Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to examine and compare two automated quantitative software tools (PMOD and MIMneuro) for the quantification of amyloid positron emission tomography (PET).
Methods
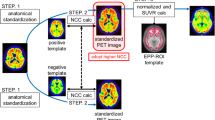
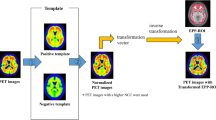
A total of 30 subjects—15 Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients and 15 cognitively normal age- and sex-matched controls—were enrolled. All subjects underwent structural volumetric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and amyloid PET scans with F-18 florbetaben. Regional standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) using the cerebellar cortex as a reference region were obtained using PMOD and MIMneuro.
Results
The SUVRs using both PMOD and MIMneuro showed high discriminatory power between the AD patients and cognitively normal controls. While PMOD and MIMneuro yielded significantly different SUVRs in some brain regions, the two methods had good overall agreement.
Conclusion
MIMneuro provides comparable performance to PMOD without the need to acquire brain MRI. Therefore, MIMneuro might be suitable for clinical use to determine amyloid positivity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy J, Allsop D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991;12:383–8.
Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP, et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:306–19.
FDA approves 18F-florbetapir PET agent. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:15n.
GE beta-amyloid agent approved. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:10n.
US Food and Drug Administration. Neuraceq (florbetaben F 18 injection): clinical pharmacology and biopharmaceutics review(s). 2014. http://www.fda.gov. Accessed 10 April 2016.
Rinne J, Brooks D, Rossor M, Fox N, Bullock R, Klunk W, et al. 11C-PiB PET assessment of change in fibrillar amyloid-beta load in patients with Alzheimer’s disease treated with bapineuzumab: a phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:363–72.
Liu E, Schmidt M, Margolin R, Sperling R, Koeppe R, Mason N, et al. Amyloid-β 11C-PiB-PET imaging results from 2 randomized bapineuzumab phase 3 AD trials. Neurology. 2015;85:692–700.
Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997;15:300–8.
Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993;43:2412–4.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–44.
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage. 2002;15:273–89.
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44:837–45.
Lopresti BJ, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, Lu X, et al. Simplified quantification of Pittsburgh Compound B amyloid imaging PET studies: a comparative analysis. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1959–72.
Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–59.
Thal DR, Rub U, Orantes M, Braak H. Phases of A beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology. 2002;58:1791–800.
Becker GA, Ichise M, Barthel H, Luthardt J, Patt M, Seese A, et al. PET quantification of 18F-florbetaben binding to beta-amyloid deposits in human brains. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:723–31.
Barthel H, Luthardt J, Becker G, Patt M, Hammerstein E, Hartwig K, et al. Individualized quantification of brain beta-amyloid burden: results of a proof of mechanism phase 0 florbetaben PET trial in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:1702–14.
Svedberg MM, Hall H, Hellstrom-Lindahl E, Estrada S, Guan Z, Nordberg A, et al. [(11)C]PIB-amyloid binding and levels of Abeta40 and Abeta42 in postmortem brain tissue from Alzheimer patients. Neurochem Int. 2009;54:347–57.
Barthel H, Gertz HJ, Dresel S, Peters O, Bartenstein P, Buerger K, et al. Cerebral amyloid-beta PET with florbetaben (18F) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls: a multicentre phase 2 diagnostic study. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:424–35.
Pike K, Savage G, Villemagne V, Ng S, Moss S, Maruff P, et al. Beta-amyloid imaging and memory in non-demented individuals: evidence for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2007;130:2837–44.
Rowe CC, Ng S, Ackermann U, Gong SJ, Pike K, Savage G, et al. Imaging beta-amyloid burden in aging and dementia. Neurology. 2007;68:1718–25.
Destrieux C, Fischl B, Dale A, Halgren E. Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage. 2010;53:1–15.
Fleisher AS, Chen K, Liu X, Roontiva A, Thiyyagura P, Ayutyanont N, et al. Using positron emission tomography and florbetapir F18 to image cortical amyloid in patients with mild cognitive impairment or dementia due to Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1404–11.
Joshi AD, Pontecorvo MJ, Clark CM, Carpenter AP, Jennings DL, Sadowsky CH, et al. Performance characteristics of amyloid PET with florbetapir F 18 in patients with alzheimer’s disease and cognitively normal subjects. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:378–84.
Namiki C, Takita Y, Iwata A, Momose T, Senda M, Okubo Y, et al. Imaging characteristics and safety of florbetapir ((1)(8)F) in Japanese healthy volunteers, patients with mild cognitive impairment and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Nucl Med. 2015;29:570–81.
Brendel M, Hogenauer M, Delker A, Sauerbeck J, Bartenstein P, Seibyl J, et al. Improved longitudinal [(18)F]-AV45 amyloid PET by white matter reference and VOI-based partial volume effect correction. Neuroimage. 2015;108:450–9.
Landau SM, Mintun MA, Joshi AD, Koeppe RA, Petersen RC, Aisen PS, et al. Amyloid deposition, hypometabolism, and longitudinal cognitive decline. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:578–86.
Landau SM, Fero A, Baker SL, Koeppe R, Mintun M, Chen K, et al. Measurement of longitudinal beta-amyloid change with 18F-florbetapir PET and standardized uptake value ratios. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:567–74.
Tuszynski T, Rullmann M, Luthardt J, Butzke D, Tiepolt S, Gertz HJ, et al. Evaluation of software tools for automated identification of neuroanatomical structures in quantitative beta-amyloid PET imaging to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:1077–87.
Rosario BL, Weissfeld LA, Laymon CM, Mathis CA, Klunk WE, Berginc MD, et al. Inter-rater reliability of manual and automated region-of-interest delineation for PiB PET. Neuroimage. 2011;55:933–41.
Su Y, D’Angelo GM, Vlassenko AG, Zhou G, Snyder AZ, Marcus DS, et al. Quantitative analysis of PiB-PET with FreeSurfer ROIs. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73377.
Schain M, Varnas K, Cselenyi Z, Halldin C, Farde L, Varrone A. Evaluation of two automated methods for PET region of interest analysis. Neuroinformatics. 2014;12:551–62.
Rullmann M, Dukart J, Hoffmann KT, Luthardt J, Tiepolt S, Patt M, et al. Partial-volume effect correction improves quantitative analysis of 18F-florbetaben beta-amyloid PET scans. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:198–203.
Villemagne VL, Ong K, Mulligan RS, Holl G, Pejoska S, Jones G, et al. Amyloid imaging with (18)F-florbetaben in Alzheimer disease and other dementias. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1210–7.
Wong DF, Rosenberg PB, Zhou Y, Kumar A, Raymont V, Ravert HT, et al. In vivo imaging of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer disease using the radioligand 18F-AV-45 (florbetapir [corrected] F 18). J Nucl Med. 2010;51:913–20.
Vandenberghe R, Van Laere K, Ivanoiu A, Salmon E, Bastin C, Triau E, et al. 18F-flutemetamol amyloid imaging in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: a phase 2 trial. Ann Neurol. 2010;68:319–29.
Stankoff B, Freeman L, Aigrot MS, Chardain A, Dolle F, Williams A, et al. Imaging central nervous system myelin by positron emission tomography in multiple sclerosis using [methyl-(1)(1)C]-2-(4′-methylaminophenyl)-6-hydroxybenzothiazole. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:673–80.
Saint-Aubert L, Nemmi F, Peran P, Barbeau EJ, Payoux P, Chollet F, et al. Comparison between PET template-based method and MRI-based method for cortical quantification of florbetapir (AV-45) uptake in vivo. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:836–43.
Edison P, Carter SF, Rinne JO, Gelosa G, Herholz K, Nordberg A, et al. Comparison of MRI based and PET template based approaches in the quantitative analysis of amyloid imaging with PIB-PET. Neuroimage. 2013;70:423–33.
Landau SM, Breault C, Joshi AD, Pontecorvo M, Mathis CA, Jagust WJ, et al. Amyloid-beta imaging with Pittsburgh compound B and florbetapir: comparing radiotracers and quantification methods. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:70–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, W.H., Um, Y.H., Jung, W.S. et al. Automated quantification of amyloid positron emission tomography: a comparison of PMOD and MIMneuro. Ann Nucl Med 30, 682–689 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-016-1115-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-016-1115-6