Abstract
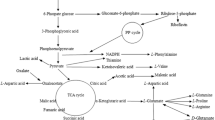
Bacillus subtilis NX-2 produces γ-polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA) when using glucose and l-glutamate as carbon sources. The conversion of carbon sources into γ-PGA was analyzed with the 13C-NMR method after enriching the media with 13C-labeled glucose. The results showed that the percentage of γ-PGA monomers derived from glucose was relatively low, approximately 6% and 9%, respectively, with an initial glucose concentration of 30 and 40 g L−1. It was concluded that glucose was utilized mainly as the growth-limiting substrate for cell growth and supplied the required energy during γ-PGA biosynthesis, while l-glutamate was preferred as the main substrate for γ-PGA formation. To achieve an efficient conversion of l-glutamate and enhance the γ-PGA production, a fed-batch culture was proposed by feeding of glucose. By this method, supplied l-glutamate (40 g L−1) was completely depleted, and γ-PGA yield was attained 42 g L−1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shih, L., & Van, Y. T. (2001). Bioresource Technology, 79, 207–225.
Sun, M. H., Park, C., Kim, C. J., et al. (2005). The Chemical Record, 5, 352–366.
Goto, A., & Kunioka, M. (1992). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 56, 1031–1035.
Gregory, A., Birre, Cromwick, A. M., & Cross, R. A. (1994). International Journal of Macromolecules, 16, 265–274.
Kunioka, M. (1995). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 44, 501–506.
Cromwick, A. M., & Gross, R. A. (1995). Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 41, 902–909.
Cromwick, A. M., Gregory, A., Birrer, & Gross, R. A. (1996). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 50, 222–227.
Young, H. K., & Gross, R. A. (1998). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 57, 430–437.
Xu, H., Jiang, M., Li, H., et al. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 519–523.
Wu, Q., Xu, H., Xu, L., & Ouyang, P. K. (2006). Process Biochemistry, 41, 1650–1655.
Yao, J., Xu, H., Wang, J., & Ouyang, P. K. (2007). Journal of Biomaterials Science. Polymer ed., 18, 193–204.
Sonntag, & Eggeling, K. (1993). European Journal of Biochemistry, 213, 1325–1331.
Karsten, S., & Nørregaard, C. (1999). Lars Metabolic Engineering, 1, 166–179.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Fundamental Research Program (973) of China (2007CB714304), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2006AA03Z453), the Nature Science Foundation of China (20674308) and the High Technology Research of Jiangsu Province (BG20055042), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2009357), Jiangsu Province Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 0901011C), the College Nature Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (09KJB530007) and the Science Foundation of Nan**g Medical University (08NMUZ007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, J., Xu, H., Shi, N. et al. Analysis of Carbon Metabolism and Improvement of γ-Polyglutamic Acid Production from Bacillus subtilis NX-2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 2332–2341 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8798-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8798-2