Abstract
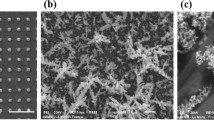
Simple and highly sensitive SERS substrates were produced using Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) prepared by laser ablation in water and available Digital Video Discs (DVDs). We used the simple “drop-cast’’ method to deposit AuNPs on the grating pattern surface of a DVD in place of the other methods such as electrochemical deposition, electrophoretic deposition and sputtering method which require some more equipment. AuNPs were proposed to be synthesized in water by laser ablation to form a nearly circular AuNP stain of small size on a DVD surface. The protecting polycarbonate layer of a DVD was removed from the DVD surface. The bare metallic DVD surface was rinsed carefully with ethanol and distilled water. The width of tracks on a DVD surface is around 300 nm and distance between them is around 450 nm. We prepared AuNPs by pulsed laser ablation of a gold piece in distilled water. The colloidal gold nanoparticles were deposited on DVD templates. We studied to produce an effective layer of AuNPs on DVD template for SERS substrates (AuNPs/DVD). The average SERS enhancement factor of the AuNPs/DVD SERS substrates is about 106. The SERS substrates can detect SERS spectra of Malachite Green and Amoxicillin at low concentrations of around 0.1–1 ppm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Strobbia, E. Languirand, and B.M. Cullum, Opt. Eng. 54, 100902 (2015).
J.R. Lombardi and R.L. Birke, Acc. Chem. Res. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ar800249y.
W.E. Smith, Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 955 (2008).
J.N. Anker, W.P. Hall, O. Lyandres, N.C. Shah, J. Zhao, and R.P. Van Duyne, Nat. Mater. 7, 442 (2008).
Y.S. Huh, A.J. Chung, and D. Erickson, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 6, 285 (2009).
D. Cialla, A. März, R. Böhme, F. Theil, K. Weber, M. Schmitt, and J. Popp, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 403, 27 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5631-x.
C.L. Haynes, A.D. McFarland, and R.P.V. Duyne, Anal. Chem. 77, 338A (2005).
H. Lin, J. Mock, D. Smith, T. Gao, and M.J. Sailor, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 11654 (2004).
C. Fang, A. Agarwal, H. Ji, W.Y. Karen, and L. Yobas, Nanotechnology 20, 405604 (2009).
X.M. Lin, Y. Cui, Y.H. Xu, B. Ren, and Z.Q. Tian, Anal BioanalChem 394, 1729 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2761-5.
R.J.C. Brown and M.J.T. Milton, J. Raman Spectrosc. 39, 1313 (2008).
M.J. Banholzer, J.E. Millstone, L. Qin, and C.A. Mirkin, Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 885 (2008).
N. Marquestaut, A. Martin, D. Talaga, L. Servant, S. Ravaine, S. Reculusa, D.M. Bassani, E. Gillies, and F. Lagugné-Labarthet, Langmuir 24, 11313 (2008).
S. Mohapatra, S. Siddhanta, D.R. Kumar, C. Narayana, and T.K. Maji, Eur J InorgChem 31, 4969 (2010).
W.B. Li, Y.Y. Guo, and P. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 6413 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp100526v.
M. Erol, Y. Han, S.K. Stanley, C.M. Stafford, H. Du, and S. Sukhishvili, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 7480 (2009).
S. Jana, S. Pande, A.K. Sinha, S. Sarkar, M. Pradhan, M. Basu, S. Saha, and T. Pal, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 1386 (2009).
B.K. Jena and C.R. Raj, Chem. Mater. 20, 3546 (2008).
P.F. Liao and A. Wokaun, J. Chem. Phys. 76, 751 (1982).
F. Le, D.W. Brandl, Y.A. Urzhumov, H. Wang, J. Kundu, N.J. Halas, J. Aizpurua, and P. Nordlander, ACS Nano 2, 707 (2008).
M. Futamata, Y.Y. Yu, and T. Yajima, J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 5271 (2011).
G. Giallongo, R. Pilot, C. Durante, and G. Granozzi, Plasmonics 6, 725 (2011).
C. Leordean, B. Marta, A.-M. Gabudean, M. Focsan, I. Botiz, and S. Astilean, Appl. Surf. Sci. 349, 190 (2015).
A.I. Radu, Y.Y. Ussembayev, M. Jahn, U.S. Schubert, and K. Weber, RSC Adv. 6, 44163 (2016).
M.K. Nieuwoudt, J.W. Martin, R.N. Oosterbeek, N.I. Novikova, X. Wang, J. Malmström, D.E. William, and M.C. Simpson, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408, 4403 (2016).
T.B. Nguyen, et al., Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 3, 025016 (2012).
A.C. Ferrari and J. Robertson, Phys. Rev. B 61, 14095 (2000).
J. Hong, M.K. Park, E.J. Lee, D.E. Lee, D.S. Hwang, and S. Ryu, Sci. Rep. 3, 2700 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/s02700.
K. Sivashanmugan, J.D. Liao, B.H. Liu, C.-K. Yao, and S.-C. Luo, Sens. Actuators, B 207, 430 (2015).
Y. Zhang, W. Yu, L. Pei, K. Lai, B.A. Rasco, and Y. Huang, Food Chem. 169, 80 (2015).
Q. Cen, Y. He, M. Xu, J. Wang, and Z. Wang, J. Chem. Phys. 142, 114201 (2015).
P. Kumar, R. Khosla, M. Soni, D. Deva, and S.K. Sharma, Sens. Actuators, B 246, 477 (2017).
S. Schlücker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 2 (2014).
C.X. Fang, J.H. Li, and Y.Z. Liang, J. Instrum. Anal. 31, 541 (2011).
X. Li and Y. Lu, J. Bei**g Inf. Sci. Technol. Univ. 28, 27 (2013).
A. Calborean, D. Maniu, V. Chis, T. Iliescu, and V.K. Rastogi, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 9, 680 (2007).
A. Bebu, L. Szabo, N. Leopold, and L. David, J. Mol. Struct. 993, 52 (2011).
Wei Ji, Li Wang, He Qian, and Weirong Yao, Spectrosc. Lett. 47, 451 (2014).
E.C. Le Ru, E. Blackie, M. Mayer, and P.G. Etchegoin, J. Phys. Chem. 111, 13794 (2007).
Acknowledgments
This research work is supported by the Project ĐTĐLCN-01/18 of University of Science—VNU Hanoi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.B., Nguyen, N.A. & Ngo, G.L. A Simple and Rapid Method to Produce SERS Substrates Using Au Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation and DVD Template. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 311–317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07754-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07754-x