Abstract
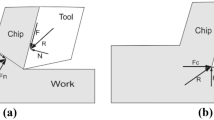
In recent years, the tool condition monitoring mechanism is necessary for analyzing the failure of the cutting tools in production practices. In a machining environment, steady and catastrophic failures of a tool are general faults associated with a machining process. The relationship between surface roughness, tool wear and vibration is explored during high-speed dry machining by using main input factor. L27 numbers of trials were performed in a CNC lathe with uncoated carbide CNMG120408 tool and alloy steel AISI 1040 workpiece. The predictable model is capable of expecting surface roughness (Ra), tool wear (VBc), and vibration of amplitude using observed data when turning alloy steel. The vibration was recorded only in the turning direction with a uniaxial accelerometer. Additionally, tool flank wear and finished work surface roughness are measured at various combinations of parameters. The outcomes of the work show that the axial feed rate is the main effective turning variable that influences surface roughness largely (91.97%). Optimization of turning process variables plays a significant role in turning to develop quality, manufacturing production rate and decrease production price. In this analysis, an advanced weighted principal component analysis strategy was initiated to optimize process variables in turning of 1040 alloy steel and the optimum relation was found to be d3 (0.5 mm)–f1 (0.06 mm/rev)–v3 (300 m/min). Higher depth of cutting along with largest cutting speed confirms the larger production rate which is desirable for industrial concern. Also, at the optimal setting, the excellent finish of surface with low wear and low acceleration is noticed with an improved S/N ratio of CQL from initial setting. However, the current work presented a better co-relation between tool vibrations, tool wear, and test surface finish which will be beneficial for the industrial uses.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Guvenc, M. Cakir, S. Mistikoglu, Experimental study on optimization of cutting parameters by using Taguchi method for tool vibration and surface roughness in dry turning of AA6013, in 10th International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Service Systems (2019), pp. 1032–1040
T. Mohanraj, S. Shankar, R. Rajasekar, N.R. Sakthivel, A. Pramanik, Tool condition monitoring techniques in milling process—a review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 1032–1042 (2019)
M.M. Faiz, M. Hairizal, A.B. Hadzley, M.F. Naim, T. Norfauzi, U.A.A. Umar, A.A. Aziz, S. Noorazizi, Effect of hydraulic pressure on hardness, density, tool wear and surface roughness in the fabrication of alumina based cutting tool. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. (JAMT) 13(2(1)) (2019)
A. Şahinoğlu, M. Rafighi, Investigation of vibration, sound intensity, machine current and surface roughness values of AISI 4140 during machining on the lathe. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45(2), 765–778 (2020)
C. Moganapriya, R. Rajasekar, K. Ponappa, R. Venkatesh, S. Jerome, Influence of coating material and cutting parameters on surface roughness and material removal rate in turning process using Taguchi method. Mater. Today Proc. 5(2), 8532–8538 (2018)
Z. Hessainia, A. Belbah, M.A. Yallese, T. Mabrouki, J.F. Rigal, On the prediction of surface roughness in the hard turning based on cutting parameters and tool vibrations. Measurement 46(5), 1671–1681 (2013)
G. Quintana, J. Ciurana, Chatter in machining processes: a review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 51(5), 363–376 (2011)
M. Siddhpura, R. Paurobally, A review of chatter vibration research in turning. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 61, 27–47 (2012)
S. Karabulut, A. Sahinoglu, Effect of the cutting parameters on surface roughness, power consumption and machine noise in machining of R260 steel. J. Polytech. Politek. 21(1), 237–244 (2018)
A. Şahinoğlu, Ş. Karabulut, A. Güllü, Study on spindle vibration and surface finish in turning of Al 7075, in Solid State Phenomena, vol. 261 (Trans Tech publications Ltd, Rijeka, 2017), pp. 321–327
R. Kishore, S.K. Choudhury, K. Orra, On-line control of machine tool vibration in turning operation using electro-magneto rheological damper. J. Manuf. Process. 31, 187–198 (2018)
A. Şahinoğlu, A. Güllü, M.A. Dönertaş, GGG50 Malzemenin Torna Tezgâhında Farklı Kesme Parametrelerinde İşlenmesinde Titreşim, Ses Şiddetininve Yüzey Pürüzlülüğünün İncelenmesi. Sinop Üniv. Fen Bilim. Derg. 2(1), 67–79 (2017)
S.A. Bagaber, A.R. Yusoff, Multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters to minimize power consumption in dry turning of stainless steel 316. J. Clean. Prod. 157, 30–46 (2017)
D.R. Salgado, F.J. Alonso, An approach based on current and sound signals for in-process tool wear monitoring. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 47(14), 2140–2152 (2007)
L. Zhou, J. Li, F. Li, Q. Meng, J. Li, X. Xu, Energy consumption model and energy efficiency of machine tools: a comprehensive literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 112, 3721–3734 (2016)
A. Şahinoğlu, A. Güllü, İ. Çiftçi, Analysis of surface roughness, sound level, vibration and current when machining AISI 1040 steel. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. Mühendis. Fen Bilim. Derg. 37(2), 423–437 (2019)
M.W. Azizi, S. Belhadi, M.A. Yallese, T. Mabrouki, J.F. Rigal, Surface roughness and cutting forces modeling for optimization of machining condition in finish hard turning of AISI 52100 steel. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26(12), 4105–4114 (2012)
I. Meddour, M.A. Yallese, H. Bensouilah, A. Khellaf, M. Elbah, Prediction of surface roughness and cutting forces using RSM, ANN, and NSGA-II in finish turning of AISI 4140 hardened steel with mixed ceramic tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97(5–8), 1931–1949 (2018)
A. Zerti, M.A. Yallese, I. Meddour, S. Belhadi, A. Haddad, T. Mabrouki, Modeling and multi-objective optimization for minimizing surface roughness, cutting force, and power, and maximizing productivity for tempered stainless steel AISI 420 in turning operations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102(1–4), 135–157 (2019)
S.R. Das, A. Kumar, D. Dhupal, Effect of machining parameters on surface roughness in machining of hardened AISI 4340 steel using coated carbide inserts. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2(4), 445–453 (2013)
A.R. Motorcu, The optimization of machining parameters using the Taguchi method for surface roughness of AISI 8660 hardened alloy steel. J. Mech. Eng. 56(6), 391–401 (2010)
K. Bouacha, M.A. Yallese, T. Mabrouki, J.F. Rigal, Statistical analysis of surface roughness and cutting forces using response surface methodology in hard turning of AISI 52100 bearing steel with CBN tool. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 28(3), 349–361 (2010)
A.K. Sahoo, B. Sahoo, Performance studies of multilayer hard surface coatings (TiN/TiCN/Al2O3/TiN) of indexable carbide inserts in hard machining: part II (RSM, grey relational and techno economical approach). Measurement 46(8), 2868–2884 (2013)
M.C. Cakir, C. Ensarioglu, I. Demirayak, Mathematical modeling of surface roughness for evaluating the effects of cutting parameters and coating material. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(1), 102–109 (2009)
Ş. Karabulut, U. Gökmen, H. Çinici, Optimization of machining conditions for surface quality in milling AA7039-based metal matrix composites. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(3), 1071–1082 (2018)
V.N. Gaitonde, S.R. Karnik, L. Figueira, J.P. Davim, Machinability investigations in hard turning of AISI D2 cold work tool steel with conventional and wiper ceramic inserts. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27(4), 754–763 (2009)
S. Thamizhmanii, S. Saparudin, S. Hasan, Analyses of surface roughness by turning process using Taguchi method. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 20(1–2), 503–506 (2007)
A. Bhattacharya, S. Das, P. Majumder, A. Batish, Estimating the effect of cutting parameters on surface finish and power consumption during high speed machining of AISI 1045 steel using Taguchi design and ANOVA. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 3(1), 31–40 (2009)
G. Kant, K.S. Sangwan, Prediction and optimization of machining parameters for minimizing power consumption and surface roughness in machining. J. Clean. Prod. 83, 151–164 (2014)
A. Labidi, H. Tebassi, S. Belhadi, R. Khettabi, M.A. Yallese, Cutting conditions modeling and optimization in hard turning using RSM, ANN and desirability function. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 18(4), 1017–1033 (2018)
M.K. Gupta, G. Singh, P.K. Sood, Experimental investigation of machining AISI 1040 medium carbon steel under cryogenic machining: a comparison with dry machining. J. Inst. Eng. Series (India) C 96(4), 373–379 (2015)
N.R. Dhar, S. Islam, M. Kamruzzaman, S. Paul, Wear behavior of uncoated carbide inserts under dry, wet and cryogenic cooling conditions in turning C-60 steel. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 28(2), 146–152 (2006)
B.S. Prasad, Y.R. Reddy, Analysis of real-time vibration assisted tool condition monitoring in drilling. Int. J. Manuf. Res. 14(2), 101–117 (2019)
R. Suresh, S. Basavarajappa, G.L. Samuel, Some studies on hard turning of AISI 4340 steel using multilayer coated carbide tool. Measurement 45(7), 1872–1884 (2012)
A. Das, N. Tirkey, S.K. Patel, S.R. Das, B.B. Biswal, A comparison of machinability in hard turning of EN-24 alloy steel under mist cooled and dry cutting environments with a coated cermet tool. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 19(1), 115–130 (2019)
A. Panda, A. Sahoo, A. Rout, Statistical regression modeling and machinability study of hardened AISI 52100 steel using cemented carbide insert. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 8(1), 33–44 (2017)
A. Erçetin, Ü.A. Usca, An experimental investigation of effect of turning AISI 1040 steel at low cutting speed on tool wear and surface roughness steel. Turkish J. Nat. Sci. 5(1), 29–36 (2016)
L. Huang, J.C. Chen, A multiple regression model to predict in-process surface roughness in turning operation via accelerometer. J. Ind. Technol. 17(2), 1–8 (2001)
B.C. Routara, S.D. Mohanty, S. Datta, A. Bandyopadhyay, S.S. Mahapatra, Combined quality loss (CQL) concept in WPCA-based Taguchi philosophy for optimization of multiple surface quality characteristics of UNS C34000 brass in cylindrical grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 51(1–4), 135–143 (2010)
D. Das, P. Mishra, S. Singh, A. Chaubey, B. Routara, Machining performance of aluminium matrix composite and use of WPCA based Taguchi technique for multiple response optimization. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 9(4), 551–564 (2018)
R. Kumar, A. Modi, A. Panda, A.K. Sahoo, A. Deep, P.K. Behra, R. Tiwari, Hard turning on JIS S45C structural steel: an experimental, modelling and optimisation approach. Int. J. Autom. Mech. Eng. 16(4), 7315–7340 (2019)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to KIIT Deemed to be University, Bhubaneswar, for providing the sufficient facilities to fulfill the current experimental research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swain, S., Panigrahi, I., Sahoo, A.K. et al. Effect of Tool Vibration on Flank Wear and Surface Roughness During High-Speed Machining of 1040 Steel. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 20, 976–994 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00905-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00905-x