Abstract
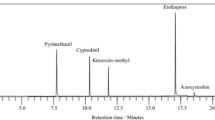
A specific and sensitive LC-MS/MS method was firstly established for the simultaneous extraction and determination of cyadox and its three main metabolites—1,4-bisdesoxycyadox, 4-desoxycyadox, and quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid—in chicken muscle, liver, kidney, and fat tissues. Samples were subjected to extraction using ethyl acetate and followed by acetonitrile–chloroform (1:4, v/v) and further purified by Oasis mixed mode anion exchange SPE cartridge. Analysis was performed on a C18 column by detection with MS in multiple-reaction monitoring mode. A gradient elution program with 0.1 % formic acid solution, acetonitrile, and 1 % formic acid (adjusted to pH 8 with ammonia) was performed at a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1. The correlation coefficients (r) for each calibration curve are higher than 0.99 within the experimental concentration range. The recoveries of the four target analytes at three spiking levels of 2.5, 25 and 250 μg kg−1 were between 74.5 and 93.8 %, with relative standard deviations less than 12 %. The decision limits (CCαs) of the four analytes in chicken edible tissues ranged from 0.3 to 1.5 μg kg−1, and the detection capabilities (CCβs) were below 2.3 μg kg−1. The developed method demonstrated a satisfactory applicability in incurred chicken tissue samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts MM, Beek WM, Keukens HJ, Brinkman U (1988) Determination of residues of carbadox and some of its metabolites in swine tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography using on line precolumn enrichment and post column derivatization with UV–vis detection. J Chromatogr A 456:105–119
De Vries H, Bojarski J, Donker AA, Bakri A, Beyersbergen van Henegouwen GM (1990) Photochemical reactions of quindoxin, olaquindox, carbadox and cyadox with protein, indicating photoallergic properties. Toxicology 63(1):85–95
European Commission (EC) Regulation No. 2788/98 (1998) Off J Eur Communities L347:32
European Commission Decision 2002/657/EC (2002) Off J Eur Communities L221:8–36
FAO/WHO (1990) Joint expert committee on food additives: evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 799:45–54
FAO/WHO (1995) Joint expert committee on food additives: evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 851:19–28
He QH, Fang GJ, Wang YL, Wei ZC, Wang DJ, Zhou SQ, Fan SX, Yuan ZH (2006) Experimental evaluation of cyadox phototoxicity to Balb/c mouse skin. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 22:100–104
He LM, Liu KY, Su YJ, Zhang JH, Liu YH, Zeng ZL, Fang BH, Zhang GJ (2011) Simultaneous determination of cyadox and its metabolites in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 34:755–1762
Huang LL, Wang YL, Tao YF, Chen DM, Yuan ZH (2008) Development of high performance liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of cyadox and its metabolites in plasma and tissues of chicken. J Chromatogr B 874:7–14
Hutchinson MJ, Young PY, Hewitt SA, Faulkner D, Kennedy DG (2002) Development and validation of an improved method for confirmation of the carbadox metabolite, quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid, in porcine liver using LC–electrospray MS-MS according to revised EU criteria for veterinary drug residue analysis. Analyst 127:342–346
Hutchinson MJ, Young PB, Kennedy DG (2005) Confirmation of carbadox and olaquindox metabolites in porcine liver using liquid chromatography–electrospray, tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 816:15–20
Liu ZY, Huang LL, Dai MH, Chen DM, Tao YF, Wang YL, Yuan ZH (2009) Metabolism of cyadox in rat, chicken and pig liver microsomes and identification of metabolites by accurate mass measurements using electrospray ionization hybrid ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:2026–2034
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC–MS/MS. Anal Chem 75(13):3019–3030
Stará V, Kopanica M (1986) Determination of some quinoxaline-N-dioxide derivatives by adsorptive strip** voltammetry. Anal Chim Acta 186:21–30
Wang X, Fang GJ, Wang YL, Ihsan A, Huang LL, Zhou W, Liu ZL, Yuan ZH (2011a) Two generation reproduction and teratogenicity studies of feeding cyadox in Wistar rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1068–1079
Wang X, He QH, Wang YL, Ihsan A, Huang LL, Zhou W, Su SJ, Liu ZL, Yuan ZH (2011b) A chronic toxicity study of cyadox in Wistar rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 59(2):324–333
Wu YJ, Yu H, Wang YL, Huang LL, Tao YF, Chen DM, Peng DP, Liu ZL, Yuan ZH (2007) Development of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous quantification of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in animal tissues. J Chromatogr A 1146:1–7
Xu N, Huang LL, Liu ZL, Pan YH, Wang X, Tao YF, Chen DM, Wang YL, Peng DP, Yuan ZH (2011) Metabolism of cyadox by the intestinal mucosa microsomes and gut flora of swine, and identification of metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography combined with ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 25:2333–2344
Zhang YL, Huang LL, Chen DM, Fan SX, Wang YL, Tao YF, Yuan ZH (2005) Development of HPLC methods for the determination of cyadox and its main metabolites in goat tissues. Anal Sci 21:1495–1499
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the 973 Fund, the Ministry of Science and Technology, P.R. China (No. 2009CB118805), for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dandan Yan and Limin He contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, D., He, L., Zhang, G. et al. Simultaneous Determination of Cyadox and Its Metabolites in Chicken Tissues by LC-MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 5, 1497–1505 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-012-9398-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-012-9398-2