Abstract
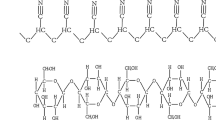
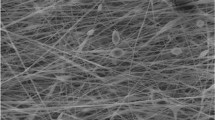
This study takes polyacrylonitrile (PAN) as a raw material for PAN-based nanofiber nonwoven prepared using electrospinning. First we construct a thermal-stable process for the fabrication of oxidized nanofiber nonwovens as the precursor. A semi-open high-temperature erect furnace is then used with steam as the activator, through carbonization and activation processes to prepare carbon nanofiber absorbents continuously. The experiment varies the production rate and activator flow rate to prepare carbon nanofiber absorbents. Experimental results show that carbon nanofiber adsorbents are primarily made up of micropores and mesopores, averaging under 20 Å. Given a production rate of 10–20 cm/min with a matching activator feed rate of 120 ml/min, the specific surface area can reach about 1000 m2/g, producing an adsorption ratio of carbon tetrachloride over 200 %.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.-I. Su, Z.-Y. Jiang, and C.-H. Lu, Fiber. Polym., 1, 38 (2012).
C. H. Wang, U. S. Patent, 5819350 (1998).
P. H. Wang, J. Appl. Polymer. Sci., 67, 1185 (1998).
M. C. Rocco, R. S. William, and P. Alivisiatos, “Nanotechnology Research Directions”, IWGN Workshop Report, NSTC, Sept, 1999.
W. Watt and W. Johnson, Nature, 257, 210 (1975).
J. D. López-González, F. Martínez-Víchez, and F. Rodríguez-Reinoso, Carbon, 18, 413 (1980).
K. Gergova, N. Petrov, and S. Eser, Carbon, 32, 693 (1994).
S. Lowell and J. E. Shields, “Powder Surface Area and Porosity”, Chapman and Hall Pub., USA, 1984.
M. J. Muñoz-Guillena, M. J. Illán-Gómez, J. M. Martin-Martínez, A. Linares-Solano, and C. Salinas-Martínez de Lecea, Energy Fuels, 6, 9 (1992).
S. J. Greeg and K. S. W. Sing, “Adsorption Surface Areas and Porosity”, Academic Press, London and New York, 1982.
J. W. McBain, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 57, 699 (1935).
E. P. Barrett, L. G. Joyner, and P. P. Halenda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 73, 373 (1951).
S. C. Bennett and D. J. Johnson, Carbon, 17, 25 (1979).
M. Balasubramanian, M. K. Jain, S. K. Bhattacharya, and A. S. Abhiraman, J. Mater. Sci., 22, 3864 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, CI., Huang, YX., Wong, JW. et al. PAN-based carbon nanofiber absorbents prepared using electrospinning. Fibers Polym 13, 436–442 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0436-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0436-x