Abstract
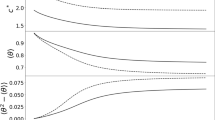
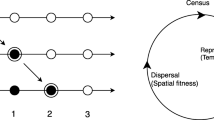
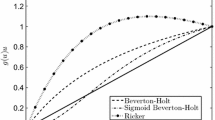
Although past work has considered how evolution and Allee effects each shape population spread, these factors have rarely been considered together. We develop an integrodifference equation model that tracks individuals of multiple dispersal types (i.e., short- and long-distance dispersers) of male and female individuals subject to a strong Allee effect due to mate-finding process. We use our model to explore how mutation between different dispersal types affects the rate of population spread, since this evolutionary mechanism has been shown to lead to both faster and slower spread in a previous individual-based model. We ask, under what conditions does mutation cause the population to spread faster (or slower) than it spreads without mutation (from the same initial conditions)? We find that mutation can both speed up and slow down invasions. Speeding up occurs in a relatively small range of parameter space near the Allee threshold of the population. Slowing down occurs across a broad range of parameters.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Code is available from https://github.com/FrithjofL/LPS_Theoretical_Ecology.
References
Bénichou O, Calvez V, Meunier N, Voituriez R (2012) Front acceleration by dynamic selection in Fisher population waves. Phys Rev E 86(4):041908
Bonte D, Van Dyck H, Bullock JM, Coulon A, Delgado M, Gibbs M, Lehouck V, Matthysen E, Mustin K, Saastamoinen M, Schtickzelle N, Stevens VM, Vandewoestijne S, Baguette M, Barton KA, Benton TG, Chaput-Bardy A, Clobert J, Dytham C, Hovestadt T, Meier CM, Palmer SCF, Turlure C, Travis JMJ (2012) Costs of dispersal. Biol Rev 87(2):290–312
Bouin E, Calvez V (2014) Travelling waves for the cane toads equation with bounded traits. Nonlinearity 27(9):2233
Bouin E, Calvez V, Meunier N, Mirrahimi S, Perthame B, Raoul G, Voituriez R (2012) Invasion fronts with variable motility: phenotype selection, spatial sorting and wave acceleration. CR Math 350(15–16):761–766
Bouin E, Chan MH, Henderson C, Kim PS (2018) Influence of a mortality trade-off on the spreading rate of cane toads fronts. Comm Partial Differential Equations 43(11):1627–1671
Bouin E, Henderson C, Ryzhik L (2017) Super-linear spreading in local and non-local cane toads equations. Journal de mathématiques Pures et Appliquées 108(5):724–750
Bullock JM, Mallada González L, Tamme R, Götzenberger L, White SM, Pärtel M, Hooftman DAP (2017) A synthesis of empirical plant dispersal kernels. J Ecol 105(1):6–19
Burton OJ, Phillips BL, Travis JMJ (2010) Trade-offs and the evolution of life-histories during range expansion. Ecol Lett 13(10):1210–1220
Edmonds CA, Lillie AS, Cavalli-Sforza LL (2004) Mutations arising in the wave front of an expanding population. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(4):975–979
Elliott EC, Cornell SJ (2013) Are anomalous invasion speeds robust to demographic stochasticity? PLoS ONE 8(7):e67871
Gascoigne J, Berec L, Gregory S, Courchamp F (2009) Dangerously few liaisons: a review of mate-finding Allee effects. Popul Ecol 51(3):355–372
Girardin L (2017) Non-cooperative Fisher-KPP systems: traveling waves and long-time behavior. Nonlinearity 31(1):108
Iida M, Lui R, Ninomiya H (2011) Stacked fronts for cooperative systems with equal diffusion coefficients. SIAM J Math Anal 43(3):1369–1389
Keenan VA, Cornell SJ (2021) Anomalous invasion dynamics due to dispersal polymorphism and dispersal-reproduction trade-offs. Proc R Soc B 288(1942):20202825
Korolev KS (2015) Evolution arrests invasions of cooperative populations. Phys Rev Lett 115(20):208104
Kot M, Lewis MA, van den Driessche P (1996) Dispersal data and the spread of invading organisms. Ecology 77(7):2027–2042
Lui R (1989) Biological growth and spread modeled by systems of recursions. I Mathematical theory. Math Biosci 93:269–295
Lutscher F (2019) Integrodifference equations in spatial ecology. Springer
Marculis N, Lui R (2016) Modelling the biological invasion of carcinus maenas (the European green crab). J Biol Dyn 10(1):140–163
Miller TE, Shaw AK, Inouye BD, Neubert MG (2011) Sex-biased dispersal and the speed of two-sex invasions. Am Nat 177(5):549–561
Miller TEX, Angert AL, Brown CD, Lee-Yaw JA, Lewis M, Lutscher F, Marculis NG, Melbourne BA, Shaw AK, Szücs M, Tabares O, Usui T, Weiss-Lehman C, Williams JL (2020) Eco-evolutionary dynamics of range expansion. Ecology 101(10):e03139
Nathan R, Klein E, Robledo-Arnuncio JJ, Revilla E (2012) Dispersal kernels: review. Dispersal ecology and evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 185–248
Perkins AT, Phillips BL, Baskett ML, Hastings A (2013) Evolution of dispersal and life history interact to drive accelerating spread of an invasive species. Ecol Lett 16(8):1079–1087
Phillips BL (2015) Evolutionary processes make invasion speed difficult to predict. Biol Invasions 17(7):1949–1960
Phillips BL, Brown GP, Travis JMJ, Shine R (2008) Reid’s paradox revisited: the evolution of dispersal kernels during range expansion. Am Nat 172:S34–S48
Phillips BL, Brown GP, Webb JK, Shine R (2006) Invasion and the evolution of speed in toads. Nature 439(7078):803
Ramanantoanina A, Ouhinou A, Hui C (2014) Spatial assortment of mixed propagules explains the acceleration of range expansion. PLoS ONE 9(8):e103409
Shaw AK, Kokko H (2015) Dispersal evolution in the presence of Allee effects can speed up or slow down invasions. Am Nat 185(5):631–639
Shaw AK, Kokko H, Neubert MG (2018) Sex difference and Allee effects shape the dynamics of sex-structured invasions. J Anim Ecol 87(1):36–46
Shine R, Brown GP, Phillips BL (2011) An evolutionary process that assembles phenotypes through space rather than through time. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(14):5708–5711
Stephens PA, Sutherland WJ, Freckleton RP (1999) What is the Allee effect? Oikos 87:185–190
Travis JMJ, Dytham C (2002) Dispersal evolution during invasions. Evol Ecol Res 4:1119–1129
Travis JMJ, Mustin K, Benton TG, Dytham C (2009) Accelerating invasion rates result from the evolution of density-dependent dispersal. J Theor Biol 259:151–158
Veit RR, Lewis MA (1996) Dispersal, population growth, and the Allee effect: dynamics of the house finch invasion of eastern North America. Am Nat 148(2):255–274
Wang M-H, Kot M, Neubert MG (2002) Integrodifference equations, Allee effects, and invasions. J Math Biol 44:150–168
Weinberger HF (1982) Long-time behavior of a class of biological models. SIAM J Math Anal 13:353–396
Weinberger H, Lewis M, Li B (2007) Anomalous spreading speeds of cooperative recursion systems. J Math Biol 55:207–222
Williams JL, Snyder RE, Levine JM (2016) The influence of evolution on population spread through patchy landscapes. Am Nat 188(1):15–26
Acknowledgements
FL is grateful for teaching release through the UOttawa–CRM membership agreement (Fall 2020). AKS is grateful for a sabbatical leave from the University of Minnesota to l’Université de Montréal with support from Fulbright Canada.
Funding
FL and LP are funded by Discovery Grants program from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (RGPIN-2016-0495 and RGPIN-2015-06573).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AKS conceived of the topic; FL derived the model and performed the analysis; all authors discussed the results; FL and AKS wrote the initial draft; all authors discussed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All persons entitled to authorship have been so named. The authors have approved the submission of this manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutscher, F., Popovic, L. & Shaw, A.K. How mutation shapes the rate of population spread in the presence of a mate-finding Allee effect. Theor Ecol 16, 255–269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12080-022-00540-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12080-022-00540-2