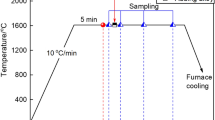
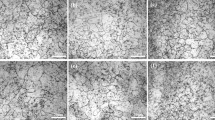
Abstract
The effect of cerium addition on the rolling contact fatigue (RCF) life of a high-carbon chromium bearing steel was studied using laboratory experiments. The RCF life (L10 and L50) of bearing steels with and without cerium was tested using a thrust type rolling contact fatigue tester, and the result showed that under the experimental condition of the current study, the L10 and L50 of cerium-containing bearing steel were 1.2 times and 2 times that of the cerium-free bearing steel. The composition, size, distribution, and number density of inclusions in the steel were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with the function of automatic inclusion detection. The addition of trace cerium in bearing steel mainly modified initial large CaO-MgO-Al2O3 complex inclusions into small CeAlO3 and Ce2O2S inclusions. The statistics of extreme values (SEV) method was used to estimate the characteristic size of different kinds of maximum inclusions in the sample to compare with the RCF life which was measured by experiments. As a result, the RCF life of the bearing steel decreased with the increase of characteristic sizes of the maximum inclusion (CMSI), and oxide inclusions were determined as the most detrimental. In addition, the stress distribution of the RCF sample was analyzed using finite element simulation, and combined with the observation of the fatigue cracks initiated from inclusions, the range of dangerous areas under experimental Hertz stress was proposed. The distribution of inclusions on the cross-section and the number density of inclusions in the sample showed that the effect of the number density of inclusions on the rolling contact fatigue life was much less than the inclusion size.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Lund and J. Åkesson: ASTM International, 1988, pp. 308–30.
J. Monnot, B. Heritier and J.Y. Cogne: ASTM International, 1988, pp. 149–65.
G. Lundberg and A. Palmgren: Acta Polytech. Scand., 1947, vol. 1, pp. 1–52.
P. Becker: Met. Technol., 1981, vol. 8, pp. 234–43.
W. Duckworth and E. Ineson: Clean steel, 1963, vol. 77, pp. 87–103.
Y. Murakami: Metal Fatigue, 1993, vol. 28, pp. 13–23.
T. Uesugi: Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1988, vol. 74, pp. 1889–94.
J. Zhang, S. Li, Z. Yang, G. Li, W. Hui, and Y. Weng: Int. J. Fatigue, 2007, vol. 29, pp. 765–71.
A. Medvedeva, J. Bergström and S. Gunnarsson: Steel Res. Int., 2008, vol. 79, pp. 376–81.
Y. Liu, Z. Yang, Y. Li, S. Chen, S. Li, W. Hui, and Y. Weng: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 517, pp. 180–84.
T. Lund, J. Beswick, and S.W. Dean: J. ASTM Int., 2010, vol. 7, p. 102559.
Z. Yang, S. Li, Y. Li, Y. Liu, W. Hui, and Y. Weng: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 559–64.
K. Hashimoto, K. Hiraoka, K. Kida, and E. CostaSantos: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 28, pp. 39–43.
C. Yang, Y. Luan, D. Li, and Y. Li: Int. J. Fatigue, 2018, vol. 116, pp. 396–408.
C. Gu, J. Lian, Y. Bao, and S. Münstermann: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2019, vol. 751, pp. 133–41.
D. Spriestersbach, P. Grad, and E. Kerscher: Int. J. Fatigue, 2014, vol. 64, pp. 114–20.
U. Karr, R. Schuller, M. Fitzka, B. Schönbauer, D. Tran, B. Pennings, and H. Mayer: J. Mater. Sci., 2017, vol. 52, pp. 5954–67.
K. Hashimoto, T. Fujimatsu, N. Tsunekage, K. Hiraoka, K. Kida, and E.C. Santos: Mater. Des., 2011, vol. 32, pp. 1605–11.
Y. Furuya, H. Hirukawa, T. Kimura, and M. Hayaishi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 1722–30.
H. Li, Y.-C. Yu, X. Ren, S.-H. Zhang, and S.-B. Wang: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2017, vol. 24, pp. 925–34.
Q. Ren and L. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 589–600.
Z. Shaohua, Y. Yanchong, W. Shebin, and L. Hao: J. Rare Earths, 2017, vol. 35, pp. 518–24.
C. Yang, Y. Luan, D. Li, and Y. Li: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 1298–1308.
C. Yang, Y. Luan, D. Li, and Y. Li: Int. J. Fatigue, 2020, vol. 131, p. 105263.
Z. Cao, Z. Shi, F. Yu, G. Wu, W. Cao, and Y. Weng: Int. J. Fatigue, 2019, vol. 126, pp. 1–5.
H. Fu, J.J. Rydel, A.M. Gola, F. Yu, K. Geng, C. Lau, H. Luo, and P.E. Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo: Int. J. Fatigue, 2019, vol. 129, pp. 48–79.
S.M. Moghaddam, F. Sadeghi, K. Paulson, N. Weinzapfel, M. Correns, V. Bakolas, and M. Dinkel: Int. J. Fatigue, 2015, vol. 80, pp. 203–15.
W. Ma, Y. Bao, M. Wang, and L. Zhao: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 536–42.
G. Cheng, L. Zhang, and Y. Ren: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2020, vol. 47, pp. 1217–25.
X. Wang, G. Li, Y. Liu, F. Wang, and Q. Wang: ISIJ Int., 2021, vol. 61, pp. 1850–59.
X. Liu, J. Yang, F. Zhang, X. Fu, H. Li, and C. Yang: J. Rare Earths, 2021, vol. 39, pp. 477–86.
W. Meng and G. Eesley: Thin Solid Films, 1995, vol. 271, pp. 108–16.
S. Davis and G. Gutiérrez: J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 2011, vol. 23, p. 495401.
Y. Liu, Y. Jiang, J. Feng, and R. Zhou: Physica B, 2013, vol. 419, pp. 45–50.
J. Feng, B. **ao, J. Chen, Y. Du, J. Yu, and R. Zhou: Mater. Des., 2011, vol. 32, pp. 3231–39.
S. Pugh: Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci., 1954, vol. 45, pp. 823–43.
Y. Murakami: Int. J. Fatigue, 1994, vol. 3, pp. 345–51.
E.J. Gumbel: Statistics of Extremes. Columbia University Press, Columbia, 1958.
M. Nagao, K. Hiraoka, and Y. Unigame: Sanyo Tech. Rep., 2005, vol. 12, pp. 38–45.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1860206, No.51725402), S&T Program of Hebei (Grant No. 20311006D), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. E2021203062), and the High Steel Center (HSC) at North China University of Technology, Yanshan University, and University of Science and Technology Bei**g.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Ren, Q. & Zhang, L. Effects of Cerium on Non-metallic Inclusions and Rolling Contact Fatigue Life of a High-Carbon Chromium Bearing Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 167–178 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-022-06856-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-022-06856-2