Abstract
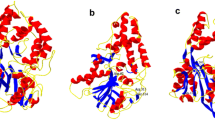
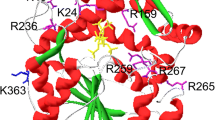
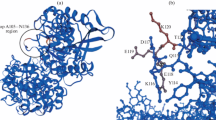
Neutral phytase is used as a feed additive for degradation of anti-nutritional phytate in aquatic feed industry. Site-directed mutagenesis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DSM 1061 phytase was performed with an aim to increase its activity. Mutation residues were chosen based on multiple sequence alignments and structure analysis of neutral phytsaes from different microorganisms. The mutation sites on surface (D148E, S197E and N156E) and around the active site (D52E) of phytase were selected. Analysis of the phytase variants showed that the specific activities of mutants D148E and S197E remarkably increased by about 35 and 13 % over a temperature range of 40–75 °C at pH 7.0, respectively. The k cat of mutants D148E and S197E were 1.50 and 1.25 times than that of the wild-type phytase, respectively. Both D148E and S197E showed much higher thermostability than that of the wild-type phytase. However, mutants N156E and D52E led to significant loss of specific activity of the enzyme. Structural analysis revealed that these mutations may affect conformation of the active site of phytase. The present mutant phytases D148E and S197E with increased activities and thermostabilities have application potential as additives in aquaculture feed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh, B., Kunze, G., & Satyanarayana, T. (2011). Biotechnology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 3, 69–87.
Mukhametzyanova, A. D., Akhmetova, A. I., & Sharipova, M. R. (2012). Microbiology, 3, 267–275.
Fu, S. J., Sun, J. Y., Qian, L. C., & Li, Z. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 151, 1–8.
Li, M., Wang, H., & Bun, N. T. (2013). Protein & Peptide Letters, 20, 459–466.
Nielsen, A. V. F., Tetens, I., & Meyer, A. S. (2013). Nutrients, 5, 3074–3098.
Roy, S., Mehta, A., & Mishra, R. R. (2013). Vegetos, 26, 83–87.
Cheng, W., Chiu, C. S., & Guu, Y. K. (2013). Aquaculture Nutrition, 19, 117–127.
Akhmetova, A. I., Nyamsuren, C. H., Balaban, N. P., & Sharipova, M. R. (2013). Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, 39, 384–389.
Park, I., Lee, J., & Cho, J. (2012). Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 25, 1466–1472.
Fei, B., Xu, H., Cao, Y. U., Ma, S., Guo, H., Song, T., Qiao, D., & Cao, Y. J. (2013). Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 40, 457–464.
Mullaney, E. J., Daly, C. B., Kim, T., & Sethumadhavan, K. (2002). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 297, 1016–1020.
Shimizu, M. (1993). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 12, 1364–1368.
Kim, M. S., Weaver, J. D., & Lei, X. G. (2008). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 79, 751–758.
Bei, J., Chen, Z., & Fu, J. (2009). Journal of Biotechnology, 139, 186–193.
Zhang, W., & Lei, X. G. (2008). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77, 1033–1040.
Yao, M. Z., Lu, W. L., Chen, T. G., Wang, W., Fu, Y. J., Yang, B. S., & Liang, A. H. (2014). Annals of Microbiology, 64, 1123–1131.
Kim, Y. O., Kim, H. K., & Bac, K. S. (1998). Enzyme Microbiological Technology, 12, 45–48.
Powar, V. K., & Jagannathan, V. (1982). Journal of Bacteriology, 151, 1102–1108.
Choi, Y. M., Suh, H. J., & Kim, J. M. (2001). Protein Chemistry, 143, 231–235.
Farhat, A., Chouayekh, H., & Ben, F. M. (2008). Molecular Biotechnology, 40, 127–135.
Hmida-Sayari, A., Elgharbi, F., Farhat, A., Rekik, H., Blondeau, K., & Bejar, S. (2014). Molecular Biotechnology, 56, 839–848.
Borgi, M. A., Khila, M., Boudebbouze, S., Aghajari, N., Szukala, F., Pons, N., Maguin, E., & Rhimi, M. (2014). Applied Mcrobiology and Biotechnology, 98, 5937–5947.
Belgaroui, N., Zaidi, I., Farhat, A., Chouayekh, H., Bouain, N., Chay, S., Curie, C., Mari, S., Masmoudi, K., Davidian, J. C., Berthomieu, P., Rouached, H., & Hanin, M. (2014). Plant Cell Physiology, 55, 1912–1924.
Tran, T. T., Mamo, G., & Mattiasson, B. (2010). Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 143, 231–235.
Yu, P., & Chen, Y. (2013). BMC Biotechnology, 13, 78–85.
Li, Z., Zhao, A., Wang, X., **, X., Li, J., & Yu, M. (2013). Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 23, 193–202.
Miao, Y., Xu, H., Fei, B., Qiao, D., & Cao, Y. (2013). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 116, 34–38.
Vinod, K., Punesh, S., Verma, A. K., & Agrawal, S. (2014). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173, 646–659.
Viader-Salvado, J. M., Castillo-Galvan, M., & Fuentes-Garibay, J. A. (2013). Biotechnology Progress, 29, 1377–1385.
Guerrero-Olazarán, M., Rodríguez-Blanco, L., Carreon-Treviño, J. G., Gallegos-López, J. A., & Viader-Salvadó, J. M. (2010). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 5601–5608.
Blum, J. K., Ricketts, M. D., & Bommarius, A. S. (2012). Journal of Biotechnology, 160, 214–221.
Xu, W., Yan, M., Xu, L., Ding, L., & Ouyang, P. (2009). Enzyme Microbiological Technology, 44, 77–83.
Siloto, R. M. P., & Weselake, R. J. (2012). Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 1, 181–189.
Xu, W., Cai, P., Yan, M., Xu, L., & Ouyang, P. (2009). Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 22, 467–472.
Oh, B. C., Chang, B. S., & Park, K. H. (2001). Biochemistry, 40, 9669–9676.
Tung, E. T., Ma, H. W., & Cheng, C. (2008). Protein and Peptide Letters, 15, 297–299.
Viader-Salvadó, J. M., Gallegos-López, J. A., Carreón-Trevino, J. G., Castillo-Galván, M., Rojo-Domnguez, A., & Guerrero-Olazarn, M. (2010). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 6423–6430.
Farhat-Khemakhem, A., Ben, A. M., & Boukhris, I. (2013). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 54, 9–15.
Tran, T. T., Mamo, G., Búxo, L., Le, N. N., Gaber, Y., Mattiasson, B., & Hatti-Kaul, R. (2011). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 49, 177–182.
Farias, S. T., & Bonato, M. C. M. (2002). Genome Biology, 3, 1–18.
Kumwenda, B., Litthauer, D., Bishop, Ö. T., & Reva, O. (2013). Evolutionary Bioinformatics, 9, 327–342.
Lu, G., Xu, W., Shao, R., & Yun, Z. (2012). China Biotechnology, 33, 153–156.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
King, E. J. (1932). Biochemical Journal, 26, 292–297.
Guex, N., Diemand, A., & Peitsch, M. C. (1999). Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 24, 364–367.
Sayle, R. A., & Milner-White, E. J. (1995). Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 20, 374–376.
Lu, B. S., Wang, G. L., & Huang, P. T. (1998). Acta Microbiologia Sinca, 1, 20–28.
Böttcher, D., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2010). Current Opinion in Microbiology, 3, 274–282.
Shin, S., Ha, N. C., & Oh, B. C. (2001). Structure, 9, 851–858.
Zhang, R., Yang, P., Huang, H., Yuan, T., Shi, P., Meng, K., & Yao, B. (2011). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 92, 317–325.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31101912), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (No. BK2011420), and Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Shao, R., Wang, Z. et al. Improving the Neutral Phytase Activity from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DSM 1061 by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 3184–3194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1495-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1495-4