Abstract
Xylose mother liquor (XML) is a by-product of xylose production through acid hydrolysis from corncobs, which can be used potentially for alternative fermentation feedstock. Sixteen Clostridia including 13 wild-type, 1 industrial strain, and 2 genetically engineered strains were screened in XML, among which the industrial strain Clostridium acetobutylicum EA 2018 showed the highest titer of solvents (12.7 g/L) among non-genetic populations, whereas only 40 % of the xylose was consumed. An engineered strain (2018glcG-TBA) obtained by combination of glcG disruption and expression of the d-xylose proton-symporter, d-xylose isomerase, and xylulokinase was able to completely utilize glucose and l-arabinose, and 88 % xylose in XML. The 2018glcG-TBA produced total solvents up to 21 g/L with a 50 % enhancement of total solvent yield (0.33 g/g sugar) compared to that of EA 2018 (0.21 g/g sugar) in XML. This XML-based acetone–butanol–ethanol fermentation using recombinant 2018glcG-TBA was estimated to be economically promising for future production of solvents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiao, J. S., & Sun, Z. H. (2007). Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 13(1–3), 12–14.
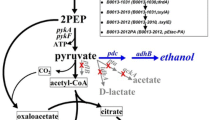
Gu, Y., Jiang, Y., Wu, H., Liu, X., Li, Z., Li, J., **ao, H., Shen, Z., Dong, H., Yang, Y., Li, Y., Jiang, W., & Yang, S. (2011). Biotechnol. J., 6(11), 1348–1357.
Ni, Y., & Sun, Z. (2009). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 83(3), 415–423.
**ao, H., Li, Z., Jiang, Y., Yang, Y., Jiang, W., Gu, Y., & Yang, S. (2012). Metabolic Engineering, 14(5), 569–578.
Zhang, W. L., Liu, Z. Y., Liu, Z., & Li, F. L. (2012). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 55(3), 240–246.
Cheng, H., Wang, B., Lv, J., Jiang, M., Lin, S., and Deng, Z., 2011. Microbial Cell Factories, 10: p. 5.
Carter, B., Gilcrease, P. C., & Menkhaus, T. J. (2011). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108(9), 2046–2052.
Keating, J. D., Panganiban, C., & Mansfield, S. D. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 93(6), 1196–1206.
Rao, R. S., Jyothi Ch, P., Prakasham, R. S., Sarma, P. N., & Rao, L. V. (2006). Bioresource Technology, 97(15), 1974–1978.
Wierckx, N., Koopman, F., Bandounas, L., de Winde, J. H., & Ruijssenaars, H. J. (2010). Microbial Biotechnology, 3(3), 336–343.
Ezeji, T., & Blaschek, H. P. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99(12), 5232–5242.
Ezeji, T., Qureshi, N., & Blaschek, H. P. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 97(6), 1460–1469.
Ren, C., Gu, Y., Hu, S., Wu, Y., Wang, P., Yang, Y., Yang, C., Yang, S., & Jiang, W. (2010). Metabolic Engineering, 12(5), 446–454.
**ao, H., Gu, Y., Ning, Y., Yang, Y., Mitchell, W. J., Jiang, W., & Yang, S. (2011). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(22), 7886–7895.
Wiesenborn, D. P., Rudolph, F. B., & Papoutsakis, E. T. (1988). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54(11), 2717–2722.
Baer, S. H., Blaschek, H. P., & Smith, T. L. (1987). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 53(12), 2854–2861.
Mermelstein, L. D., & Papoutsakis, E. T. (1993). In vivo methylation in Escherichia coli by the Bacillus subtilis phage phi 3T I methyltransferase to protect plasmids from restriction upon transformation of Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59(4), 1077–1081.
Chambel, P., Oliveira, M., Andrade, P., Seabra, R., & Ferreira, M. (1997). Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 20(18), 2949–2957.
Ounine, K., Petitdemange, H., Raval, G., & Gay, R. (1985). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 49(4), 874–878.
Hu, S.Y., Zheng, H.J., Gu, Y., Zhao, J.B., Zhang, W.W., Yang, Y.L., Wang, S.Y., Zhao, G.P., Yang, S., and Jiang, W.H., 2011. BMC Genomics, 12
Gosseringer, R., Kuster, E., Galinier, A., Deutscher, J., & Hillen, W. (1997). Journal of Molecular Biology, 266(4), 665–676.
Dahl, M. K., & Hillen, W. (1995). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 132(1–2), 79–83.
Dahl, M. K., Schmiedel, D., & Hillen, W. (1995). Journal of Bacteriology, 177(19), 5467–5472.
Schmiedel, D., & Hillen, W. (1996). Molecular and General Genetics, 250(3), 259–266.
Heap, J. T., Pennington, O. J., Cartman, S. T., & Minton, N. P. (2009). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 78, 79–85.
Jiang, Y., Xu, C., Dong, F., Yang, Y., Jiang, W., & Yang, S. (2009). Metabolic Engineering, 11(4–5), 284–291.
Han, B., Ujor, V., Lai, L. B., Gopalan, V., & Ezehi, T. C. (2013). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(1), 282–293.
Li, J., Zhao, J. B., Zhao, M., Yang, Y. L., Jiang, W. H., & Yang, S. (2010). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 50(4), 373–379.
Kuyper, M., Toirkens, M. J., Diderich, J. A., Winkler, A. A., van Dijken, J. P., & Pronk, J. T. (2005). FEMS Yeast Research, 5(10), 925–934.
Shao, L., Hu, S., Yang, Y., Gu, Y., Chen, J., Yang, Y., Jiang, W., & Yang, S. (2007). Cell Research, 17(11), 963–965.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270140), the Knowledge Innovation Program of Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences(2012KIP509), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2012BAD32B07, 2011AA02A208, and 2012CB721105), and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-EW-J-12, KSCX2-EW-G-13-5, and KSCX2-EW-G-1). We thank Eleftherios T. Papoutsakis (University of Delaware, Newark, USA) for offering plasmids pIMP1-Pptb and Shandong Longlive Bio-technology Co. Ltd. for providing xylose mother liquor. Dr. Yu Jiang gratefully acknowledges the support of SA-SIBS Scholarship Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhin Li and Han **ao contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
(DOC 568 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., **ao, H., Jiang, W. et al. Improvement of Solvent Production from Xylose Mother Liquor by Engineering the Xylose Metabolic Pathway in Clostridium acetobutylicum EA 2018. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171, 555–568 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0414-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0414-9



