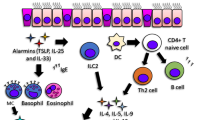
Abstract
Numerous studies have clearly shown that the Th2 cytokine, interleukin (IL)-13, is the central regulator of the allergic diathesis. Initial studies in animal models of disease provided compelling evidence that IL-13, independent of other Th2 cytokines, was both necessary and sufficient to induce all features of allergic asthma. The importance of IL-13 in allergic disorders in humans is supported by consistent associations between tissue IL-13 levels and genetic variants in the IL-13 gene with asthma and related traits. With the preponderance of evidence continuing to support the importance of IL-13 in allergic disorders, attention is now turned toward understanding the mechanisms by which this cytokine might mediate the pathophysiologic features of allergic disease. The emerging paradigm is that IL-13 induces features of the allergic response via its actions on epithelial cells and smooth muscle cells, not through traditional effector pathways involving eosinophils and IgE-mediated events. In light of these recent developments, in this review our current understanding of the role of IL-13 in the pathogenesis of asthma is explored, with a particular focus on new insights into the mechanisms by which IL-13 induces the features of asthma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Coyle AJ, Le Gros G, Bertrand C, et al.: Interleukin-4 is required for the induction of lung Th2 mucosal immunity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1995, 13:54–59.
Rankin JA, Picarella DE, Geba GP, et al.: Phenotypic and physiologic characterization of transgenic mice expressing interleukin 4 in the lung: lymphocytic and eosinophilic inflammation without airway hyperreactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93:7821–7825.
Hogan SP, Matthaei Ki, Young JM, et al.: A novel T cell-regulated mechanism modulating allergen-induced airways hyperreactivity in BALB/c mice independently of IL-4 and IL-5. J Immunol 1998, 161:1501–1509.
Cohn L, Tepper JS, Bottomly K: Cutting edge: IL-4-independent induction of airway hyperresponsiveness by Th2, but not Th1, cells. J Immunol 1998, 161:3813–3816.
Gavett SH, O’Hearn DJ, Karp CL, et al.: Interleukin-4 receptor blockade prevents airway responses induced by antigen challenge in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 1997, 272:L253-L261.
Kuperman D, Schofield B, Wills-Karp M, et al.: Signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 6 (Stat6)-deficient mice are protected from antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and mucus production. J Exp Med 1998, 187:939–948.
Wills-Karp M, Luyimbazi J, Xu X, et al.: Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 1998, 282:2258–2261.
Grunig G, Warnock M, Wakil AE, et al.: Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 1998; 282:2261–2262.
Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, et al.: Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest 1999, 102:779–788.
McKenzie GJ, Emson CL, Bell SE, et al.: Impaired development of Th2 cells in IL-13 deficient mice. Immunity 1998, 9:423–432.
Walter DM, McIntire JJ, Berry G, et al.: Critical role for IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. J Immunol 2001, 167:4668–4675.
Akbari O, Stock P, Meyer E, et al.: Essential role of NKT cells producing IL-4 and IL-13 in the development of allergeninduced airway hyperreactivity. Nat Med 2003, 9:582–588.
Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Altznauer F, Fischer B, et al.: Eosinophils express functional IL-13 in eosinophilic inflammatory diseases. J Immunol 2002, 169:1021–1027.
Mattes J, Yang M, Mahalingam S, et al.: Intrinsic defect in T cell production of interleukin (IL)-13 in the absence of both IL-5 and eotaxin precludes the development of eosinophilia and airways hyperreactivity in experimental asthma. J Exp Med 2002, 195:1433–1444.
Grunstein MM, Hakonarson H, Leiter J, et al.: IL-13-dependent autocrine signaling mediates altered responsiveness of IgEsensitized airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002, 282:L520-L528.
Temann UA, Geba GP, Rankin JA, et al.: Expression of interleukin 9 in the lungs of transgenic mice causes airway inflammation, mast cell hyperplasia, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J Exp Med 1998, 188:1307–1320.
Temann UA, Ray P, Flavell RA: Pulmonary overexpression of IL-9 induces Th2 cytokine expression, leading to immune pathology. J Clin Invest 2002, 109:29–39.
Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, et al.: IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity 2001, 5:985–995.
Hurst SD, Muchamuel T, Gorman DM, et al.: New IL-17 family members promote Th1 or Th2 responses in the lung: in vivo function of the novel cytokine IL-25. J Immunol 2002, 169:443–453.
Elliott KA, Osna NA, Scofield MA, et al.: Regulation of IL-13 production by histamine in cloned murine T helper type 2 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 2001, 1:1923–1937.
Blackburn MR, Lee CG, Young HWJ, et al.: Adenosine mediates IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling in the lung and interacts in an IL 13-adenosine amplification pathway. J Clin Invest 2003, 112:332–344.
Kishikawa H, Sun J, Choi A, et al.: The cell type-specific expression of the murine IL-13 gene is regulated by GATA-3. J Immunol 2002, 167:4414–4420.
Lavenu-Bombled C, Trainor CD, Makeh I, et al.: Interleukin-13 gene expression is regulated by GATA-3 in T cells. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:18313–18321.
Graber P, Gretener D, Herren S, et al.: The distribution of IL-13 receptor alpha 1 expression on B cells, T cells, and monocytes and its regulation by IL-13 and IL-4. Eur J Immunol 1998, 28:4286–4298.
Mattes J, Yang M, Siqueira A, et al.: IL-13 induces airways hyperreactivity independently of the IL-4R alpha chain in the allergic lung. J Immunol 2001, 167:1683–1692.
Chiaramonte MG, Mentink-Kane M, Jacobson BA, et al.: Regulation and function of the interleukin 13 receptor alpha during a T helper cell type 2-dominant immune response. J Exp Med 2003, 197:687–701.
Zheng T, Liu W, Lee CG, et al.: Cytokine regulation of IL-13RA2 and IL-13RA1 in vivo and in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003, 111:720–728.
Daines MO, Hershey GKK: A novel mechanism by which interferon-gamma can regulate interleukin(IL)-13 responses. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:10387–10393.
Dienger KM, Herman NS, Donaldson D, et al.: The complex role of IL-13 receptor alpha 2 knockout mice in allergic responses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 167:A727.
Pope SM, Brandt EB, Mishra A, et al.: IL-13 induces eosinophil recruitment into the lung by an IL-5 and eotaxin-dependent mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001, 108:594–601.
Li L, **a Y, Nguyen A, et al.: Effects of Th2 cytokines on chemokine expression in the lung: IL-13 potently induces eotaxin expression by airway epithelial cells. J Immunol 1999, 162:2477–2487.
Hirst SJ, Hallsworth MP, Peng QI, et al.: Selective induction of eotaxin release by interleukin-13 or interleukin-4 in human airway smooth muscle cells is synergistic with interleukin-1B and is mediated by the interleukin-4 receptor a-chain. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002, 165:1161–1171.
Moore PE, Church TL, Chism DD, et al.: IL-13 and IL-4 cause eotaxin release in human airway smooth muscle cells: a role for ERK. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002, 282:847–853.
Chibana K, Ishii Y, Asakura T, Fukuda T: Up-regulation of cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor by IL-13 enables human lung fibroblasts to respond to leukotriene C4 and produce eotaxin. J Immunol 2003, 170:4290–4295.
Zheng T, Zhu Z, Wang Z, et al.: Inducible targeting of IL-13 to the adult lung causes matrix metalloproteinase-and cathepsindependent emphysema. J Clin Invest 2000, 106:1081–1093.
Chiaramonte MG, Donaldson DD, Cheever AW, et al.: An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response. J Clin Invest 1999, 104:777–785.
Richter A, Puddicombe SM, Lordan JL, et al.: The contribution of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 to the epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001, 25:385–391.
Wen FQ, Kohyama T, Liu X, et al.: Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-enhanced transforming growth factor beta-2 production in cultured human bronchial epithelial cells is attenuated by interferon-gamma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002, 26:484–490.
Liu X, Kohyama T, Wang H, Zhu YK, et al.: Th2 cytokine regulation of type I collagen gel contraction mediated by human lung mesenchymal cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002, 282:L1049-L1056.
Ingram JL, Rice A, Geisenhoffer K, et al.: Interleukin-13 stimulates the proliferation of lung myofibroblasts via a signal transducer and activator of transcription-6 dependent mechanism. Chest 2003, 123:422S-424S.
Cohn L, Homer RJ, MacLeod H, et al.: Th2-induced airway mucus production is dependent on IL-4Ralpha, but not on eosinophils. J Immunol 1999, 162:6178–6183.
McMillan SJ, Bishop B, Townsend MJ, et al.: The absence of interleukin-9 does not affect the development of allergenionduced pulmonary inflammation nor airway hyperreactivity. J Exp Med 2002, 195:51–57.
Dudley KL, Chiaramonte M, Wills-Karp M: Upregulation of mucin related genes is associated with susceptibility to allergen-induced hyperresponsiveness. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002, A693.
Booth BW, Adler KB, Bonner JC, et al.: Interleukin-13 induces proliferation of human airway epithelial cells in vitro via a mechanism mediated by transforming growth factor-alpha. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001, 25:739–743.
Laoukili J, Perret E, Willems T, et al.: IL-13 alters mucociliary differentiation and ciliary beating of human respiratory epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 2001, 108:1817–1824.
Dabahay H, Atherton H, Jones G, et al.: Interleukin-13 induces a hypersecretory ion transport phenotype in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002, 282:L226-L236.
Nakanishi A, Morita S, Iwashita H, et al.: Role of gob-5 in mucus overproduction and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98:5175–5180.
Zhou Y, Dong Q, Louahed J, et al.: Characterization of a calciumactivated chloride channel as a shared target of Th2 cytokine pathways and its potential involvement in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001, 25:486–491.
Leverkoehne I, Gruber AD: The murine mCLCA3 (alias gob-5) protein is localized in the mucin granule membranes of intestinal, respiratory, and uterine goblet cells. J Histochem Cytochem 2002, 50:829–838.
Izuhara K: The role of interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 in the non-immunologic aspects of asthma pathogenesis. Clin Chem Lab Med 2003, 41:860–864.
Singer M, Lefort J, Vargaftig BB: Granulocyte depletion and dexamethasone differentially modulate airways hyperreactivity, inflammation, mucus accumulation, and secretion induced by rmIL-13 or antigen. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002, 26:74–84.
Venkayya R, Lam M, Willkom M, et al.: The Th2 lymphocyte products IL-4 and IL-13 rapidly induce airway hyperresponsiveness through direct effects on resident airway cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002, 26:202–208.
Yang M, Hogan SP, Henry PJ, et al.: Interleukin-13 mediates airways hyperreactivity through the IL-4 receptor-alpha chain and STAT-6 independently of IL-5 and eotaxin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001, 25:522–530.
Laporte JC, Moore PE, Baraldo S, et al.: Direct effects of interleukin-13 on signaling pathways for physiological responses in cultured human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001, 164:141–148.
Espinosa K, Bosse Y, Stankova J, Rola-Pleszczynski M: CysLT1 receptor upregulation by TGF-beta and IL-13 is associated with bronchial smooth muscle cell proliferation in response to LTD4. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003, 111:1032–1040.
Kuperman DA, Huang X, Koth LL, et al.: Direct effects of interleukin-13 on epithelial cells cause airway hyperreactivity and mucus overproduction in asthma. Nat Med 2002, 8:885–889. An intriguing study implicating the IL-13/IL-4 signaling pathway in the epithelium as the primary regulator of airway hyperresponsiveness.
Meurs H, McKay S, Maarsingh H, et al.: Increased arginase activity underlies allergen-induced deficiency of cNOSderived nitric oxide and airway hyperresponsiveness. Br J Pharmacol 2002, 136:391–398.
Zimmerman N, King NE, Laporte J, et al.: Dissection of experimental asthma with DNA microarray analysis identifies arginase in asthma pathogenesis. J Clin Invest 2003, 111:1815–1817.
Dienger KM, Wills-Karp M: Interleukin-13 regulation of complement factor 3 production by human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002, A733.
Bautsch W, Hoymann HG, Zhang Q, et al.: Cutting edge: guinea pigs with a natural C3a-receptor defect exhibit decreased bronchoconstriction in allergic airway disease: evidence for an involvement of the C3a anaphylatoxin in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Immunol 2000, 165:5401–5405.
Humbles AA, Lu B, Nilsson CA, et al.: A role for the C3a anaphylatoxin receptor in the effector phase of asthma. Nature 2000, 406:998–1001.
Huang SK, **ao HQ, Kleine-Tebbe J, et al.: IL-13 expression at the sites of allergen challenge in patients with asthma. J Immunol 1995, 155:2688–2694.
Humbert M, Durham SR, Kimmitt P, et al.: Elevated expression of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding IL-13 in the bronchial mucosa of atopic and nonatopic subjects with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1997, 99:657–665.
Gabrielsson S, Soderland A, Paulie S, et al.: Specific immunotherapy prevents increased levels of allergen-specific IL-4 and IL-13-producing cells during pollen season. Allergy 2001, 56:293–300.
Naseer T. Minshall EM, Leung DY, et al.: Expression of IL-12 and IL-13 mRNA in asthma and their modulation in response to steroid therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997, 155:845–851.
Ohshima Y, Yasutomi M, Omata N, et al.: Dysregulation of IL-13 production by cord blood CD4+ T cells is associated with the subsequent development of atopic disease in infants. Pediatr Res 2002, 51:195–200.
van der Pouw Kraan TC, van Veen A, Boeije LCM, et al.: An IL-13 promoter polymorphism associated with increased risk of allergic asthma. Genes Immun 1999, 1:61–65.
Graves PE, Kabesch M, Halonen M, et al.: A cluster of seven tightly linked polymorphisms in the IL-13 gene is associated with total serum IgE levels in three populations of white children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000, 105:506–513.
Heinzmann A, Mao XQ, Akaiwa M, et al.: Genetic variants of IL-13 signalling and human asthma and atopy. Hum Mol Genet 2000, 9:549–559.
Celedon JC, Soto-Quiros ME, Palmer LJ, et al.: Lack of association between a polymorphism in the interleukin-13 gene and total serum immunoglobulim E level among nuclear families in Costa Rica. Clin Exp Allergy 2002, 32:387–390.
Arima K, Umeshita-Suyama R, Sakata Y, et al.: Upregulation of IL-13 concentration in vivo by the IL13 variant associated with bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002, 109:980–987. This excellent study provides a potential functional mechanism for the strong association between the Gln110 variant in the IL-13 gene and asthma-related traits.
Mohrs M, Blankespoor CM, Wang ZE, et al.: Deletion of a coordinate regulator of type 2 cytokine expression in mice. Nat Immunol 2001, 2:842–847.
Noguchi E, Nukaga-Nishio Y, Jian Z, et al.: Haplotypes of the 5’ region of the IL-4 gene and SNPs in the intergene sequence between the IL-4 and IL-13 genes are associated with atopic asthma. Hum Immunol 2001, 62:1251–1257.
Howard TD, Koppelman GH, Xu J, et al.: Gene-gene interaction in asthma: IL4RA and IL13 in a Dutch population with asthma. Am J Hum Genet 2002, 70:230–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karp, M.W. Interleukin-13 in asthma pathogenesis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 4, 123–131 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-004-0057-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-004-0057-6