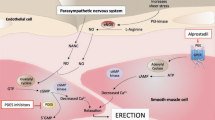
Abstract
Introduction
It has been shown on experimental rat models that type 5-phosphodiesterase isoenzyme (PDE5) inhibitors have anti-fibrotic effects for Peyronie’s disease (PD); however, this issue has not been addressed clinically. The aim of this study was to document the effects of PDE5 inhibitors used for erectile dysfunction (ED) seen in PD patients on the main course of the PD clinically.
Methods
A total of 39 PD patients with ED were divided into two groups. Patients in Group 1 (n = 18) served as controls and received 400 IU vitamin E per day. Those in Group 2 (n = 21) received 50 mg sildenafil per day for 12 weeks. Penile plaque volume was assessed by palpation and by duplex ultrasound. Erectile capacity, penile deformity and plaque characteristics were assessed by the International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire form (IIEF-5) and penile duplex ultrasound.
Results
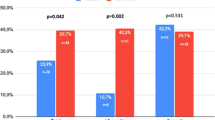
Statistically significant improvement in all parameters was observed within both groups except for IIEF score in Group 1 when compared with the initial values. Significant reduction in plaques and pain were observed in 7 (33.3 %) and 14 (66.6 %) patients in Group 2 and 6 (33.3 %) and 9 patients (42.8 %) in Group 1, respectively. At the end of the therapy, improvement in IIEF score and reduction in pain were statistically significant in Group 2 compared with Group 1 (p = 0.028 and p = 0.045, respectively).
Conclusion
We conclude that continuous administration of oral PDE5 inhibitors may be a candidate for medical treatment of PD; however, more controlled studies are needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor FL, Levine LA (2007) Peyronie’s disease. Urol Clin North Am 34:517–534
Gholami SS, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Lin CS et al (2003) Peyronie’s disease: a review. J Urol 169:1234–1241
Müller A, Mulhall JP (2009) Peyronie’s disease intervention trials: methodological challenges and issues. J Sex Med 6:848–861
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J (2009) Experimental models of Peyronie’s disease. Implications for new therapies. J Sex Med 6:303–313
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J (2010) Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with PDE5 inhibitors: an anti-fibrotic strategy. Nat Rev Urol 7:215–221
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD et al (1999) Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 11:319–326
Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ, Brock G, Morales AM (2013) Standardization of vascular assessment of erectile dysfunction: standard operating procedures for duplex ultrasound. J Sex Med 10:120–129
Kumar R, Nehra A (2009) Surgical and minimally invasive treatments for Peyronie’s disease. Curr Opin Urol 19:589–594
Hauck EW, Diemer T, Schmelz HU et al (2009) A critical analysis of nonsurgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol 49:987–997
Hellstrom WJ (2009) Medical management of Peyronie’s disease. J Androl 30:397–405
Vanni AJ, Bennett NE (2009) Current treatment and management of the acute phase of Peyronie’s disease. Arch Esp Urol 62:614–622
Erdogru T, Savas M, Yilmaz N et al (2002) Evaluation of penile hemodynamic status and adjustment of treatment alternatives in Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl 4(1):87–90
Lopez JA, Jarow JP (1993) Penile vascular evaluation of men with Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 149:53–55
Deveci S, Palese M, Parker M et al (2006) Erectile function profiles in men with Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 175:1807–1811
Kadioğlu A, Tefekli A, Erol H et al (2000) Color Doppler ultrasound assessment of penile vascular system in men with Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res 12:263–267
Weidner W, Schroeder-Printzen I, Weiske WH et al (1997) Sexual dysfunction in Peyronie’s disease: an analysis of 222 patients without previous local plaque therapy. J Urol 157:325–328
Levine LA, Latchamsetty KC (2002) Treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with Peyronie’s disease using sildenafil citrate. Int J Impot Res 14:478–482
El-Sakka AI, Hassoba HM, Chui RM et al (1997) An animal model of Peyronie’s-like condition associated with an increase of transforming growth factor beta mRNA and protein expression. J Urol 158:2284–2290
Ferrini MG, Vernet D, Magee TR et al (2002) Anti-fibrotic role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide 6:283–294
Gabbiani G (2003) The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol 200:500–503
Nagayama T, Zhang M, Hsu S et al (2008) Sustained soluble guanylate cyclase stimulation offsets nitric-oxide synthase inhibition to restore acute cardiac modulation by sildenafil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:380–387
Yildirim A, Ersoy Y, Ercan F et al (2010) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition by sildenafil citrate in a rat model of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 23:215–221
Vernet D, Ferrini MG, Valente EGA et al (2002) Effect of nitric oxide on fibroblast differentiation in to myofibroblasts in cell cultures from the Peyronie’s fibrotic plaque and in its rat model in vivo. Nitric Oxide 7(262):276
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Ignarro L, Rajfer J (1999) Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in the penis. Mol Urol 3:51–59
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, U., Yesil, S., Goktug, H.N.G. et al. Effects of sildenafil treatment on patients with Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction. Ir J Med Sci 183, 449–453 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-013-1036-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-013-1036-5