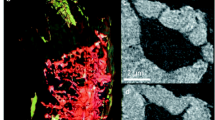
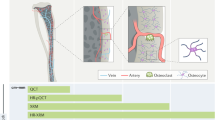
Abstract
Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT)—a version of X-ray CT operating at high spatial resolution—has had a considerable success for the investigation of trabecular bone micro-architecture. Currently, there is a lot of interest in exploiting CT techniques at even higher spatial resolutions to assess bone tissue at the cellular scale. After recalling the basic principles of micro-CT, we review the different existing system, based on either standard X-ray tubes or synchrotron sources. Then, we present recent applications of micro- and nano-CT for the analysis of osteocyte lacunae and the lacunar-canalicular network. We also address the question of the quantification of bone ultrastructure to go beyond the sole visualization.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Seeman E. Bone quality: the material and structural basis of bone strength. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26:1–8.
Compston J. Bone quality: what is it and how is it measured? Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2006;50:579–85.
Nijweide PJ, Burger EH, Klein Nulend J. The Osteocyte [Internet]. Academic Press; 2002 [Accessed March 31, 2009]. Available at: http://dare.uva.nl/record/103838.
Knothe Tate ML, Adamson JR, Tami AE, Bauer TW. The osteocyte. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1–8.
Klein-Nulend J, Bacabac RG, Mullender MG. Mechanobiology of bone tissue. Pathol Biol. 2005;53:576–80.
Bonewald LF. Mechanosensation and transduction in osteocytes. Bonekey Osteovision. 2006;3:7–15.
Burger EH, Klein-Nulend J. Mechanotransduction in bone—role of the lacuno-canalicular network. FASEB J. 1999;13:101–12.
Hazenberg JG, Freeley M, Foran E, Lee TC, Taylor D. Microdamage: a cell transducing mechanism based on ruptured osteocyte processes. J Biomech. 2006;39:2096–103.
Taylor D, Hazenberg JG, Lee TC. Living with cracks: damage and repair in human bone. Nat Mater. 2007;6:263–8.
Rochefort GY, Pallu S, Benhamou CL. Osteocyte: the unrecognized side of bone tissue. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21:1457–69.
Bonewald LF. The amazing osteocyte. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:229–38.
Bonewald LF, Kneissel M, Johnson M. Preface: the osteocyte. Bone. 2013;54:181.
Klein-Nulend J, Bakker AD, Bacabac RG, Vatsa A, Weinbaum S. Mechanosensation and transduction in osteocytes. Bone. 2013;54:182–90.
Kalajzic I, Matthews BG, Torreggiani E, Harris MA, Divieti Pajevic P, Harris SE. In vitro and in vivo approaches to study osteocyte biology. Bone. 2013;54:296–306.
Seeman E. Osteocytes—martyrs for integrity of bone strength. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17:1443–8.
Canè V, Marotti G, Volpi G, Zaffe D, Palazzini S, Remaggi F, et al. Size and density of osteocyte lacunae in different regions of long bones. Calcif Tissue Int. 1982;34:558–63.
Marotti G, Ferretti M, Remaggi F, Palumbo C. Quantitative evaluation on osteocyte canalicular density in human secondary osteons. Bone. 1995;16:125–8.
Marotti G. Osteocyte orientation in human lamellar bone and its relevance to the morphometry of periosteocytic lacunae. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res. 1979;1(4):325–33.
Marotti G, Ferretti M, Palumbo C. The problem of bone lamellation: an attempt to explain different proposed models. J Morphol. 2013;274:543–50.
Mullender MG, van der Meer DD, Huiskes R, Lips P. Osteocyte density changes in aging and osteoporosis. Bone. 1996;18:109–13.
Schneider P, Meier M, Wepf R, Müller R. Towards quantitative 3D imaging of the osteocyte lacuno-canalicular network. Bone. 2010;47:848–58. Highlights the need and possible solutions for the investigation of the lacuno-canalicular network in 3D.
Cardoso L, Fritton SP, Gailani G, Benalla M, Cowin SC. Advances in assessment of bone porosity, permeability and interstitial fluid flow. J Biomech. 2013;46:253–65.
Jones CW, Smolinski D, Keogh A, Kirk TB, Zheng MH. Confocal laser scanning microscopy in orthopaedic research. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2005;40:1–71.
Sugawara Y, Kamioka H, Honjo T, Tezuka K, Takano-Yamamoto T. Three-dimensional reconstruction of chick calvarial osteocytes and their cell processes using confocal microscopy. Bone. 2005;36:877–83.
Kamioka H, Honjo T, Takano-Yamamoto T. A three-dimensional distribution of osteocyte processes revealed by the combination of confocal laser scanning microscopy and differential interference contrast microscopy. Bone. 2001;28:145–9.
McCreadie BR, Hollister SJ, Schaffler MB, Goldstein SA. Osteocyte lacuna size and shape in women with and without osteoporotic fracture. J Biomech. 2004;37:563–72.
Tonar Z, Khadang I, Fiala P, Nedorost L, Kochová P. Quantification of compact bone microporosities in the basal and alveolar portions of the human mandible using osteocyte lacunar density and area fraction of vascular canals. Ann Anat. 2011;193:211–9.
Sugawara Y, Ando R, Kamioka H, Ishihara Y, Honjo T, Kawanabe N, et al. The three-dimensional morphometry and cell-cell communication of the osteocyte network in chick and mouse embryonic calvaria. Calcif Tissue Int. 2011;88:416–24.
Kamioka H, Kameo Y, Imai Y, Bakker AD, Bacabac RG, Yamada N, et al. Microscale fluid flow analysis in a human osteocyte canaliculus using a realistic high-resolution image-based three-dimensional model. Integr Biol (Camb). 2012;4:1198–206.
Kerschnitzki M, Kollmannsberger P, Burghammer M, Duda GN, Weinkamer R, Wagermaier W, et al. Architecture of the osteocyte network correlates with bone material quality. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28:1837–45. Highlights the role of osteocytes in bone homeostasis.
Sharma D, Ciani C, Marin PAR, Levy JD, Doty SB, Fritton SP. Alterations in the osteocyte lacunar—canalicular microenvironment due to estrogen deficiency. Bone. 2012;51:488–97.
Schneider P, Meier M, Wepf R, Müller R. Serial FIB/SEM imaging for quantitative 3D assessment of the osteocyte lacuno-canalicular network. Bone. 2011;49:304–11.
Muller R. Hierarchical microimaging of bone structure and function. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5:373–81.
Bousson V, Peyrin F, Bergot C, Hausard M, Sautet A, Laredo JD. Cortical bone of the human femoral neck : three-dimensional appearance and porosity using synchrotron radiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19:794–801.
Cooper DM, Thomas CD, Clement JG, Hallgrímsson B. Three-dimensional microcomputed tomography imaging of basic multicellular unit-related resorption spaces in human cortical bone. Anat Rec A: Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2006;288:806–16.
Boutroy S, Bouxsein ML, Munoz F, Delmas PD. In vivo assessment of trabecular bone microarchitecture by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:6508–15.
Rüegsegger P, Koller B, Müller R. A microtomographic system for the nondestructive evaluation of bone architecture. Calcif Tissue Int. 1996;58:24–9.
Feldkamp LA, Davis LC, Kress JW. Practical cone-beam algorithm. J Opt Soc Am. 1984;1:612–9.
Engelke K, Graeff W, Meiss L, Hahn M, Delling G. High spatial resolution imaging of bone mineral using computed microtomography. Comparison with microradiography and undecalcified histologic sections. Investig Radiol. 1993;28:341–9.
Salome M, Peyrin F, Cloetens P, Odet C, Laval-Jeantet A, Baruchel J, et al. A synchrotron radiation microtomography system for the analysis of trabecular bone samples. Med Phys. 1999;26:2194–204.
Nuzzo S, Peyrin F, Cloetens P, Baruchel J, Boivin G. Quantification of the degree of mineralization of bone in three dimension using Synchrotron Radiation Microtomography. Med Phys. 2002;19:2672–81.
Nuzzo S, Peyrin F, Martín-Badosa E, Lafage-Proust MH, Boivin G. Quantitative analysis of mineral bone variation in 3D synchrotron radiation microtomography images. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:760–8.
Martin-Badosa E, Amblard D, Nuzzo S, Elmoutaouakkil A, Vico L, Peyrin F. Excised bone structures in mice: imaging at three-dimensional synchrotron radiation micro CT. Radiology. 2003;229:921–8.
Peter Z, Bousson V, Bergot C, Peyrin F. A constrained region growing approach based on watershed for the segmentation of low contrast structures in bone micro-CT. Pattern Recogn. 2008;41:2358–68.
Cooper DML, Erickson B, Peele AG, Hannah K, Thomas CDL, Clement JG. Visualization of 3D osteon morphology by synchrotron radiation micro‐CT. J Anat. 2011;219:481–9.
Weitkamp T, Tafforeau P, Boller E, Cloetens P, Valade J-P, Bernard P, et al. Parallel-beam imaging at the ESRF beamline ID19: current status and plans for the future. Melbourne (Australia); 2010 [Accessed August 19, 2011]. p. 83–6. Available at: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010AIPC.1234.83W.
Cloetens P, Pateyron M, Buffière JY, Peix G, Baruchel J, Peyrin F, et al. Observation of microstructure and damage in materials by phase sensitive radiography and tomography. J Appl Phys. 1997;81:5878–86.
Langer M, Cloetens P, Guigay JP, Peyrin F. Quantitative comparison of direct phase retrieval algorithms in in-line phase tomography. Med Phys. 2008;35:4556–66.
Mokso R, Cloetens P, Maire E, Ludwig W, Buffière J-Y. Nanoscale zoom tomography with hard x rays using Kirkpatrick-Baez optics. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;90:144104.
Barth HD, Launey ME, Macdowell AA, Ager III JW, Ritchie RO. On the effect of X-ray irradiation on the deformation and fracture behavior of human cortical bone. Bone. 2010;46:1475–85.
Pacureanu A, Langer M, Boller E, Tafforeau P, Peyrin F. Nanoscale imaging of the bone cell network with synchrotron X-ray tomography: optimization of acquisition setup. Med Phys. 2012;39:2229–38. First report of synchrotron nano CT to image the lacuno-canalicular network in 3D and in entire osteons.
Barth HD, Zimmermann EA, Schaible E, Tang SY, Alliston T, Ritchie RO. Characterization of the effects of x-ray irradiation on the hierarchical structure and mechanical properties of human cortical bone. Biomaterials. 2011;32:8892–904.
Draenert ME, Draenert AI, Forriol F, Cerler M, Kunzelmann K-H, Hickel R, et al. Value and limits of μ-CT for nondemineralized bone tissue processing. Microsc Res Tech. 2012;75:416–24.
Vatsa A, Breuls RG, Semeins CM, Salmon PL, Smit TH, Klein-Nulend J. Osteocyte morphology in fibula and calvaria—is there a role for mechanosensing? Bone. 2008;43:452–8.
Van Hove RP, Nolte PA, Vatsa A, Semeins CM, Salmon PL, Smit TH, et al. Osteocyte morphology in human tibiae of different bone pathologies with different bone mineral density—is there a role for mechanosensing? Bone. 2009;45:321–9.
Peyrin F, Salomé-Pateyron M, Cloetens P, Laval-Jeantet AM, Ritman E, Ruegsegger P. Micro-CT examinations of trabecular bone samples at different resolutions: 14, 7, and 2 micron level. Technol Health Care. 1998;6:391–401.
Peyrin F, Salome-Pateyron M, Nuzzo S, Cloetens P, Laval-Jeantet AM, Baruchel J. Perspectives in three-dimensional analysis of bone samples using synchrotron radiation microtomography. Cell Mol Biol. 2000;46:1089–102.
Schneider P, Stauber M, Voide R, Stampanoni M, Donahue LR, Müller R. Ultrastructural properties in cortical bone vary greatly in two inbred strains of mice as assessed by synchrotron light based micro- and nano-CT. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:1557–70.
Carriero A, Doube M, Vogt M, Busse B, Zustin J, Levchuk A, et al. Altered lacunar and vascular porosity in osteogenesis imperfecta mouse bone as revealed by synchrotron tomography contributes to bone fragility. Bone. 2014;61:116–24.
Tommasini SM, Trinward A, Acerbo AS, De Carlo F, Miller LM, Judex S. Changes in intracortical microporosities induced by pharmaceutical treatment of osteoporosis as detected by high resolution micro-CT. Bone. 2012;50:596–604.
Britz HM, Carter Y, Jokihaara J, Leppänen OV, Järvinen TLN, Belev G, et al. Prolonged unloading in growing rats reduces cortical osteocyte lacunar density and volume in the distal tibia. Bone. 2012;51:913–9.
Hannah KM, Thomas CDL, Clement JG, De Carlo F, Peele AG. Bimodal distribution of osteocyte lacunar size in the human femoral cortex as revealed by micro-CT. Bone. 2010;47:866–71.
Carter Y, Thomas CDL, Clement JG, Peele AG, Hannah K, Cooper DML. Variation in osteocyte lacunar morphology and density in the human femur—a synchrotron radiation micro-CT study. Bone. 2013;52:126–32.
Carter Y, Thomas CDL, Clement JG, Cooper DML. Femoral osteocyte lacunar density, volume and morphology in women across the lifespan. J Struct Biol. 2013;183:519–26. Reports the 3D properties of osteocyte lacunae in women from 3D synchrotron micro-CT in a large age range.
Dong P, Haupert S, Hesse B, Langer M, Gouttenoire P-J, Bousson V, et al. 3D osteocyte lacunar morphometric properties and distributions in human femoral cortical bone using synchrotron radiation micro-CT images. Bone. 2014;60:172–85. Reports a methodology for the 3D assessment of osteocyte lacunae.
Mader KS, Schneider P, Müller R, Stampanoni M. A quantitative framework for the 3D characterization of the osteocyte lacunar system. Bone. 2013;57:142–54. Reports a new methodology for the 3D assessment of osteocyte lacunae.
Pacureanu A, Larrue A, Langer M, Olivier C, Muller C, Lafage-Proust M-H, et al. Adaptive filtering for enhancement of the osteocyte cell network in 3D microtomography images. IRBM. 2013;34:48–52.
Pacureanu A, Rollet J, Revol-Muller C, Buzuloiu V, Langer M, Peyrin F. Segmentation of 3D cellular networks from SR-micro-CT images. 2011 I.E. International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro. IEEE; 2011. p. 1970–3.
Zuluaga MA, Orkisz M, Dong P, Pacureanu A, Gouttenoire P-J, Peyrin F. Bone canalicular network segmentation in 3D nano-CT images through geodesic voting and image tessellation. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59:2155.
Andrews JC, Almeida E, van der Meulen MCH, Alwood JS, Lee C, Liu Y, et al. Nanoscale X-ray microscopic imaging of mammalian mineralized tissue. Microsc Microanal. 2010;16:327–36.
Dierolf M, Menzel A, Thibault P, Schneider P, Kewish CM, Wepf R, et al. Ptychographic X-ray computed tomography at the nanoscale. Nature. 2010;467:436–9.
Nango N, Kubota S, Takeuchi A, Suzuki Y, Yashiro W, Momose A, et al. Talbot-defocus multi-scan tomography using the synchrotron X-ray microscope to study the lacuno-canalicular network in mouse bone. Biomed Opt Express. 2013;4:917–23.
Langer M, Pacureanu A, Suhonen H, Grimal Q, Cloetens P, Peyrin F. X-ray phase nanotomography resolves the 3D human bone ultrastructure. PLoS One. 2012;7:e35691. First report of the lacuno-canalicular network using phase nano-CT at 60nm.
Varga P, Pacureanu A, Langer M, Suhonen H, Hesse B, Grimal Q, et al. Investigation of the three-dimensional orientation of mineralized collagen fibrils in human lamellar bone using synchrotron X-ray phase nano-tomography. Acta Biomater. 2013;9:8118–27. First analysis of collagen fibrils orientation from 3D phase nano-CT at 60 nm.
Hesse B, Langer M, Varga P, Pacureanu A, Dong P, Schrof S, et al. Alterations of mass density and 3D osteocyte lacunar properties in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrotic human jaw bone, a synchrotron μCT study. PLoS One. 2014;9:e88481.
Granke M, Gourrier A, Rupin F, Raum K, Peyrin F, Burghammer M, et al. Microfibril orientation dominates the microelastic properties of human bone tissue at the lamellar length scale. PLoS One. 2013;8:e58043.
Reznikov N, Shahar R, Weiner S. Three-dimensional structure of human lamellar bone: the presence of two different materials and new insights into the hierarchical organization. Bone. 2014;59:93–104.
Schneider P, Voide R, Stampanoni M, Donahue LR, Müller R. The importance of the intracortical canal network for murine bone mechanics. Bone. 2013;53:120–8.
Verbruggen SW, Vaughan TJ, McNamara LM. Strain amplification in bone mechanobiology: a computational investigation of the in vivo mechanics of osteocytes. J R Soc Interface. 2012;9:2735–44.
Varga P, Hesse B, Langer M, Schrof S, Männicke N, Suhonen H, et al. Synchrotron X-ray phase nano-tomography-based analysis of the lacunar-canalicular network morphology and its relation to the strains experienced by osteocytes in situ as predicted by case-specific finite element analysis. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2014.
Acknowledgments
The images of bone samples were acquired at ESRF within the Long Term Project MD431. This work was performed within the framework of the LABEX PRIMES (ANR-11-LABX-0063) of Université de Lyon. The authors also want to thank Felix W. Wehrli for editing the manuscript.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
F. Peyrin, P. Dong, A. Pacureanu, and M. Langer declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All studies by the authors involving animal and/or human subjects were performed after approval by the appropriate institutional review boards. When required, written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peyrin, F., Dong, P., Pacureanu, A. et al. Micro- and Nano-CT for the Study of Bone Ultrastructure. Curr Osteoporos Rep 12, 465–474 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-014-0233-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-014-0233-0