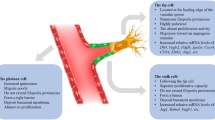
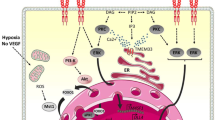
Abstract
Angiogenesis is a critical, fine-tuned, multi-staged biological process. Tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling are the building blocks of sprouting angiogenesis. Accumulated evidences show that tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling are regulated by a variety of physical, chemical and biological factors, especially the interaction among multiple genes, their products and environments. The classic Notch-VEGFR, Slit-Robo, ECM-binding integrin, semaphorin and CCN family play important roles in tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling. In this review, we outline the progress and prospect in the mechanism and the roles of the various molecules and related signaling pathways in endothelial tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling. In the future, the regulators of tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling would be the potential markers and targets for angiogenesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adada MM et al (2015) Intracellular sphingosine kinase 2-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate mediates epidermal growth factor-induced ezrin-radixin-moesin phosphorylation and cancer cell invasion. FASEB J 29(11):4654–4669
Adam MG et al (2013) Synaptojanin-2 binding protein stabilizes the notch ligands DLL1 and DLL4 and inhibits sprouting angiogenesis. Circ Res 113(11):1206–1218
Adams RH, Alitalo K (2007) Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(6):464–478
Basile JR, Gavard J, Gutkind JS (2007) Plexin-B1 utilizes RhoA and rho kinase to promote the integrin-dependent activation of Akt and ERK and endothelial cell motility. J Biol Chem 282(48):34888–34895
Belair DG et al (2016) Human iPSC-derived endothelial cell sprouting assay in synthetic hydrogel arrays. Acta Biomater 39:12–24
Benedito R et al (2012) Notch-dependent VEGFR3 upregulation allows angiogenesis without VEGF-VEGFR2 signalling. Nature 484(7392):110–114
Benn A et al (2017) Role of bone morphogenetic proteins in sprouting angiogenesis: differential BMP receptor-dependent signaling pathways balance stalk vs. tip cell competence. FASEB J 31(11):4720–4733
Bentley K, Gerhardt H, Bates PA (2008) Agent-based simulation of notch-mediated tip cell selection in angiogenic sprout initialisation. J Theor Biol 250(1):25–36
Bentley K et al (2014) The role of differential VE-cadherin dynamics in cell rearrangement during angiogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 16(4):309–321
Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):592–603
Boareto M et al (2015) Jagged mediates differences in normal and tumor angiogenesis by affecting tip-stalk fate decision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(29):E3836–E3844
Brandes RP et al (2016) The cytosolic NADPH oxidase subunit NoxO1 promotes an endothelial stalk cell phenotype. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36(8):1558–1565
Butler GS et al (2017) Degradomic and yeast 2-hybrid inactive catalytic domain substrate trap** identifies new membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP14) substrates: CCN3 (Nov) and CCN5 (WISP2). Matrix Biol 59:23–38
Cantelmo AR, Brajic A, Carmeliet P (2015) Endothelial metabolism driving angiogenesis: emerging concepts and principles. Cancer J 21(4):244–249
Carlier A et al (2012) MOSAIC: a multiscale model of osteogenesis and sprouting angiogenesis with lateral inhibition of endothelial cells. PLoS Comput Biol 8(10):e1002724
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. nature 407(6801):249
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473:298–307
Carmeliet P et al (2009) Branching morphogenesis and antiangiogenesis candidates: tip cells lead the way. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(6):315–326
Carra S et al (2018) Zebrafish Tmem230a cooperates with the Delta/notch signaling pathway to modulate endothelial cell number in angiogenic vessels. J Cell Physiol 233(2):1455–1467
Chen C-C, Lau LF (2009) Functions and mechanisms of action of CCN matricellular proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41(4):771–783
Chen HX, Cleck JN (2009) Adverse effects of anticancer agents that target the VEGF pathway. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(8):465–477
Chintala H et al (2015) The matricellular protein CCN1 controls retinal angiogenesis by targeting VEGF, Src homology 2 domain phosphatase-1 and notch signaling. Development 142(13):2364–2374
Chuang J-Y et al (2015) WISP-1, a novel angiogenic regulator of the CCN family, promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma angiogenesis through VEGF-A expression. Oncotarget 6(6):4239–4252
Costa G et al (2016) Asymmetric division coordinates collective cell migration in angiogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 18(12):1292–1301
Dang LTH et al (2017) Hyperactive FOXO1 results in lack of tip stalk identity and deficient microvascular regeneration during kidney injury. Biomaterials 141:314–329
De Bock K et al (2013) Role of PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in vessel sprouting. Cell 154(3):651–663
De Smet F et al (2009) Mechanisms of vessel branching: filopodia on endothelial tip cells lead the way. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(5):639–649
Delgado VM et al (2011) Modulation of endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis: a novel function for the "tandem-repeat" lectin galectin-8. FASEB J 25(1):242–254
Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM (2000) Akt takes center stage in angiogenesis signaling. Circ Res 86(1):4–5
Eelen G et al (2013) Control of vessel sprouting by genetic and metabolic determinants. Trends Endocrinol Metab 24(12):589–596
Eelen G et al (2018) Endothelial cell metabolism. Physiol Rev 98(1):3–58
Estrach S et al (2011) Laminin-binding integrins induce Dll4 expression and notch signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 109(2):172–182
Fantin A et al (2013) NRP1 acts cell autonomously in endothelium to promote tip cell function during sprouting angiogenesis. Blood 121:2352–2362
Ferrara N (2002) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol 29(6 Suppl 16):10–14
Fischer RS et al (2018) Filopodia and focal adhesions: an integrated system driving branching morphogenesis in neuronal pathfinding and angiogenesis. Dev Biol
Fish JE et al (2017) Dynamic regulation of VEGF-inducible genes by an ERK/ERG/p300 transcriptional network. Development 144(13):2428–2444
Fukushi J-i, Makagiansar IT, Stallcup WB (2004) NG2 proteoglycan promotes endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis via engagement of galectin-3 and α3β1 integrin. Mol Biol Cell 15(8):3580–3590
Gately S, Li WW (2004) Multiple roles of COX-2 in tumor angiogenesis: a target for antiangiogenic therapy. Semin Oncol 31(2 Suppl 7):2–11
Gerhardt H et al (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161(6):1163–1177
Geudens I, Gerhardt H (2011) Coordinating cell behaviour during blood vessel formation. Development 138(21):4569–4583
Gimenez F et al (2015) Robo 4 counteracts angiogenesis in herpetic stromal keratitis. PLoS One 10(12):e0141925
Hellström M, Phng L-K, Gerhardt H (2007) VEGF and notch signaling. Cell Adhes Migr 1(3):133–136
Henrot P et al (2018) CCN proteins as potential actionable targets in scleroderma. Exp Dermatol
Herbert SP, Stainier DYR (2011) Molecular control of endothelial cell behaviour during blood vessel morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:551–564
Huang H et al (2017) Role of glutamine and interlinked asparagine metabolism in vessel formation. EMBO J 36(16):2334–2352
Jakobsson L et al (2010) Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nat Cell Biol 12(10):943–953
Jun JI, Lau LF (2011) Taking aim at the extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(12):945–963
Kangsamaksin T, Tattersall IW, Kitajewski J (2014) Notch functions in developmental and tumour angiogenesis by diverse mechanisms. Biochem Soc Trans 42(6):1563–1568
Kangsamaksin T et al (2015) NOTCH decoys that selectively block DLL/NOTCH or JAG/NOTCH disrupt angiogenesis by unique mechanisms to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Discov 5(2):182–197
Kerbel RS (2008) Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 358(19):2039–2049
Kim B et al (2017) Glutamine fuels proliferation but not migration of endothelial cells. EMBO J 36(16):2321–2333
Kim Y, Stolarska MA, Othmer HG (2011) The role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and invasion. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 106(2):353–379
Kitamura T et al (2008) Regulation of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis by the Akt/PKB substrate Girdin. Nat Cell Biol 10(3):329–337
Koch AW et al (2011) Robo4 maintains vessel integrity and inhibits angiogenesis by interacting with UNC5B. Dev Cell 20(1):33–46
Koch S et al (2014) NRP1 presented in trans to the endothelium arrests VEGFR2 endocytosis, preventing angiogenic signaling and tumor initiation. Dev Cell 28(6):633–646
Kofler NM et al (2011) Notch signaling in developmental and tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cancer 2(12):1106–1116
Kubota S, Takigawa M (2007) CCN family proteins and angiogenesis: from embryo to adulthood. Angiogenesis 10(1):1–11
Lai Y et al (2011) Interleukin-8 induces the endothelial cell migration through the activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Rac1/RhoA pathway. Int J Biol Sci 7(6):782–791
Lamalice L, Le Boeuf F, Huot J (2007) Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ Res 100(6):782–794
Lamont RE et al (2016) The LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Islet2a promotes angioblast migration. Dev Biol 414(2):181–192
Lebrand C et al (2004) Critical role of Ena/VASP proteins for Filopodia formation in neurons and in function downstream of Netrin-1. Neuron 42(1):37–49
Li L et al (2016) Neuropilin-1 is associated with clinicopathology of gastric cancer and contributes to cell proliferation and migration as multifunctional co-receptors. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35(1):16
Lin CF et al (2016) WISP-1 promotes VEGF-C-dependent lymphangiogenesis by inhibiting miR-300 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. in Oncotarget
Lin C-Y et al (2017) WISP-3 inhibition of miR-452 promotes VEGF-A expression in chondrosarcoma cells and induces endothelial progenitor cells angiogenesis. Oncotarget 8(24):39571–39581
Mahabeleshwar GH et al (2007) Mechanisms of integrin–vascular endothelial growth factor receptor cross-activation in angiogenesis. Circ Res 101(6):570–580
Majumder S et al (2016) G-protein-coupled Receptor-2-interacting Protein-1 controls stalk cell fate by Inhibiting Delta-like 4-Notch1 signaling. Cell Rep 17(10):2532–2541
Moya IM et al (2012) Stalk cell phenotype depends on integration of notch and SMAD1/5 signaling cascades. Dev Cell 22(3):501–514
Nagasawa-Masuda A, Terai K (2016) ERK activation in endothelial cells is a novel marker during neovasculogenesis. Genes Cells 21(11):1164–1175
Nedvetsky PI et al (2016) cAMP-dependent protein kinase a (PKA) regulates angiogenesis by modulating tip cell behavior in a notch-independent manner. Development 143(19):3582–3590
Park YS et al (2015) CCN1 secreted by tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes endothelial cell angiogenesis via integrin αvβ3 and AMPK. J Cell Physiol 230(1):140–149
Peghaire C et al (2016) Fzd7 (Frizzled-7) expressed by endothelial cells controls blood vessel formation through Wnt/beta-catenin canonical signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36(12):2369–2380
Pitulescu ME et al (2017) Dll4 and notch signalling couples sprouting angiogenesis and artery formation. Nat Cell Biol 19(8):915–927
Poggio P et al (2011) Osteopontin controls endothelial cell migration in vitro and in excised human valvular tissue from patients with calcific aortic stenosis and controls. J Cell Physiol 226(8):2139–2149
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146(6):873–887
Prokopiou SA et al (2016) Integrative modeling of sprout formation in angiogenesis: coupling the VEGFA-Notch signaling in a dynamic stalk-tip cell selection. ar**v preprint ar**v:1606.02167
Rao G, Du L, Chen Q (2013) Osteopontin, a possible modulator of cancer stem cells and their malignant niche. Oncoimmunology 2(5):e24169
Ravelli C et al (2015) beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by immobilized ligand. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35(10):2161–2171
Ridley AJ et al (2003) Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302(5651):1704–1709
Sainson RC et al (2008) TNF primes endothelial cells for angiogenic sprouting by inducing a tip cell phenotype. Blood 111(10):4997–5007
Schober JM et al (2002) Identification of integrin alpha(M)beta(2) as an adhesion receptor on peripheral blood monocytes for Cyr61 (CCN1) and connective tissue growth factor (CCN2): immediate-early gene products expressed in atherosclerotic lesions. Blood 99(12):4457–4465
Schoors S et al (2015) Fatty acid carbon is essential for dNTP synthesis in endothelial cells. Nature 520(7546):192–197
Segarra M et al (2012) Semaphorin 6A regulates angiogenesis by modulating VEGF signaling. Blood 120(19):4104–4115
Sheldon H et al (2009) Active involvement of Robo1 and Robo4 in filopodia formation and endothelial cell motility mediated via WASP and other actin nucleation-promoting factors. FASEB J 23(2):513–522
Sheng S, Qiao M, Pardee AB (2009) Metastasis and AKT activation. J Cell Physiol 218(3):451–454
Shin M et al (2016) Vegfa signals through ERK to promote angiogenesis, but not artery differentiation. Development 143(20):3796–3805
Sjoqvist M, Andersson ER (2017) Do as I say, Not(ch) as I do: lateral control of cell fate. Dev Biol
So JH et al (2010) Gicerin/Cd146 is involved in zebrafish cardiovascular development and tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cells 15(11):1099–1110
Tamagnone L (2012) Emerging role of semaphorins as major regulatory signals and potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Cancer Cell 22(2):145–152
Tammela T et al (2008) Blocking VEGFR-3 suppresses angiogenic sprouting and vascular network formation. Nature 454:656–660
Tammela T et al (2011) VEGFR-3 controls tip to stalk conversion at vessel fusion sites by reinforcing notch signalling. Nat Cell Biol 13(10):1202–1213
Toomey DP, Murphy JF, Conlon KC (2009) COX-2, VEGF and tumour angiogenesis. Surgeon 7(3):174–180
Tsai H-C et al (2017) WISP-1 positively regulates angiogenesis by controlling VEGF-A expression in human osteosarcoma. Cell Death &Amp; Disease, 8: p. e2750
Venkatraman L, Regan ER, Bentley K (2016) Time to decide? Dynamical analysis predicts partial tip/stalk patterning states Arise during angiogenesis. PLoS One 11(11):e0166489
Weavers H, Skaer H (2014) Tip cells: master regulators of tubulogenesis? Semin Cell Dev Biol 31(100):91–99
Weinstein N et al (2017) A network model to explore the effect of the micro-environment on endothelial cell behavior during angiogenesis. Front Physiol 8:960
Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2011) Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med 17(11):1359–1370
Worzfeld T, Offermanns S (2014) Semaphorins and plexins as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(8):603–621
Xu C et al (2014) Arteries are formed by vein-derived endothelial tip cells. Nat Commun 5:5758
Yang YH et al (2011) Plexin-B1 activates NF-kappaB and IL-8 to promote a pro-angiogenic response in endothelial cells. PLoS One 6(10):e25826
Yokota Y et al (2015) Endothelial ca 2+ oscillations reflect VEGFR signaling-regulated angiogenic capacity in vivo. Elife 4
Yoshikawa M et al (2013) Robo4 is an effective tumor endothelial marker for antibody-drug conjugates based on the rapid isolation of the anti-Robo4 cell-internalizing antibody. Blood 121(14):2804–2813
Zarkada G et al (2015) VEGFR3 does not sustain retinal angiogenesis without VEGFR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(3):761–766
Zecchin A et al (2017) How endothelial cells adapt their metabolism to form vessels in tumors. Front Immunol 8:1750
Zhang F et al (2015) The Matricellular protein Cyr61 is a key mediator of platelet-derived growth factor-induced cell migration. J Biol Chem 290(13):8232–8242
Zhang J, Wu G, Dai H (2016) The matricellular protein CCN1 regulates TNF-α induced vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. Cell Biol Int 40(1):1–6
Zhang X, Groopman JE, Wang JF (2004) Extracellular matrix regulates endothelial functions through interaction of VEGFR-3 and integrin α5β1. J Cell Physiol 202(1):205–214
Zhao X, Guan JL (2011) Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(8):610–615
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31201052, 81802815). We thank Man Lu and Huiyu Li for polishing the manuscript.
Author information
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., **a, P., Wang, H. et al. The endothelial tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling during angiogenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 13, 291–301 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-019-00511-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-019-00511-z