Abstract
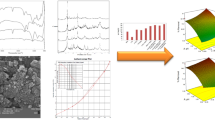
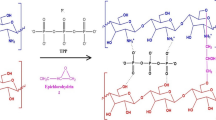
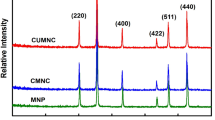
The aim of this study was to prepare the well-dispersed modified chitosan–alumina (CA) with size less than 50 nm by the facile synthesis method to evaluate the adsorption of hydroquinone and arsenic (V) ions in the aqueous solutions. Derived gamma-alumina from boehmite was coated and modified by chitosan and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and salicylic acid, respectively. The characterization of nanocomposites was studied by XRD, FTIR, FESEM, EDX TEM and BET analysis. The chitosan and SDS phases were detected in the structure of the adsorbent as confirmed by XRD achievements. A quadratic polynomial model was developed to describe the effect of the operating parameters including pH, temperature and initial concentration on the adsorption capacity of the prepared sample while the experimental data were designed by a response surface method (RSM). The maximum adsorption capacity for the best adsorbent named CSAS3 was measured to be 86.95 and 95.24 mg/g for HQ and As (V) ions by employing linear Langmuir equation, respectively. The kinetic study indicated that the experimental data were in an appropriate matching with the linearized pseudo-quadratic kinetic equation (R2 = 0.999). The results showed the successful removal of hydroquinone and arsenic ions form the aqueous after 5 consecutive cycles.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Abugazleh, B. Rougeau, H. Ali, Adsorption of catechol and hydroquinone on titanium oxide and iron (iii) oxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 104180 (2020)
M.A. Ahghari, M.R. Ahghari, M. Kamalzare, A. Maleki, Design, synthesis, and characterization of novel eco-friendly chitosan-agio3 bionanocomposite and study its antibacterial activity. Sci. Rep. 12, 10491 (2022)
F. AkbarBandari, M. Zabihi, E. Fatehifar, Remarkable adsorption of hydroquinone as an anion contaminant by using the magnetic supported bimetallic (nicu-mof@ mac) nanocomposites in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 69272 (2021)
M. Al-Yaari, T.H. Aldhyani, S. Rushd, Prediction of arsenic removal from contaminated water using artificial neural network model. Appl. Sci. 12, 999 (2022)
S. Alka, S. Shahir, N. Ibrahim, M.J. Ndejiko, D.-V.N. Vo, F. Abd Manan, Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: a mini review. J. Clean. Prod. 278, 123805 (2021)
L.A. Amola, T. Kamgaing, R.F. Tiegam Tagne, C.D. Atemkeng, I.-H.T. Kuete, S.G. Anagho, Optimized removal of hydroquinone and resorcinol by activated carbon based on shea residue (vitellaria paradoxa): thermodynamics, adsorption mechanism, nonlinear kinetics, and isotherms. J. Chem. 2022, 1 (2022)
F. Amri, S. Husseinsyah, K. Hussin, Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene/chitosan composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 26, 878 (2013)
S. Ashraf, A. Siddiqa, S. Shahida, S. Qaisar, Titanium-based nanocomposite materials for arsenic removal from water: a review. Heliyon 5, e01577 (2019)
N. Assaad, G. Sabeh, M. Hmadeh, Defect control in zr-based metal–organic framework nanoparticles for arsenic removal from water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 8997 (2020)
R.E.K. Billah, M.A. Islam, H. Lgaz, E.C. Lima, Y. Abdellaoui, Y. Rakhila, O. Goudali, H. Majdoubi, A.A. Alrashdi, M. Agunaou, Shellfish waste-derived mesoporous chitosan for impressive removal of arsenic (v) from aqueous solutions: a combined experimental and computational approach. Arab. J. Chem. 15, 104123 (2022)
J.C. Burillo, L. Ballinas, G. Burillo, E. Guerrero-Lestarjette, D. Lardizabal-Gutierrez, H. Silva-Hidalgo, Chitosan hydrogel synthesis to remove arsenic and fluoride ions from groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 417, 126070 (2021)
S. Chatterjee, H.N. Tran, O.-B. Godfred, S.H. Woo, Supersorption capacity of anionic dye by newer chitosan hydrogel capsules via green surfactant exchange method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 3604 (2018)
T.S. Choong, T. Chuah, Y. Robiah, F.G. Koay, I. Azni, Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: an overview. Desalination 217, 139 (2007)
K.D. Dobson, A.J. McQuillan, In situ infrared spectroscopic analysis of the adsorption of aliphatic carboxylic acids to Tio2, Zro2, Al2O3, and Ta2O5 from aqueous solutions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 55, 1395 (1999)
H. Ebadollahzadeh, M. Zabihi, Competitive adsorption of methylene blue and pb (ii) ions on the nano-magnetic activated carbon and alumina. Mater. Chem. Phys. 248, 122893 (2020)
A. El-araby, L. El Ghadraoui, F. Errachidi, Usage of biological chitosan against the contamination of post-harvest treatment of strawberries by Aspergillus niger. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6, 881434 (2022)
M. Gallegos-Garcia, K. Ramírez-Muñiz, S. Song, Arsenic removal from water by adsorption using iron oxide minerals as adsorbents: a review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 33, 301 (2012)
M.R. Gandhi, G. Kousalya, N. Viswanathan, S. Meenakshi, Sorption behaviour of copper on chemically modified chitosan beads from aqueous solution. Carbohyd. Polym. 83, 1082 (2011)
A. Ghosh, M.A. Ali, Studies on physicochemical characteristics of chitosan derivatives with dicarboxylic acids. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 1196 (2012)
X. Guo, F. Chen, Removal of arsenic by bead cellulose loaded with iron oxyhydroxide from groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 6808 (2005)
M. Habuda-Stanić, M. Nujić, Arsenic removal by nanoparticles: a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 8094 (2015)
Y.-S. Han, J.-H. Park, Y. Min, D.-H. Lim, Competitive adsorption between phosphate and arsenic in soil containing iron sulfide: xas experiment and dft calculation approaches. Chem. Eng. J. 397, 125426 (2020)
A. Hassan, A. Abdel-Mohsen, H. Elhadidy, Adsorption of arsenic by activated carbon, calcium alginate and their composite beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 68, 125 (2014)
C. Hu, H. Liu, G. Chen, J. Qu, Effect of aluminum speciation on arsenic removal during coagulation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 86, 35 (2012)
M.M. Islam, M.N. Khan, S. Biswas, T.R. Choudhury, P. Haque, T.U. Rashid, M.M. Rahman, Preparation and characterization of bijoypur clay-crystalline cellulose composite for application as an adsorbent. Adv. Mater. Sci. (2017). https://doi.org/10.15761/AMS.1000126
E.-K. Jeon, S. Ryu, S.-W. Park, L. Wang, D.C. Tsang, K. Baek, Enhanced adsorption of arsenic onto alum sludge modified by calcination. J. Clean. Prod. 176, 54 (2018)
X. Jiang, H.-Y. Chen, L.-L. Liu, L.-G. Qiu, X. Jiang, Fe3O4 embedded zif-8 nanocrystals with ultra-high adsorption capacity towards hydroquinone. J. Alloy. Compd. 646, 1075 (2015)
C. Lasko, K. Adams, E. DeBenedet, P. West, A simple sulfuric acid pretreatment method to improve the adsorption of cr (vi) by chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 93, 2808 (2004)
L. Li, L. Fan, M. Sun, H. Qiu, X. Li, H. Duan, C. Luo, Adsorbent for hydroquinone removal based on graphene oxide functionalized with magnetic cyclodextrin–chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 58, 169 (2013)
W.-Y. Li, J. Liu, H. Chen, Y. Deng, B. Zhang, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, S. Hong, Application of oxalic acid cross-linking activated alumina/chitosan biocomposites in defluoridation from aqueous solution. Investigation of adsorption mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 225, 865 (2013)
H. Lun, J. Ouyang, H. Yang, Enhancing dispersion of halloysite nanotubes via chemical modification. Phys. Chem. Miner. 41, 281 (2014)
W. Luo, Z. Bai, Y. Zhu, Fast removal of co (ii) from aqueous solution using porous carboxymethyl chitosan beads and its adsorption mechanism. RSC Adv. 8, 13370 (2018)
Y. Mamindy-Pajany, C. Hurel, N. Marmier, M. Roméo, Arsenic (v) adsorption from aqueous solution onto goethite, hematite, magnetite and zero-valent iron: effects of ph, concentration and reversibility. Desalination 281, 93 (2011)
T. Mishra, D.K. Mahato, A comparative study on enhanced arsenic (v) and arsenic (iii) removal by iron oxide and manganese oxide pillared clays from ground water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 1224 (2016)
E. Nematollahi, M. Pourmadadi, F. Yazdian, H. Fatoorehchi, H. Rashedi, M.N. Nigjeh, Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone coated nanoporous γ-alumina as a ph-sensitive carrier for controlled release of quercetin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 183, 600 (2021)
N.R. Nicomel, K. Leus, K. Folens, P. Van Der Voort, G. Du Laing, Technologies for arsenic removal from water: current status and future perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 13, 62 (2016)
D.Q. Oliveira, M. Gonçalves, L.C. Oliveira, L.R. Guilherme, Removal of as (v) and cr (vi) from aqueous solutions using solid waste from leather industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 151, 280 (2008)
B.S. Rathi, P.S. Kumar, A review on sources, identification and treatment strategies for the removal of toxic arsenic from water system. J. Hazard. Mater. 418, 126299 (2021)
F. Sadegh-Zadeh, B.J. Seh-Bardan, Adsorption of as (iii) and as (v) by fe coated biochars and biochars produced from empty fruit bunch and rice husk. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 1, 981 (2013)
N. Salahudeen, A.S. Ahmed, H. Ala’a, M. Dauda, S.M. Waziri, B.Y. Jibril, Synthesis of gamma alumina from kankara kaolin using a novel technique. Appl. Clay Sci. 105, 170 (2015)
S. Shengli, L. Jun**, L. Qi, N. Fangru, F. Jia, X. Shulian, Optimized preparation of phragmites australis activated carbon using the box-behnken method and desirability function to remove hydroquinone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 165, 411 (2018)
F. Silerio-Vázquez, J.B. Proal Nájera, J. Bundschuh, M.T. Alarcon-Herrera, Photocatalysis for arsenic removal from water: considerations for solar photocatalytic reactors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 61594 (2022)
A.L. Srivastav, T.D. Pham, S.C. Izah, N. Singh, P.K. Singh, Biochar adsorbents for arsenic removal from water environment: a review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 108, 616 (2021)
S. Suresh, V. Chandra Srivastava, I. Mani Mishra, Adsorption of hydroquinone in aqueous solution by granulated activated carbon. J. Environ. Eng. 137, 1145 (2011)
A. Tarlani, M. Isari, A. Khazraei, M. Eslami Moghadam, New sol–gel derived aluminum oxide-ibuprofen nanocomposite as a controlled releasing medication. Nanomed. Res. J. 2, 28 (2017)
B.R. Vieira, A.M. Pintor, R.A. Boaventura, C.M. Botelho, S.C. Santos, Arsenic removal from water using iron-coated seaweeds. J. Environ. Manag. 192, 224 (2017)
H. Wang, X. Liang, Y. Liu, T. Li, K.-Y.A. Lin, Recycling spent iron-based disposable-chemical-warmer as adsorbent for As (v) removal from aqueous solution. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 168, 105284 (2021)
H. Wang, W. Sun, X. Liang, H. Zou, X. Jiao, K.A. Lin, T. Li, Two-dimensional Fe2o3 nanosheets as adsorbent for the removal of Pb (ii) from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 335, 116197 (2021)
Y. Wang, Z. Liu, W. Huang, J. Lu, S. Luo, B. Czech, T. Li, H. Wang, Capture-reduction mechanism for promoting Cr (vi) removal by sulfidated microscale zerovalent iron/sulfur-doped graphene-like biochar composite. Carbon Res 2, 11 (2023)
Z. Wen, J. Lu, Y. Zhang, G. Cheng, S. Huang, J. Chen, R. Xu, Y.-A. Ming, Y. Wang, R. Chen, Facile inverse micelle fabrication of magnetic ordered mesoporous iron cerium bimetal oxides with excellent performance for arsenic removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 383, 121172 (2020)
C. Wu, L. Huang, S.-G. Xue, Y.-Y. Huang, W. Hartley, M.-Q. Cui, M.-H. Wong, Arsenic sorption by red mud-modified biochar produced from rice straw. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24, 18168 (2017)
X. **e, C. Lu, R. Xu, X. Yang, L. Yan, C. Su, Arsenic removal by manganese-doped mesoporous iron oxides from groundwater: performance and mechanism. Sci. Total. Environ. 806, 150615 (2022)
N. Yıldız, R. Gönülşen, H. Koyuncu, A. Çalımlı, Adsorption of benzoic acid and hydroquinone by organically modified bentonites. Colloids Surf. A 260, 87 (2005)
M. Zaw, M.T. Emett, Arsenic removal from water using advanced oxidation processes. Toxicol. Lett. 133, 113 (2002)
K. Zhou, J. Zhang, Y. **ao, Z. Zhao, M. Zhang, L. Wang, X. Zhang, C. Zhou, High-efficiency adsorption of and competition between phenol and hydroquinone in aqueous solution on highly cationic amino-poly (vinylamine)-functionalized go-(o-mwcnts) magnetic nanohybrids. Chem. Eng. J. 389, 124223 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors are greatly acknowledging the assistance of environmental engineering research center, Sahand University of Technology, Tabriz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Noormohammadi, M., Zabihi, M. & Faghihi, M. Design, Characterization and Performance of the Modified Chitosan–Alumina Nanocomposites for the Adsorption of Hydroquinone and Arsenic (V) Ions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 41, 1535–1550 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-024-00078-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-024-00078-5