Abstract
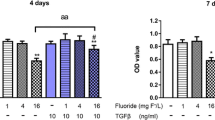
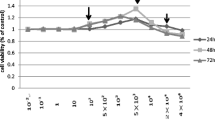
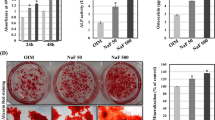
The receptor activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) and its decoy receptor, osteoprotegerin (OPG), are important for maintaining the balance between bone formation and resorption. However, the regulation of microelements on these factors remains unclear. In this study, we used murine osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells to examine the impact of sodium fluoride (NaF) and/or sodium selenite (Na2SeO3) on the OPG/RANKL system. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with OPG or RANKL siRNA (or left untreated), and subsequently divided into a control group and five experimental groups, which were exposed to different concentrations of NaF and/or Na2SeO3, and subsequently analysed at 24 h. In particular, we examined cell viability, OPG and RANKL mRNA and protein expression, caspase-3 activity, and the cell cycle of the various cell groups. In summary, our findings suggest that the administration of NaF and/or Na2SeO3 affects the expression of OPG in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells, thereby contributing to the proliferation and apoptosis induced by the OPG.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gabuda SP, Kozlova AAGSG, Allan NL (2006) Structural forms of fluorides in bone tissue of animals under chronic fluoride intoxication. J Struct Chem 47:258–266
Anuradha CDKS, Hirano S (2001) Oxidative damage to mitochondria is a preliminary step to caspase-3 activation in fluoride-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 31:367–373
Flora SJ, Mittal M, Mishra D (2009) Co-exposure to arsenic and fluoride on oxidative stress, glutathione linked enzymes, biogenic amines and DNA damage in mouse brain. J Neurol Sci 285:198–205
Karube H, Nishitai G, Inageda K, Kurosu H, Matsuoka M (2009) NaF activates MAPKs and induces apoptosis in odontoblast-like cells. J Dent Res 88:461–465
Maleki N, Safavi A, Doroodmand MM (2005) Determination of selenium in water and soil by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry using solid reagents. Talanta 66:858–862
Parfitt AM (2000) The mechanism of coupling: a role for the vasculature. Bone 26:319–323
Hofbauer LC, Khosla S, Dunstan CR, Lacey DL, Boyle WJ, Riggs BL (2000) The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res 15:2–12
Nakashima T, Kobayashi Y, Yamasaki S, Kawakami A, Eguchi K, Sasaki H, Sakai H (2000) Protein expression and functional difference of membrane-bound and soluble receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand: modulation of the expression by osteotropic factors and cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:768–775
Quinn JM, Elliott J, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ (1998) A combination of osteoclast differentiation factor and macrophage-colony stimulating factor is sufficient for both human and mouse osteoclast formation in vitro. Endocrinology 139:4424–4427
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Goto M, Mochizuki SI, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Suda T, Higashio K (1999) A novel molecular mechanism modulating osteoclast differentiation and function. Bone 25:109–113
Buckley KA, Fraser WD (2002) Receptor activator for nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin: regulators of bone physiology and immune responses/potential therapeutic agents and biochemical markers. Ann Clin Biochem 39:551–556
Ren G, Ferreri M, Wang Z, Su Y, Han B, Su J (2011) Sodium fluoride affects proliferation and apoptosis through insulin-like growth factor I receptor in primary cultured mouse osteoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-011-9059-0
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Sher LB, Woitge HW, Adams DJ, Gronowicz GA, Krozowski Z, Harrison JR, Kream BE (2004) Transgenic expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in osteoblasts reveals an anabolic role for endogenous glucocorticoids in bone. Endocrinology 145:922–929
Sun L, Yu F, Xu Z, Zeng X, Ferreri M, Han B (2010) Alteration of osteocalcin mRNA expression in ovine osteoblasts in dependence of sodium fluoride and sodium selenite medium supplementation. Acta Biol Hung 61:52–63
Guan ZZ, **ao KQ, Zeng XY, Long YG, Cheng YH, Jiang SF, Wang YN (2000) Changed cellar membrane lipid composition and prooxidation of kidney in rats with chronic fluorosis. Arch Toxicol 74:602–608
Allan CB, Lacourciere GM, Stadtman TC (1999) Responsiveness of selenoproteins to dietary selenium. Annu Rev Nutr 19:1–16
Kralova V, Brigulova K, Cervinka M, Rudolf E (2009) Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of sodium selenite in human colon cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23:1497–1503
Li L (2003) The biochemistry and physiology of metallic fluoride: action, mechanism, and implications. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 14:100–114
Refsnes M, Schwarze PE, Holme JA, Lag M (2003) Fluoride-induced apoptosis in human epithelial lung cells (A549 cells): role of different G protein-linked signal systems. Hum Exp Toxicol 22:111–123
Saravanapavan P, Jones JR, Verrier S, Beilby R, Shirtliff VJ, Hench LL, Polak JM (2004) Binary CaO-SiO(2) gel-glasses for biomedical applications. Biomed Mater Eng 14:467–486
Mendoza-Schulz A, Solano-Agama C, Arreola-Mendoza L, Reyes-Marquez B, Barbier O, Del Razo LM, Mendoza-Garrido ME (2009) The effects of fluoride on cell migration, cell proliferation, and cell metabolism in GH4C1 pituitary tumour cells. Toxicol Lett 190:179–186
Romanowska M, Kikawa KD, Fields JR, Maciag A, North SL, Shiao YH, Kasprzak KS, Anderson LM (2007) Effects of selenium supplementation on expression of glutathione peroxidase isoforms in cultured human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. Lung Cancer 55:35–42
Zhang M, Wang A, He W, He P, Xu B, **a T, Chen X, Yang K (2007) Effects of fluoride on the expression of NCAM, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Toxicology 236:208–216
Zeng H, Combs GF Jr (2008) Selenium as an anticancer nutrient: roles in cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion. J Nutr Biochem 19:1–7
Humphrey EL, Williams JH, Davie MW, Marshall MJ (2006) Effects of dissociated glucocorticoids on OPG and RANKL in osteoblastic cells. Bone 38:652–661
Li Q, Yu K, Tian X, Kong F, You Y, Chen Z, Zou P (2009) 17beta-Estradiol overcomes human myeloma RPMI8226 cell suppression of growth, ALP activity, and mineralization in rat osteoblasts and improves RANKL/OPG balance in vitro. Leuk Res 33:1266–1271
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Scientific Funds of China (nos. 30571362 and 30972230). We are grateful to Prof. Shi-jun Zheng (Infectious Diseases Lab, CAU) for providing flow cytometry-relevant equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gaixian Ren and Kai Wang contributed equally to this work and share the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, G., Wang, K., Chang, R. et al. Simultaneous Administration of Fluoride and Selenite Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis in Murine Osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 Cells by Altering Osteoprotegerin. Biol Trace Elem Res 144, 1437–1448 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9130-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9130-x