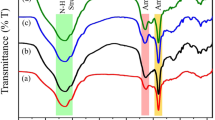
Abstract
In this study, the solubilization of waste coarse wool as a precursory step for the large-scale valorization of keratin was investigated using a green deep eutectic solvent (DES) based on L-cysteine and lactic acid. The investigation was undertaken via the response surface methodology and based on the Box–Behnken design for four process variables of temperature (70–110 °C), dissolution time (2–10 h), the mass of L-cysteine (0.5–2.5 g) in 20 mL of lactic acid, and wool load in the DES (0.2–0.6 g). Temperature was the most significant process variable influencing keratin yield from the waste coarse wool. The optimum keratin yield (93.77 wt.%) was obtained at the temperature of 105 °C, 8 h dissolution time, with 1.6 g L-cysteine in 20 mL of lactic acid using 0.5 g of wool. This study suggests L-cysteine and lactic acid as a green solvent with the potential to scale up keratin recovery from waste wool without significant destruction in the structure of the recovered keratin.
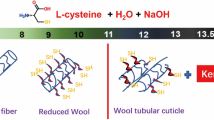
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Amir B, Pougnet P, and El Hami A (2020) 6 - Meta-model development. In Embedded mechatronic systems 2 (Second Edition), El Hami A, and Pougnet P, Editors., ISTE. pp 157–187
Aluigi A et al (2014) Keratins extracted from Merino wool and Brown Alpaca fibres as potential fillers for PLLA-based biocomposites. J Mater Sci 49(18):6257–6269
Box GE, Hunter JS, Hunter WG (2005) Statistics for experimenters: design, innovation, and discovery, vol 2. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Braun M, Altan H, Beck SJAE (2014) Using regression analysis to predict the future energy consumption of a supermarket in the UK. Appl Energy 130:305–313
Brown EM et al (2016) Comparison of methods for extraction of keratin from waste wool. Agric Sci 7(10):670
Fernández-d’Arlas B (2019) Tough and functional cross-linked bioplastics from sheep wool keratin. Scientific Reports, 9(1):14810
Feroz S et al (2020) Keratin - Based materials for biomedical applications. Bioactive Mater 5(3):496–509
Fitz-Binder C, Pham T, Bechtold T (2019) A second life for low-grade wool through formation of all-keratin composites in cystine reducing calcium chloride–water–ethanol solution. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94(10):3384–3392
Ghosh A et al (2014) Thermal effects of ionic liquid dissolution on the structures and properties of regenerated wool keratin. Polym Degrad Stab 108:108–115
Greenwold MJ et al (2014) Dynamic evolution of the alpha (α) and beta (β) keratins has accompanied integument diversification and the adaptation of birds into novel lifestyles. BMC Evol Biol 14(1):249
Haly A, Snaith J (1967) Differential thermal analysis of wool—the phase-transition endotherm under various conditions1. Text Res J 37(10):898–907
He J et al (2020) Highly efficient extraction of large molecular-weight keratin from wool in a water/ethanol co-solvent. Text Res J 90(9–10):1084–1093
Idris A et al (2014) Dissolution and regeneration of wool keratin in ionic liquids. Green Chem 16(5):2857–2864
Jiang Z et al (2018) Dissolution and regeneration of wool keratin in the deep eutectic solvent of choline chloride-urea. Int J Biol Macromol 119:423–430
Khosa M, Ullah AJJFP (2013) A sustainable role of keratin biopolymer in green chemistry: a review. J Food Process Beverages 1(1):8
Kumar GS, Thamizhavel A, Girija EK (2012) Microwave conversion of eggshells into flower-like hydroxyapatite nanostructure for biomedical applications. Mater Lett 76:198–200
Lee D-H, Jeong I-J, Kim K-J (2018) A desirability function method for optimizing mean and variability of multiple responses using a posterior preference articulation approach. Qual Reliab Eng Int 34(3):360–376
Love B (2017) Chapter 2 - Cell expression: proteins and their characterization. In: Love B (ed) Biomaterials. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 25–44
Maiuolo L et al (2020) Recent developments on 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions by catalysis in green solvents. Catalyst 10(1):65
McKittrick J et al (2012) The structure, functions, and mechanical properties of keratin. JOM 64(4):449–468
Mohammadi R et al (2016) Extraction optimization of pepsin-soluble collagen from eggshell membrane by response surface methodology (RSM). Food Chem 190:186–193
Moore KE et al (2016) Wool deconstruction using a benign eutectic melt. RSC Adv 6(24):20095–20101
Numata K, Kaplan DL (2011) 20 - Biologically derived scaffolds. In: Farrar D (ed) Advanced wound repair therapies. Woodhead Publishing, Delhi, pp 524–551
Nuutinen E-M et al (2019) Green process to regenerate keratin from feathers with an aqueous deep eutectic solvent. RSC Adv 9(34):19720–19728
Okoro OV, Sun Z, Birch J (2017) Meat processing dissolved air flotation sludge as a potential biodiesel feedstock in New Zealand: A predictive analysis of the biodiesel product properties. J Clean Prod 168:1436–1447
Okoro OV, Sun Z, Birch JJS (2018) Catalyst-free biodiesel production methods: a comparative technical and environmental evaluation. Sustainability 10(1):127
Okoro OV, Sun Z, Birch J (2019) Thermal depolymerization of biogas digestate as a viable digestate processing and resource recovery strategy. In: Advances in eco-fuels for a sustainable environment. Elsevier, pp 277–308
Polari L et al (2020) Keratin intermediate filaments in the colon: guardians of epithelial homeostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 129:105878
Pourjavaheri F et al (2019) Extraction of keratin from waste chicken feathers using sodium sulfide and l-cysteine. Process Biochem 82:205–214
Reddy, N. and M.S. Santosh (2016) Chapter 14 - Recovery and applications of feather proteins. In Protein Byproducts, G. Singh Dhillon, Editor. Academic Press, Cambridge pp 255–274
Roosta M, Ghaedi M, Asfaram A (2015) Simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted removal of malachite green and safranin O by copper nanowires loaded on activated carbon: central composite design optimization. RSC Adv 5(70):57021–57029
Saha S et al (2019) Keratin as a biopolymer. In: Sharma S, Kumar A (eds) Keratin as a protein biopolymer: extraction from waste biomass and applications. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 163–185
Schindl A et al (2019) Proteins in ionic liquids: reactions. Appl Futures 7:347
Shah A et al (2019) Keratin production and its applications: current and future perspective. Keratin as a protein biopolymer. Springer, pp 19–34
Shavandi A et al (2015) Bio-mimetic composite scaffold from mussel shells, squid pen and crab chitosan for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 80:445–454
Shavandi A, Carne A, Bekhit AA, Bekhit AE-DA (2017a) An improved method for solubilisation of wool keratin using peracetic acid. J Environ Chem Eng 5(2):1977–1984
Shavandi A., Silva TH, Bekhit AA, Bekhit AE-DA (2017b) Keratin: dissolution, extraction and biomedical application. Biomater Sci 5(9):1699–1735
Shavandi A et al (2021) A sustainable solvent based on lactic acid and l-cysteine for the regeneration of keratin from waste wool. Green Chem 23(3):1171–1174
Tonin C et al (2007) Thermal and structural characterization of poly(ethylene-oxide)/keratin blend films. J Therm Anal Calorim 89(2):601–608
Vasileva-Tonkova E, Gousterova A, Neshev G (2009) Ecologically safe method for improved feather wastes biodegradation. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63(8):1008–1012
Wang D, Tang R-C (2018) Dissolution of wool in the choline chloride/oxalic acid deep eutectic solvent. Mater Lett 231:217–220
Wang K et al (2016a) Extracting keratin from wool by using L-cysteine. Green Chem 18(2):476–481
Wang K et al (2016b) Extracting keratin from wool by using L-cysteine. Green Chem 18(2):476–481
Xu W et al (2006) Modification of wool fiber using steam explosion. Eur Polymer J 42(9):2168–2173
Yamauchi K, Yamauchi A, Kusunoki T, Kohda A, Konishi Y (1996) Preparation of stable aqueous solution of keratins, and physiochemical and biodegradational properties of films. J Biomed Mater Res: an off J Soc Biomater Jpn Soc Biomater 31(4):439–444
Zhang P et al (2019) Disulfide bond reconstruction: a novel approach for grafting of thiolated chitosan onto wool. Carbohydr Polym 203:369–377
Zhao W et al (2012) Sustainable and practical utilization of feather keratin by an innovative physicochemical pretreatment: high density steam flash-explosion. Green Chem 14(12):3352–3360
Zoccola M, Aluigi A, Tonin C (2009) Characterisation of keratin biomass from butchery and wool industry wastes. J Mol Struct 938(1):35–40
Zoccola M et al (2012) Microwave-assisted chemical-free hydrolysis of wool keratin. Text Res J 82(19):2006–2018
Acknowledgements
The first author (O.V.O) gratefully acknowledges the financial support of Wallonia-Brussels International via the Wallonie-Bruxelles International (WBI) excellence Postdoctoral fellowship. H.J acknowledges Innoviris Brussels, Belgium (https://innoviris.brussels) under the project 2019–BRIDGE–4: RE4BRU for his PhD fellowship. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not represent the official views of the above-mentioned fellowship agencies.
Funding
The research did not receive external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.V.O., L.N., and A.S. contributed to conceptualization, O.V.O., H.J., and P.H. were involved in methodology, O.V.O. provided software, M.H. and A.S. contributed to validation, O.V.O., H.J., P.H., L.N., H.A., and A.S. were involved in writing—original draft preparation, and O.V.O. H.J., P.H., L.N., H.A., and A.S contributed to writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okoro, O.V., Jafari, H., Hobbi, P. et al. Enhanced keratin extraction from wool waste using a deep eutectic solvent. Chem. Pap. 76, 2637–2648 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-02029-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-02029-4