Abstract
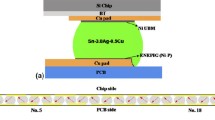
The electromigration failure mechanism in flip-chip solder joints through the rapid dissolution of the Cu metallization was studied in detail. The ambient temperature was found to be a very important factor in this failure mechanism. When the ambient temperature was changed from 100°C to 70°C, the time to failure changed from 95 min to 31 days. The results of this study indicate that temperature, as an experimental variable, is not less important than the current density in electromigration study. The surface temperatures of the chip and substrate during electromigration were also measured. The temperature of the Si chip was reasonably homogeneous because of the fact that Si is a very good thermal conductor. It was also reasoned that the high thermal conductivity of the PbSn solder could not support a temperature gradient large enough to induce thermomigration across the solder joint in the present study. Experimentally, no evidence of mass transport caused by thermomigration was observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semiconductor Industry Association, 1999 International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor (San Jose, CA: Semiconductor Industry Association, 1999).
S. Brandenberg and S. Yeh, Proc. 1998 Surface Mount Int. Conf. Exhib. (Edina, MN: SMTA, 1998), p. 337.
T.Y. Lee, K.N. Tu, and D.R. Frear, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 4502 (2001).
E.C.C. Yeh, W.J. Choi, K.N. Tu, P. Elenius, and H. Balkan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 580 (2002).
K. Zeng and K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 38, 55 (2002).
J.D. Wu, P.J. Zheng, K. Lee, C.T. Chiu, and J.J. Lee, Proc. 2002 Electronic Components and Technology Conf. (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2002), pp. 452–457.
Y.C. Hu, Y.H. Lin, C.R. Kao, and K.N. Tu, J. Mater. Res. 18, 2544 (2003).
K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5451 (2003).
H. Ye, C. Basaran, and D. Hopkins, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1045 (2003).
J.R. Black, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. ED-16, 338 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y.H., Tsai, C.M., Hu, Y.C. et al. Electromigration-induced failure in flip-chip solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 34, 27–33 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-005-0176-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-005-0176-4