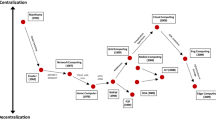
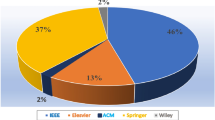
Abstract
This paper identifies and analyzes the key design approaches that have been proposed over the last decade to construct a peer-to-peer (P2P) networked virtual environment (NVE) systems. We discuss each approach, their advantages and drawbacks, and examine several representative P2P-based NVE systems based on the presented approaches, thus providing the background and literature review of P2P NVEs.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quake Live. http://www.quakelive.com/#!home
Marathon. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marathon_(video_game)
Blake Stone: aliens of gold. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blake_Stone:_Aliens_of_Gold
Star wars: dark forces. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Star_Wars:_Dark_Forces
Homeworld. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homeworld
Starcraft II: wings of liberty. http://us.battle.net/sc2/en/
Company of heroes. http://www.companyofheroes.com/
Ultima online. http://www.uo.com/ageofshadows/viscent.html
EverQuest. http://everquest.station.sony.com/
Final fantasy XI. http://www.playonline.com/ff11eu/index.shtml
EVE online. http://www.eveonline.com/
World of warcraft. http://us.battle.net/wow/en/
Calvin J, Dickens A, Gaines B, Metzger P, Miller D, Owen D (1993) The simnet virtual world architecture. In: Annual international symposium virtual reality IEEE, pp 450–455
Pullen JM, Wood DC (1995) Networking technology and dis. IEEE 83:1156–1167
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (2000) IEEE standard for modeling and simulation (m&s) high level architecture (hla)—framework and rules. IEEE Std. 1516-2000, pp i–22
FALCON 4.0. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Falcon_4.0
America’s army. http://www.americasarmy.com/
Second life official site. http://secondlife.com/
HiPiHi. http://www.hipihi.com/
The sims online. http://thesims.com/en_us/home
There. http://www.there.com/
Active worlds. http://www.activeworlds.com/
Knutsson B, Lu H, Xu W, Hopkins B (2004) Peer-to-peer support for massively multiplayer games. In: Proceeding the 23rd conference of the IEEE communications society, INFOCOM ’04, p 107
Beigbeder T, Coughlan R, Lusher C, Plunkett J, Agu E, Claypool M (2004) The effects of loss and latency on user performance in unreal tournament 2003®. In: Proceeding 3rd ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’04. ACM, New York, pp 144–151
Macedonia MR, Zyda MJ, Pratt DR, Brutzman DP, Barham PT (1995) Exploiting reality with multicast groups. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 15(5):38–45
Funkhouser TA (1995) RING: a client-server system for multi-user virtual environments. In: Proceeding the 1995 symposium on interactive 3D graphics, SI3D ’95. ACM, New York, pp 85–ff
Barrus JW, Waters RC, Anderson DB (1996) Locales: supporting large multiuser virtual environments. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 16(6):50–57
Abrams H, Watsen K, Zyda M (1998) Three-tiered interest management for large-scale virtual environments. In: Proceeding the ACM symposium on virtual reality software and technology, VRST ’98. ACM, New York, pp 125–129
Hu S-Y, Chang S-C, Jiang J-R (2008) Voronoi state management for peer-to-peer massively multiplayer online games. In: 5th IEEE consumer communications and networking conference, CCNC ’08, pp 1134–1138
Yu AP, Vuong ST (2005) MOPAR: a mobile peer-to-peer overlay architecture for interest management of massively multiplayer online games. In: Proceeding the international workshop on network and operating systems support for digital audio and video, NOSSDAV ’05. ACM, New York, pp 99–104
GauthierDickey C, Lo V, Zappala D (2005) Using N-Trees for scalable event ordering in peer-to-peer games. In: Proceeding the international workshop on network and operating systems support for digital audio and video, NOSSDAV ’05. ACM, New York, pp 87–92
Yamamoto S, Murata Y, Yasumoto K, Ito M (2005) A distributed event delivery method with load balancing for MMORPG. In: Proceeding 4th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’05. ACM, New York, pp 1–8
Rieche S, Wehrle K, Fouquet M, Niedermayer H, Petrak L, Carle G (2007) Peer-to-peer-based infrastructure support for massively multiplayer online games. In: 4th annual IEEE consumer communications and networking conference, CCNC ’07
Kulkarni S, Douglas S, Churchill D (2010) Badumna: a decentralised network engine for virtual environments. Comput Netw 54(12):1953–1967. P2P technologies for emerging wide-area collaborative services and applications
De Chiara R, Erra U, Scarano V (2009) Some considerations on the design of a P2P infrastructure for massive simulations. In: International conference on ultra modern telecommunication, ICUMT ’09
Morillo P, Moncho W, Orduña JM, Duato J (2006) Providing full awareness to distributed virtual environments based on peer-to-peer architectures. In: Proceeding the 24th computer graphics international conference, lecture notes in computer science, CGI ’06, vol 4035. Springer, Berlin, pp 11–127
Varvello M, Diot C, Biersack E (2009) A walkable Kademlia network for virtual worlds. In: International workshop on peer-to-peer systems, IPTPS ’09
Correia RCM, Pellegrino SRM (2005) Scalable distributed virtual environments using multicast application level. In: Proceeding the ninth international conference on computer supported cooperative work in design, vol 1, pp 140–145
Hampel T, Bopp T, Hinn R (2006) A peer-to-peer architecture for massive multiplayer online games. In: Proceeding 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’06. ACM, New York, pp 48
Chen A, Muntz RR (2006) Peer clustering: a hybrid approach to distributed virtual environments. In: Proceeding 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’06. ACM, New York, p 11
Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S, Oliveira JC (2009) A hybrid p2p communications architecture for zonal mmogs. Multimed Tools Appl 45(1–3):313–345
Tumbde A, Venugopalan S (2004) A voronoi partitioning approach to support massively multiplayer online games. Technical Report CS 740 Project. University of Wisconsin, Madison
Frey D, Royan J, Piegay R, Kermarrec A-M, Anceaume E, Le Fessant F (2008) Solipsis: a decentralized architecture for virtual environments. In: Proceeding the 1st international workshop on massively multiuser virtual environments, MMVE ’08
Denault A, Cañas C, Kienzle J, Kemme B (2011) Triangle-based obstacle-aware load balancing for massively multiplayer games. In: Proceedings of the 10th annual workshop on network and systems support for games, NetGames ’11. IEEE Press, Piscataway, pp 4:1–4:6
Iimura T, Hazeyama H, Kadobayashi Y (2004) Zoned federation of game servers: a peer-to-peer approach to scalable multi-player online games. In: Proceeding ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’04. ACM, New York, pp 116–120
Chan L, Yong J, Bai J, Leong B, Tan R (2007) Hydra: a massively-multiplayer peer-to-peer architecture for the game developer. In: Proceeding the 6th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’07. ACM, New York, pp 37–42
Kim KC, Yeom I, Lee J (2004) HYMS: a hybrid MMOG server architecture. IEICE Trans Inf Syst E87-D(12):2706–2713
Fan L, Taylor H, Trinder P (2007) Mediator: a design framework for P2P MMOGs. In: Proceeding the 6th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’07. ACM, New York, pp 43–48
Botev J, Hohfeld A, Schloss H, Scholtes I, Sturm P, Esch M (2008) The hyperVerse—concepts for a federated and torrent-based ‘3D Web’. Int J Adv Media Commun 2(4):331–350
Kulkarni S (2009) Badumna network suite: a decentralized network engine for massively multiplayer online applications. In: 9th international conference on peer-to-peer computing, IEEE P2P ’09
Rowstron A, Druschel P (2001) Pastry: scalable, distributed object location and routing for large-scale peer-to-peer systems. In: Proceeding IFIP/ACM international conference on distributed systems platforms. Middleware, pp 329–350
Ratnasamy S, Francis P, Handley M, Karp R, Schenker S (2001) A scalable content-addressable network. In: Proceeding the 2001 conference on applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications, SIGCOMM ’01. ACM, New York, pp 161–172
Stoica I, Morris R, Karger D, Kaashoek MF, Balakrishnan H (2001) Chord: a scalable peer-to-peer lookup service for internet applications. In: Proceeding the 2001 conference on applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications, SIGCOMM ’01. ACM, New York, pp 149–160
Tanin E, Harwood A, Samet H, Nayar D, Nutanong S (2006) Building and querying a P2P virtual world. Geoinformatica 10(1):91–116
Bharambe A, Pang J, Seshan S (2006) Colyseus: a distributed architecture for online multiplayer games. In: Proceedings the 3rd conference on networked systems design & implementation, NSDI ’06. USENIX Association, Berkeley, pp 12–12
Hariri B, Shirmohammadi S, Pakravan MR (2008) LOADER: a location-aware distributed virtual environment architecture. In: IEEE conference on virtual environments, human-computer interfaces and measurement systems, VECIMS ’08, pp 97–101
Ratti S, Hariri B, Shirmohammadi S (2008) NL-DHT: a non-uniform locality sensitive DHT architecture for massively multi-user virtual environment applications. In: Proceeding the 2008 14th IEEE international conference on parallel and distributed systems, ICPADS ’08. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 793–798
Castro M, Druschel P, Kermarrec AM, Rowstron AIT (2002) SCRIBE: a large-scale and decentralized application-level multicast infrastructure. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 20(8):1489–1499
Bharambe AR, Agrawal M, Seshan S (2004) Mercury: supporting scalable multi-attribute range queries. SIGCOMM Comput Commun Rev 34(4):353–366
Delaney D, Ward T, McLoone S (2006) On consistency and network latency in distributed interactive applications: a survey–part I. Presence: Teleoper Virtual Environ 15(2):218–234
Lety E, Turletti T, Baccelli F (2004) SCORE: a scalable communication protocol for large-scale virtual environments. IEEE/ACM Trans Networking 12(2):247–260
Frecon E (2004) DIVE: communication architecture and programming model. IEEE Commun Mag 42(4):34–40
de Oliveira JC, Georganas ND (2002) VELVET: an adaptive hybrid architecture for very large virtual environments. In: IEEE international conference on communications, ICC ’02, vol 4, pp 2491–2495
Nguyen CD, Safaei F, Boustead P (2004) Performance evaluation of a proxy system for providing immersive audio communication to massively multi-player games. In: IEEE global telecommunications conference workshops, GlobeCom workshops 2004, pp 192–199
Chu Y-h, Rao SG, Seshan S, Zhang H (2002) A case for end system multicast. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 20(8):1456–1471
Vogel J, Widmer J, Farin D, Mauve M, Effelsberg W (2003) Priority-based distribution trees for application-level multicast. In: Proceeding the 2nd workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ‘03. ACM, New York, pp 148–157
Rooney S, Bauer D, Deydier R (2004) A federated peer-to-peer network game architecture. IEEE Commun Mag 42(5):114–122
Chen F, Kalogeraki V (2005) Adaptive real-time update dissemination in distributed virtual simulation environments. In: Proceeding the eighth IEEE international symposium on object-oriented real-time distributed computing, ISORC ‘05. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 233–236
Singhal SK (2007) Scalable networked virtual environments using unstructured overlays. In: Proceeding the 13th international conference on parallel and distributed systems, ICPADS ’07. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 1–8
Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S, de Oliveira JC (2006) A novel method for supporting massively multi-user virtual environments. In: IEEE international workshop on haptic audio visual environments and their applications, HAVE ’06, pp 72–77
Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S (2010) A fault tolerance procedure for p2p online games. In: 10th international conference, information sciences signal processing and their applications (ISSPA), 2010, pp 614–617
Ito S, Saito H, Sogawa H, Tobe Y (2006) A propagation of virtual space information using a peer-to-peer architecture for massively multiplayer online games. In: 26th IEEE international conference on distributed computing systems workshops, ICDCS workshops 2006, p 44
**ang-bin S, Yue W, Qiang L, Ling D, Fang L (2008) An interest management mechanism based on N-Tree. In: Proceeding the 2008 9th ACIS international conference on software engineering, artificial intelligence, networking, and parallel/distributed computing, SNPD ’08. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 917–922
Lee J, Lee H, Ihm S, Gim T, Junehwa S (2005) APOLO: ad-hoc peer-to-peer overlay network for massively multi-player online games. Technical report cs/tr-2005-248. Korea Advanced Institute Of Science And Technology, (KAIST)
Jiang J-R, Huang Y-L, Hu S-Y (2008) Scalable AOI-cast for peer-to-peer networked virtual environments. In: Proceeding the 28th international conference on distributed computing systems workshops, ICDCSW ’08. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 447–452
Schmieg A, Stieler M, Jeckel S, Kabus P, Kemme B, Buchmann A (2008) pSense - maintaining a dynamic localized peer-to-peer structure for position based multicast in games. In: Proceeding the 2008 eighth international conference on peer-to-peer computing, P2P ’08. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 247–256
Diot C, Levine BN, Lyles B, Kassem H, Balensiefen D (2000) Deployment issues for the IP multicast service and architecture. IEEE Netw 14(1):78–88
Hosseini M, Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S, Georganas ND (2007) A survey of application-layer multicast protocols. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 9(3):58–74
Lao L, Cui J-H, Gerla M, Chen S (2007) A scalable overlay multicast architecture for large-scale applications. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 18:449–459
Steed A, Angus C (2006) Enabling scalability by partitioning virtual environments using frontier sets. Presence: Teleoper Virtual Environ 15(1):77–92
Bharambe A, Douceur JR, Lorch JR, Moscibroda T, Pang J, Seshan S, Zhuang X (2008) Donnybrook: enabling large-scale, high-speed,peer-to-peer games. In: Proceeding the ACM SIGCOMM 2008 conference on data communication, SIGCOMM ’08. ACM, New York, pp 389–400
Steed A, Angus C (2005) Supporting scalable peer to peer virtual environments using frontier sets. In: Proceeding the 2005 IEEE conference 2005 on virtual reality, VR ’05. IEEE Computer Society, pp 27–34
Makbily Y, Gotsman C, Bar-Yehuda R (1999) Geometric algorithms for message filtering in decentralized virtual environments. In: Proceeding the 1999 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics, I3D ’99. ACM, New York, pp 39–46
Goldin A, Gotsman C (2004) Geometric message-filtering protocols for distributed multiagent environments. Presence: Teleoper Virtual Environ. 13(3):279–295
Teller SJ, Séquin CH (1991) Visibility preprocessing for interactive walkthroughs. SIGGRAPH Comput Graph 25(4):61–70
Robson JG, Graham N (1981) Probability summation and regional variation in contrast sensitivity across the visual field. Vis Res 21(3):409–418
Cowan N (2001) The magical number 4 in short-term memory: a reconsideration of mental storage capacity. Behav Brain Sci 24(01):87–114
Manku GS, Naor M, Wieder U (2004) Know thy neighbor’s neighbor: the power of lookahead in randomized P2P networks. In: Proceeding the thirty-sixth annual ACM symposium on theory of computing, STOC ’04. ACM, New York, pp 54–63
Kawahara Y, Morikawa H, Aoyama T (2002) A peer-to-peer message exchange scheme for large scale networked virtual environments. In: Proceeding IEEE international conference on communication systems, ICCS ’02. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 957–961
Chen J-F, Lin W-C, Bai H-S, Dai S-Y (2005) A message interchange protocol based on routing information protocol in a virtual world. In: Proceeding the 19th international conference on advanced information networking and applications, AINA ’05. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 377–384
Kawahara Y, Aoyama T, Morikawa H (2004) A peer-to-peer message exchange scheme for large-scale networked virtual environments. Telecommun Syst 25(3–4):353–370
Matsumoto N, Kawahara Y, Morikawa H, Aoyama T (2004) A scalable and low delay communication scheme for networked virtual environments. In: Proceeding IEEE international workshop on networking issues in multimedia entertainment, NIME ’04, pp 529–535
Hu S-Y, Chen J-F, Chen T-H (2006) VON: a scalable peer-to-peer network for virtual environments. IEEE Netw 20(4):22–31
Backhaus H, Krause S (2009) QuON—a quad-tree based overlay protocol for distributed virtual worlds. In: Proceeding the 2nd international workshop on massively multiuser virtual environments, MMVE ’09.
Keller J, Simon G (2003) Solipsis: a massively multi-participant virtual world. In: Proceeding the international conference on parallel and distributed processing techniques and applications, PDPTA ’03, vol 1. CSREA Press, pp 262–268
Buyukkaya E, Abdallah M (2009) Efficient triangulation for p2p networked virtual environments. Multimedia Tools Appl 45:291–312
Ghaffari M, Hariri B, Shirmohammadi S (2009) A delaunay triangulation architecture supporting churn and user mobility in MMVEs. In: Proceeding the 18th international workshop on network and operating systems support for digital audio and video, NOSSDAV ‘09. ACM, New York, pp 61–66
Yao AC-C (1982) On constructing minimum spanning trees in k-dimensional spaces and related problems. SIAM J Comput 11(4):721–736
Simon G (2004) Conception et réalisation d’un système pour environnement virtuel massivement partagé. PhD thesis, Université de Rennes 1
Keller J, Simon G (2002) Toward a peer-to-peer shared virtual reality. In: Proceeding the 22nd international conference on distributed computing systems, ICDCSW ’02. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 695–700
Hu S-Y, Liao G-M (2004) Scalable peer-to-peer networked virtual environment. In: Proceeding 3rd ACM SIGCOMM workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ‘04. ACM, New York, pp 129–133
Aurenhammer F (1991) Voronoi diagrams–a survey of a fundamental geometric data structure. ACM Comput Surv 23(3):345–405
Shun-Yun Hu (2005) Scalable peer-to-peer networked virtual environment. Master’s thesis, Tamkang University
de Berg M, van Kreveld M, Overmars M, Schwarzkopf O (1997) Computational geometry: algorithms and applications. Springer-Verlag
GauthierDickey C, Zappala D, Lo V, Marr J (2004) Low latency and cheat-proof event ordering for peer-to-peer games. In: Proceeding of the 14th international workshop on Network and operating systems support for digital audio and video, NOSSDAV ’04. ACM, New York, pp 134–139
Chan M-C, Hu S-Y, Jiang J-R (2008) An efficient and secure event signature (eases) protocol for peer-to-peer massively multiplayer online games. Comput Netw 52:1838–1845
Liu H-I, Lo Y-T (2008) Dacap—a distributed anti-cheating peer to peer architecture for massive multiplayer on-line role playing game. In: 8th IEEE international symposium, cluster computing and the grid CCGRID ’08, pp 584–589
Lin Y, Kemme B, Patino-Martinez M, Jimenez-Peris R (2006) Applying database replication to multi-player online games. In: Proceeding of 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, NetGames ’06.ACM, New York
Griwodz C (2002) State replication for multiplayer games. In: Proceedings of the 1st workshop on network and system support for games, NetGames ’02. ACM, New York, pp 29–35
OnLive. http://www.onlive.com/
Gaika. http://www.gaikai.com/
PeerSon. http://www.peerson.net/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buyukkaya, E., Abdallah, M. & Simon, G. A survey of peer-to-peer overlay approaches for networked virtual environments. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 8, 276–300 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-013-0231-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-013-0231-5