B., Drewelow, B., Derendorf, H., and Butterweck, V., Hyperforin in St. John’s wort drug interactions. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 62, 225–233 (2006).
Mahady, G. B., Global harmonization of herbal health claims. J. Nutr., 131, 1120s–1123s (2001).
Mai, I., Krüger, H., Budde, K., Johne, A., Brockmöller, J., Neumayer, H. H., and Roots, I., Hazardous pharmacokinetic interaction of Saint John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) with the immunosuppressant cyclosporin. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 38, 500–502 (2000).
Mai, I., Bauer, S., Perloff, E. S., Johne, A., Uehleke, B., Frank, B., Budde, K., and Roots, I., Hyperforin content determines the magnitude of the St John’s wort-cyclosporine drug interaction. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 76, 330–340 (2004).
Mannel, M., Drug interactions with St John’s wort: mechanisms and clinical implications. Drug Saf., 27, 773–797 (2004).
Markowitz, J. S., Donovan, J. L., Lindsay DeVane, C., Sipkes, L., and Chavin, K. D., Multiple-dose administration of Ginkgo biloba did not affect cytochrome P-450 2D6 or 3A4 activity in normal volunteers. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol., 23, 576–581 (2003).
McGinnity, D. F., Berry, A. J., Kenny, J. R., Grime, K., and Riley, R. J., Evaluation of time-dependent cytochrome P450 inhibition using cultured human hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos., 34, 1291–1300 (2006).
Mills, E., Montori, V. M., Wu, P., Gallicano, K., Clarke, M., and Guyatt, G., Interaction of St John’s wort with conventional drugs: systematic review of clinical trials. BMJ, 329, 27–30 (2004a).
Mills, J. B. Rose, K. A., Sadagopan, N., Sahi, J., and de Morais, S. M., Induction of drug metabolism enzymes and MDR1 using a novel human hepatocyte cell line. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 309, 303–309 (2004b).
Modarai, M., Gertsch, J., Suter, A., Heinrich, M., and Kortenkamp, A., Cytochrome P450 inhibitory action of Echinacea preparations differs widely and co-varies with alkylamide content. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 59, 567–573 (2007).
Mohamed, M. E. and Frye, R. F., Effects of herbal supplements on drug glucuronidation. Review of clinical, animal, and in vitro studies. Planta Med., 77, 311–321 (2011).
Mohutsky, M. A., Anderson, G. D., Miller, J. W., and Elmer, G. W., Ginkgo biloba: evaluation of CYP2C9 drug interactions in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Ther., 13, 24–31 (2006).
Na, D. H., Metabolism study of botanical drugs. Arch. Pharm. Res., 33, 1877–1879 (2010).
Nakajima, M., Tanaka, E., Kobayashi, T., Ohashi, N., Kume, T., and Yokoi, T., Imipramine N-glucuronidation in human liver microsomes: biphasic kinetics and characterization of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms. Drug Metab. Dispos., 30, 636–642 (2002).
Nishiyama, T., Kobori, T., Arai, K., Ogura, K., Ohnuma, T., Ishii, K., Hayashi, K., and Hiratsuka, A., Identification of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoform(s) responsible for the C-glucuronidation of phenylbutazone. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 454, 72–79 (2006).
Obach, R. S., Walsky, R. L., and Venkatakrishnan, K., Mechanism-based inactivation of human cytochrome p450 enzymes and the prediction of drug-drug interactions. Drug Metab. Dispos., 35, 246–255 (2007).
Ohnishi, N., Kusuhara, M., Yoshioka, M., Kuroda, K., Soga, A., Nishikawa, F., Koishi, T., Nakagawa, M., Hori, S., Matsumoto, T., Yamashita, M., Ohta, S., Takara, K., and Yokoyama, T., Studies on interactions between functional foods or dietary supplements and medicines. I. Effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on the pharmacokinetics of diltiazem in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 26, 1315–1320 (2003).
Ohno, S. and Naka**, S., Determination of mRNA expression of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and application for localization in various human tissues by realtime reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Drug Metab. Dispos., 37, 32–40 (2009).
Otten, J. N., Hingorani, G. P., Hartley, D. P., Kragerud, S. D., and Franklin, R. B., An in vitro, high throughput, seven CYP cocktail inhibition assay for the evaluation of new chemical entities using LC-MS/MS. Drug Metab. Lett., 5, 17–24 (2011).
Pal, D. and Mitra, A. K., MDR- and CYP3A4-mediated drugherbal interactions. Life Sci., 78, 2131–2145 (2006).
Parkinson, A., Kazmi, F., Buckley, D. B., Yerino, P., Ogilvie, B. W., and Paris, B. L., System-dependent outcomes during the evaluation of drug candidates as inhibitors of cytochrome p450 (CYP) and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes: human hepatocytes versus liver microsomes versus recombinant enzymes. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 25, 16–27 (2010).
Patwardhan, B. and Vaidya, A. D., Natural products drug discovery: accelerating the clinical candidate development using reverse pharmacology approaches. Indian J. Exp. Biol., 48, 220–227 (2010).
Pelkonen, O., Mäenpää, J., Taavitsainen, P., Rautio, A., and Raunio, H., Inhibition and induction of human cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. Xenobiotica, 28, 1203–1253 (1998).
Pelkonen, O., Turpeinen, M., Hakkola, J., Honkakoski, P., Hukkanen, J., and Raunio, H., Inhibition and induction of human cytochrome P450 enzymes: current status. Arch. Toxicol., 82, 667–715 (2008).
Polasek, T. M. and Miners, J. O., In vitro approaches to investigate mechanism-based inactivation of CYP enzymes. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol., 3, 321–329 (2007).
Rengelshausen, J., Banfield, M., Riedel, K. D., Burhenne, J., Weiss, J., Thomsen, T., Walter-Sack, I., Haefeli, W. E., and Mikus, G., Opposite effects of short-term and longterm St. John’s wort intake on voriconazole pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 78, 25–33 (2005).
Robertson, S. M., Davey, R. T., Voell, J., Formentini, E., Alfaro, R. M., and Penzak, S. R., Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on lopinavir, midazolam and fexofenadine pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects. Curr. Med. Res. Opin., 24, 591–599 (2008).
Sahai, J., Gallicano, K., Pakuts, A., and Cameron, D. W., Effect of fluconazole on zidovudine pharmacokinetics in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Infect. Dis., 169, 1103–1107 (1994).
Schwarz, U. I., Hanso, H., Oertel, R., Miehlke, S., Kuhlisch, E., Glaeser, H., Hitzl, M., Dresser, G. K., Kim, R. B., and Kirch, W., Induction of intestinal P-glycoprotein by St John’s wort reduces the oral bioavailability of talinolol. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 81, 669–678 (2007).
Sevior, D. K., Hokkanen, J., Tolonen, A., Abass, K., Tursas, L., Pelkonen, O., and Ahokas, J. T., Rapid screening of commercially available herbal products for the inhibition of major human hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes using the N-in-one cocktail. Xenobiotica, 40, 245–254 (2010).
Shord, S. S., Shah, K., and Lukose, A., Drug-botanical interactions: a review of the laboratory, animal, and human data for 8 common botanicals. Integr. Cancer Ther., 8, 208–227 (2009).
Sinz, M., Wallace, G., and Sahi, J., Current industrial practices in assessing CYP450 enzyme induction: preclinical and clinical. AAPS J., 10, 391–400 (2008).
Skalli, S., Zaid, A., and Soulaymani, R., Drug interactions with herbal medicines. Ther. Drug Monit., 29, 679–686 (2007).
Smith, D., Sadagopan, N., Zientek, M., Reddy, A., and Cohen, L., Analytical approaches to determine cytochrome P450 inhibitory potential of new chemical entities in drug discovery. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 850, 455–463 (2007).
Soars, M. G., Petullo, D. M., Eckstein, J. A., Kasper, S. C., and Wrighton, S. A., An assessment of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase induction using primary human hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos., 32, 140–148 (2004).
Song, W. Y., Ji, H. Y., Baek, N. I., Jeong, T. S., and Lee, H. S., In vitro metabolism of jaceosidin and characterization of cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in human liver microsomes. Arch. Pharm. Res., 33, 1985–1996 (2010).
Stone, R., Biochemistry. Lifting the veil on traditional Chinese medicine. Science, 319, 709–710 (2008).
Tang, J., Sun, J., Zhang, Y., Li, L., Cui, F., and He, Z., Herbdrug interactions: Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol., 45, 2441–2445 (2007).
Testino, S. A. Jr. and Patonay, G., High-throughput inhibition screening of major human cytochrome P450 enzymes using an in vitro cocktail and liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 30, 1459–1467 (2003).
Tolonen, A., Petsalo, A., Turpeinen, M., Uusitalo, J., and Pelkonen, O., In vitro interaction cocktail assay for nine major cytochrome P450 enzymes with 13 probe reactions and a single LC/MSMS run: analytical validation and testing with monoclonal anti-CYP antibodies. J. Mass Spectrom., 42, 960–966 (2007).
Uchida, S., Yamada, H., Li, X. D., Maruyama, S., Ohmori, Y., Oki, T., Watanabe, H., Umegaki, K., Ohashi, K., and Yamada, S., Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tolbutamide and midazolam in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 46, 1290–1298 (2006).
Venkataramanan, R., Komoroski, B., and Strom, S., In vitro and in vivo assessment of herb drug interactions. Life Sci., 78, 2105–2115 (2006).
Watanabe, Y., Nakajima, M., Ohashi, N., Kume, T., and Yokoi, T., Glucuronidation of etoposide in human liver microsomes is specifically catalyzed by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1. Drug Metab. Dispos., 31, 589–595 (2003).
Weinmann, S., Roll, S., Schwarzbach, C., Vauth, C., and Willich, S. N., Effects of Ginkgo biloba in dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr., 10, 14 (2010).
Williams, J. A., Hyland, R., Jones, B. C., Smith, D. A., Hurst, S., Goosen, T. C., Peterkin, V., Koup, J. R., and Ball, S. E., Drug-drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCi/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab. Dispos., 32, 1201–1208 (2004).
Yang, A. K., He, S. M., Liu, L., Liu, J. P., Wei, M. Q., and Zhou, S. F., Herbal interactions with anticancer drugs: mechanistic and clinical considerations. Curr. Med. Chem., 17, 1635–1678 (2010).
Yin, O. Q., Tomlinson, B., Waye, M. M., Chow, A. H., and Chow, M. S., Pharmacogenetics and herb-drug interactions: experience with Ginkgo biloba and omeprazole. Pharmacogenetics, 14, 841–850 (2004).
Yoshioka, M., Ohnishi, N., Sone, N., Egami, S., Takara, K., Yokoyama, T., and Kuroda, K., Studies on interactions between functional foods or dietary supplements and medicines. III. Effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 27, 2042–2045 (2004a).
Yoshioka, M., Ohnishi, N., Koishi, T., Obata, Y., Nakagawa, M., Matsumoto, T., Tagagi, K., Takara, K., Ohkuni, T., Yokoyama, T., and Kuroda, K., Studies on interactions between functional foods or dietary supplements and medicines. IV. Effects of ginkgo biloba leaf extract on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nifedipine in healthy volunteers. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 27, 2006–2009 (2004b).
Zambon, S., Fontana, S., and Kajbaf, M., Evaluation of cytochrome P450 inhibition assays using human liver microsomes by a cassette analysis/LC-MS/MS. Drug Metab. Lett., 4, 120–128 (2010).
Zhao, P., Kunze, K. L., and Lee, C. A., Evaluation of timedependent inactivation of CYP3A in cryopreserved human hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos., 33, 853–861 (2005).
Zhou, J., Tracy, T. S., and Remmel, R. P., Bilirubin glucuronidation revisited: proper assay conditions to estimate enzyme kinetics with recombinant UGT1A1. Drug Metab. Dispos., 38, 1907–1911 (2010).
Zhou, S., Gao, Y., Jiang, W., Huang, M., Xu, A., and Paxton, J. W., Interaction of herbs with cytochrome P450. Drug Metab. Rev., 35, 35–98 (2003).
Zhou, S. F., Zhou, Z. W., Li, C. G., Chen, X., Yu, X., Xue, C. C., and Herington, A., Identification of drugs that interact with herbs in drug development. Drug Discov. Today, 12, 664–673 (2007).
Zhou, S. F., Drugs behave as substrates, inhibitors and inducers of human cytochrome P450 3A4. Curr. Drug Metab., 9, 310–322 (2008).
Zhou, S. F. and Lai, X., An update on clinical drug interactions with the herbal antidepressant St. John’s wort. Curr. Drug Metab., 9, 394–409 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, D.H., Ji, H.Y., Park, E.J. et al. Evaluation of metabolism-mediated herb-drug interactions. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1829–1842 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-1105-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-1105-0