Abstract
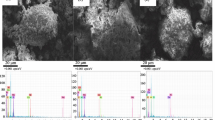
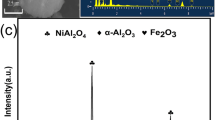
The petroleum refining industry produces a large amount of spent hydrodesulphurization (HDS) catalyst every year, representing a hazardous solid waste but also an important secondary resource. In the work presented herein, extraction of molybdenum from spent HDS catalyst by two-stage roasting followed by water leaching was investigated. The effects of sodium carbonate roasting and water leaching on the extraction of molybdenum as well as the effect of roasting on the molybdenum loss were investigated. The spent catalyst could be oxidized by blank roasting at 650°C for 2 h with molybdenum loss of 5.9%. Under the optimized conditions of sodium carbonate roasting (blank roasted spent HDS catalyst with 20 wt.% sodium carbonate addition at 650°C for 2.5 h) followed by water leaching (at 100°C for 2.5 h at liquid/solid ratio of 7 mL/g), the molybdenum leaching reached 94.0%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.B. Zhang, L. Wang, W.W. Qu, S.M. Xu, and J.L. Zhang, Mater. Rev. A 32, 772 (2018).
A. Akcil, F. Vegliò, F. Ferella, M.D. Okudan, and A. Tuncuk, Waste Manage. 45, 420 (2015).
M. Marafi and A. Stanislaus, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 53, 1 (2008).
Y. Chen, Q.M. Feng, G.F. Zhang, L.M. Ou, and Y.P. Lu, Met. Mine 7, 55 (2005).
R.E. Siemens, B.W. Jong, and J.H. Russell, Conserv. Recycl. 9, 189 (1986).
Z.P. Zhu, F.Q. Yang, Z.Y. Liang, and H. Li, China Molybdenum Ind. 27, 14 (2003).
B.B. KarInt, J. Miner. Process 75, 249 (2005).
I. Gaballah, M.D. Jona, J.C. Mugica, and R. Solozobal, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 10, 87 (1994).
E.Q. Wang, G.A. Yang, and Q.F. Hua, China Molybdenum Ind. 22, 34 (1998).
Z. Zhang, Y. Gao, and Y.Z. Liu, Liaoning Chem. Ind. 27, 234 (1998).
Y.R. Li, W.X. Gong, and Y.F. Huang, Chin. Resour. Compr. Util. 31, 19 (2013).
I.S.S. Pinto and H.M.V.M. Soares, Hydrometallurgy 129–130, 19 (2012).
K.H. Park, D. Mohapatra, and B. Ramachandra Reddy, J. Hazard. Mater. B 138, 311 (2006).
K.H. Park, B. Ramachandra Reddy, D. Mohapatra, and C.-W. Nam, J. Miner. Process 80, 261 (2006).
S.P. Barik, K.-H. Park, P.K. Parhi, and J.T. Park, Hydrometallurgy 111–112, 46 (2012).
A. Szymczycha-Madeja, J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 2157 (2011).
Y.-C. Lai, W.-J. Lee, K.-L. Huang, and C.-M. Wu, J. Hazard. Mater. 154, 588 (2008).
M.Y. Wang, B.F. Chen, S. Huang, H.X. Yang, B. Hu, C.D. Zhang, X.W. Wang, and Y.Q. Xu, Miner. Eng. 124, 63 (2018).
L. Zeng and C.Y. Cheng, Hydrometallurgy 98, 1 (2009).
P.Y. Li, N.C. Zhang, and X.B. Lin, China Molybdenum Ind. 23, 16 (1999).
G.Q. Liu, B.S. Zhang, F. Wang, and W.X. Gong, Chin. Resour. Compr. Util. 36, 17 (2018).
M.Y. Wang, X.W. Wang, and W.L. Liu, Hydrometallurgy 97, 126 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2016JJ2142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Liu, J., Zhang, C. et al. Extraction of Molybdenum from Spent HDS Catalyst by Two-Stage Roasting Followed by Water Leaching. JOM 71, 4681–4686 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03741-z