Abstract
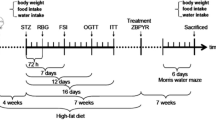
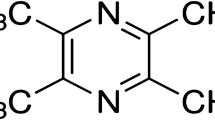
Diabetes mellitus is associated with rapid cognitive decline. Currently, there is no effective treatment for cognitive dysfunction induced by diabetes. l-3-n-Butylphthalide (L-NBP) is a nerve protective drug extracted from seeds of celery, which has been proved to improve learning and memory in vascular dementia animal models by improving microcirculation, protecting mitochondria and increasing long-term potentiation (LTP). NR2B, one of the subunits of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor, has been proved to be an important factor for the formation of LTP. The study aimed to investigate the role of NR2B in cognitive dysfunction in the rats with type 1 diabetes and define the protective effects of L-NBP on cognition. A rat model of type 1 diabetes was established by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin at 60 mg/kg. Animals were randomly allocated to four groups: normal control (NC); diabetic control (DC); diabetic + low L-NBP (DL, administered L-NBP 60 mg/kg per day for 12 weeks); and diabetic + high L-NBP (DH, administered L-NBP 120 mg/kg per day, for 12 weeks). After 12 weeks, cognitive and memory changes were investigated in the Morris water maze. The expression of NR2B was assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. Our results indicated that the escape latency was significantly increased and the number of crossing platform was significantly decreased in DC group compared to NC group. Also, the expression of NR2B was significantly declined in DC group. However, compared to DC group, the expression of NR2B of the L-NBP-treated groups was significantly increased and the escape latency was shortened with the DH group being the most obvious. Therefore, L-NBP can improve the cognitive function by up-regulating the expression of NR2B in STZ-diabetic rats, which may provide the direction for future diabetic encephalopathy therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grzeda, E., & Wiśniewska, R. J. (2008). Differentiations of the effect of NMDA on the spatial learning of rats with 4 and 12 week diabetes mellitus. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentals (Wars), 68(3), 398–406.
Peng, Y., Hu, Y., Xu, S., Li, P., Li, J., Lu, L., et al. (2012). l-3-n-Butylphthalide reduces tau phosphorylation and improves cognitive deficits in AβPP/PS1-Alzheimer’s transgenic mice. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 29(2), 379–391.
Cull-Candy, S. G., & Leszkiewicz, D. N. (2004). Role of distinct NMDA receptor subtypes at Central Synapses. Science STKE (255), re16. [PubMed:15494561].
Kerchner, G. A., & Nicoll, R. A. (2008). Silent synapses and the emergence of a postsynaptic mechanism for LTP. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(11), 813–825.
Cui, Y., **, J., Zhang, X., Xu, H., Yang, L., Du, D., et al. (2011). Forebrain NR2B overexpression facilitating the prefrontal cortex long-term potentiation and enhancing working memory function in mice. PLoS ONE, 6(5), e20312.
Bliss, T. V. (1999). Yong receptors make smart mice. Nature, 40, 25–27.
Akashi, K., Kakizaki, T., Kamiya, H., Fukaya, M., Yamasaki, M., Abe, M., et al. (2009). NMDA receptor GluN2B (GluR epsilon 2/NR2B) subunit is crucial for channel function, postsynaptic macromolecular organization, and actin cytoskeleton at hippocampal CA3 synapses. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 10869–10882.
Clayton, D. A., Mesches, M. H., Alvarez, E., Bickford, P. C., & Browning, M. D. (2002). A hippocampal NR2B deficit can mimic age-related changes in long-term potentiation and spatial learning in the Fischer 344 rat. Journal of Neuroscience, 22, 3628–3637.
Takehara, K., Kawahara, S., Munemoto, Y., Kuriyama, H., Mori, H., Mishina, M., et al. (2004). The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type glutamate receptor GluRepsilon2 is important for delay and trace eyeblink conditioning in mice. Neuroscience Letters, 364, 43–47.
Zhao, M. G., Toyoda, H., Lee, Y. S., Wu, L. J., Ko, S. W., Zhang, X. H., et al. (2005). Roles of NMDA NR2B subtype receptor in prefrontal long-term potentiation and contextual fear memory. Neuron, 47, 859–872.
Nakazawa, T., Komai, S., Watabe, A. M., Kiyama, Y., Fukaya, M., Arima-Yoshida, F., et al. (2006). NR2B tyrosine phosphorylation modulates fear learning as well as amygdaloid synaptic plasticity. EMBO Journal, 25, 2867–2877.
Gardoni, F., Mauceri, D., Malinverno, M., Polli, F., Costa, C., Tozzi, A., et al. (2009). Decreased NR2B subunit synaptic levels cause impaired long-term potentiation but not long-term depression. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 669–677.
Kiyama, Y., Manabe, T., Sakimura, K., Kawakami, F., Mori, H., & Mishina, M. (1998). Increased thresholds for long-term potentiation and contextual learning in mice lacking the NMDA-type glutamate receptor epsilon1 subunit. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(17), 6704–6712.
Tang, Y. P., Shimizu, E., Dube, G. R., Rampon, C., Kerchner, G. A., Zhuo, M., et al. (1999). Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature, 401(6748), 63–69.
Hawasli, A. H., Benavides, D. R., Nguyen, C., Kansy, J. W., Hayashi, K., Chambon, P., et al. (2007). Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation. Nature Neuroscience, 10, 880–886.
Müller, L., Tokay, T., Porath, K., Köhling, R., & Kirschstein, T. (2013). Enhanced NMDA receptor-dependent LTP in the epileptic CA1 area via upregulation of NR2B. Neurobiology of Diseases, 54, 183–193.
Hill, T. C., & Zito, K. (2013). LTP-induced long-term stabilization of individual nascent dendritic spines. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(2), 678–686.
Delibas, N., Altuntas, I., Sutcu, R., Yonden, Z., & Koylu, H. (2004). Effects of dietary long chain PUFAs on hippocampal lipid peroxidation and NMDA receptor subunits A and B concentration in streptozotocin-diabetics rats. International Journal of Neuroscience, 114(10), 1353–1364.
Zhang, T., Jia, W., & Sun, X. (2010). 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) reduces apoptosis and enhances vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) up-regulation in diabetic rats. Neurological Research, 32(4), 390–396.
Peng, Y., Xu, S., Chen, G., Wang, L., Feng, Y., & Wang, X. (2007). L-3-n-Butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 321(3), 902–910.
Vorhees, C. V., & Williams, M. T. (2006). Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nature Protocols, 1(2), 848–58. [PubMed: 17406317].
Malenka, R. C., & Bear, M. F. (2004). LTP and LTD: An embarrassment of riches. Neuron, 44(1), 5–21.
Tsien, J. Z. (2000). Linking Hebb’s coincidence-detection to memory formation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 10(2), 266–273.
Kiraly, D. D., Lemtiri-Chlieh, F., Levine, E. S., Mains, R. E., & Eipper, B. A. (2011). Kalirin binds the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor, altering its synaptic localization and function. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(35), 12554–12565.
Kessels, H. W., Nabavi, S., Malinow, R. (2013). Metabotropic NMDA receptor function is required for β-amyloid-induced synaptic depression. Proceedings of the National Academy Sciences USA, 110(10), 403 3–8. [PubMed: 23431156].
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D., & Traynelis, S. F. (1999). The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacological Reviews, 51(1), 7–61.
Zhuo, M. (2009). Plasticity of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in memory and chronic pain. Molecular Brain, 3(2), 4.
Sacktor, T. C. (2011). How does PKMζ maintain long-term memory? Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(1), 9–15.
Krapivinsky, G., Krapivinsky, L., Manasian, Y., Ivanov, A., Tyzio, R., Pellegrino, C., et al. (2003). The NMDA receptor is coupled to the ERK pathway by a direct interaction between NR2B and Ras GRF1. Neuron, 40(4), 775–784.
Delibas, N., Kilinc, I., Yonden, Z., Sutcu, R., Gultekin, F., & Koylu, H. (2004). NMDA receptor subunits 2A and 2B decrease and lipid peroxidation increase in the hippocampus of streptozotocin-diabetic rats: Effects of insulin and gliclazide treatments. International Journal of Neuroscience, 114(3), 391–401.
Di Luca, M., Ruts, L., Gardoni, F., et al. (1999). NMDA receptor subunits are modified transcriptionally and post-translationally in the brain of streptozotocin-diabetic rats [J]. Diabetologia, 42(6), 693–701.
Gardoni, F., Kamal, A., Bellone, C., et al. (2002). Effects of steptozotocin-diabetes on the hippocampal NMDA receptor complex in rats[J]. Journal of Neurochemistry, 80(3), 438–447.
Xu, H. L., & Feng, Y. P. (2000). Inhibitory effects of chiral 3-n-butylphthalide on inflammation following focal ischemic brain injury in rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 21(5), 433–438.
Dong, G. X., & Feng, Y. P. (2002). Effects of NBP on ATPase and anti-oxidant enzymes activities and lipid peroxidation in transient focal cerebral ischemic rats. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao, 24(1), 93–97.
Chang, Q., & Wang, X. L. (2003). Effects of chiral 3-n-butylphthalide on apoptosis induced by transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 24(8), 796–804.
Peng, Y., Zeng, X., Feng, Y., & Wang, X. (2004). Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activity of L-3-n-butylphthalide in rats. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 43(6), 876–881.
Peng, Y., Sun, J., Hon, S., Nylander, A. N., **a, W., Feng, Y., Wang, X., Lemere, C. A., et al. (2010). L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment and reduces amyloid-beta in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(24), 8180–8189.
Zhang, T., Yan, W., Li, Q., Fu, J., Liu, K., Jia, W., et al. (2011). 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) attenuated neuronal autophagy and amyloid-β expression in diabetic mice subjected to brain ischemia. Neurological Research, 33(4), 396–404.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, S., Zhang, L. et al. Effects of l-3-n-Butylphthalide on Cognitive Dysfunction and NR2B Expression in Hippocampus of Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Diabetic Rats. Cell Biochem Biophys 71, 315–322 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0200-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0200-5