Abstract
Background
Groin pain after total hip arthroplasty (THA) or total hip resurfacing arthroplasty can be troubling for patients and surgeons. Potential sources of pain include infection, loosening, metal hypersensitivity, or im**ement of bony structures or the iliopsoas tendon.
Questions/purposes
We compared the rate of groin pain after THA or hip resurfacing using metal-on-metal to those of other bearing surfaces.
Methods
We identified 347 (334 patients) primary total hip (n = 301) or resurfacing (n = 46) arthroplasties. Complete preoperative, operative, and postoperative data were available for 282 hips. We retrospectively reviewed the charts for the presence or absence of groin pain at a minimum of 1 year after surgery with a specific focus on etiologic factors. The minimum followup was 12 months (mean, 14 months; range 12 to 24 months).
Results
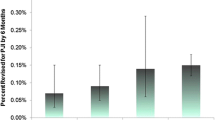
The rate of groin pain was 7% (15 of 217 patients) after THA with conventional bearing surfaces, 15% (4 of 26 patients) with metal-on-metal THA and 18% (7 of 39 patients) with total hip resurfacing. Younger patients were more likely to report groin pain postoperatively and more likely to have metal-on-metal bearing surfaces.
Conclusions
Our data at short-term followup suggest increased rates of groin pain after metal-on-metal THA or resurfacing arthroplasty versus THA using polyethylene or ceramic bearing surfaces. The reasons are not clear but they appear to be associated with younger age. Potential factors include im**ement, activity level and possibly higher expectations for patients receiving metal-on-metal bearing surfaces that may make those patients more likely to report postoperative pain.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ala Eddine T, Remy F, Chantelot C, Giraud F, Migaud H, Duquennoy A. Anterior iliopsoas im**ement after total hip arthroplasty: diagnosis and conservative treatment in 9 cases [in French]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Mot. 2001;87:815–819.
Beaulé PE, Harvey N, Zaragoza E, Le Duff MJ, Dorey FJ. The femoral head/neck offset and hip resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:9–15.
Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, Ong K, Chiu V, Vail TP, Rubash HE, Berry DJ. The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:1614–1620.
Brand RA, Yoder SA, Pedersen DR. Interobserver variability in interpreting radiographic lucencies about total hip reconstructions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;192:237–239.
Cyteval C, Sarrabère MP, Cottin A, Assi C, Morcos L, Maury P, Taourel P. Iliopsoas im**ement on the acetabular component: radiological and computed tomography findings of a rare hip prosthesis complication in eight patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003;27:183–188.
Davies AP, Willert HG, Campbell PA, Learmouth ID, Case CP. An unusual lymphocytic perivascular infiltration in tissues around contemporary metal-on-metal joint replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:18–27.
DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;121:20–32.
Dora C, Houweling M, Koch P, Sierra RJ. Iliopsoas im**ement after total hip replacement: the results of non-operative management, tenotomy or acetabular revision. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:1031–1035.
Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. Modes of failure of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiologic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;141:17–27.
Harris WH. Wear and periprosthetic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;393:66–70.
Heaton K, Dorr LD. Surgical release of iliopsoas tendon for groin pain after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:779–781.
Jasani V, Richards P, Wynn-Jones C. Pain related to the psoas muscle after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:991–993.
Kinkel S, Wollmerstedt N, Kleinhans JA, Hendrich C, Heisel C. Patient activity after total hip arthroplasty declines with advancing age. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:2053–2058.
Korovessis P, Petsinis G, Repanti M, Repantis T. Metallosis after contemporary metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. Five to nine-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1183–1191.
Lavigne M, Rama KR, Roy A, Vendittoli PA. Painful im**ement of the hip joint after total hip resurfacing: a report of two cases. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:1074–1079.
Malchau H, Herberts P, Eisler T, Garellick G, Soderman P. The Swedish Total Hip Replacement Register. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(Suppl 2):2–20.
Nasser AB, Beaule PE, O’Neill ME, Kim PR, Fazekas A. Incidence of groin pain after metal on metal hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:392–399.
Nikolaou V, Bergeron SG, Huk OL, Zukor DJ, Antoniou J. Evaluation of persistent pain after hip resurfacing. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67:168-172.
Oparaugo PC, Clarke IC, Malchau H, Herberts P. Correlation of wear debris-induced osteolysis and revision with volumetric wear-rates of polyethylene—a survey of 8 reports in the literature. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72:22–28.
O’Sullivan M, Tai CC, Richards S, Skyrme AD, Walter WL, Walter WK. Iliopsoas Tendonitis. A complication after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:166–170.
Pandit H, Vlychou M, Whitwell D, Crook D, Luqmani R, Ostlere S, Murray DW, Athanasou NA. Necrotic granulomatous pseudotumors in bilateral resurfacing hip arthroplasties: evidence for a type IV immune response. Virchows Arch. 2008;453:529–534.
Sochard DH. Relationship of acetabular wear to osteolysis and loosening in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;363:135–150.
Taher RT, Power RA. Iliopsoas tendon dysfunction as a cause of pain after total hip arthroplasty relieved by surgical release. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18:387–388.
Temmerman OPP, Raijmakers PGHM, David EFL, Pijpers R, Molenaar MA, Hoekstra OS, Berkhof J, Manoliu RA, Teule GJJ, Heyligers IC. A comparison of radiographic and scintigraphic techniques to assess aseptic loosening of the acetabular component in a total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:2456–2463.
Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME, Berry DJ. Anterior iliopsoas im**ement after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10:546–549.
Valle CJD, Rafii M, Jaffe WL. Iliopsoas tendinitis after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:923–926.
Willert HG, Buchhorn GH, Fayyazi A, Flury R, Windler M, Koster G, Lohmann CH. Metal-on-metal bearings and hypersensitivity in patients with artificial hip joints. A clinical histomorphological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:28–36.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dirk Larson, MS for assistance with statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (RTT, RJS) has received funding from DePuy, Wright Medical Technologies, or Biomet. The institution of the authors has received funding from DePuy, Zimmer and Stryker. Each author certifies that he or she has or may receive payments or benefits from a commercial entity related to this work.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
Appendices
Appendix 1


Appendix 2



About this article
Cite this article
Bartelt, R.B., Yuan, B.J., Trousdale, R.T. et al. The Prevalence of Groin Pain After Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty and Total Hip Resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 2346–2356 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1356-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1356-y