Abstract
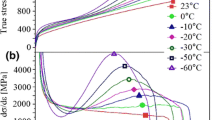
The temperature above which neither stress nor plastic strain can cause austenite to transform to martensite is determined for 304 austenitic stainless steel by X-ray diffraction measurements on specimens that were previously subjected to isothermal tension tests. The specimens were tested at 273 K, 298 K, 308 K, 333 K, and 373 K (0 °C, 25 °C, 35 °C, 60 °C, and 100 °C). A new isothermal testing technique was used not only for controlling the testing temperature but also for averting deformation-induced heating. Hence, the effect of temperature on the strain-induced martensite is decoupled from that of strain. The diffraction measurements reveal that the martensite volume fraction decreases linearly with the testing temperature up to a critical temperature, which is found by linearly extrapolating to zero martensite volume fraction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.B. Olson and M. Cohen, Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp 791-795.
Meyers, M.A. and Chawla, K.K., Mechanical Metallurgy, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1984, pp.467-493.
Z. Nishiyama, Martensitic Transformation, Academic Press, NY, 1978, pp. 263-292.
A.M. Beese, D. Mohr, Exp. Mech., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 667-676.
M. Mukherjee, S.B. Singh and O.N. Mohanty, Metall. & Mat’l Trans., 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 2319-2328.
Xu, Y., S. H. Zhang, M. Cheng, and H. W. Song: Scripta Mat., 2012, vol. 67, pp. 771-774.
S.S. Hecker, M.G.. Stout, K.P. Staudhammer and J.L. Smith, Metall. Trans., 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 619-626.
R.G. Stringfellow, D.M. Parks and G.B. Olson, Acta Metall. & Mater., 1992, vol. 40A, pp. 1703-1716.
E.S. Perdahcıoglu and H.J.M. Geijselaers, Acta Mat., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 4409-4419.
M.-G. Lee, S.-J. Kim, and H.-N. Han: Int. J. Plast., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 688–710.
L.-E. Lindgren, M. Olsson and P. Carlsson, Int’l J. Plast., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 1576-1590.
Y. Tomita and T. Iwamoto, Int’l. J. Mech. Sci., 1995, vol. 37, pp. 1295-1305.
G.L. Huang, D.K. Matlock, and G. Krauss: Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 1239-1246.
H.C. Shin, T.K. Kwon Ha, and Y.W. Chang: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 823–829.
G.W. Cullen and Y.P. Korkolis, Int’l J. Solids & Struct, 2013, vol. 50, pp. 1621-1633.
A.K. De, D.C. Murdock, M.C. Mataya, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock, Scripta Mat., 2004, vol. 50, pp. 1445-1449.
K. Tsuzaki, T. Maki, and I. Tamura: J. Phys., 1982, vol. 43, pp. C4-423–C4-428.
W.S. Farren and G.I. Taylor, Proc. Royal Soc. London, 1925, vol. A107, pp. 422-451.
G.W. Cullen and Y.P Korkolis, University of New Hampshire, unpublished research, 2013.
K.S. Raghavan and R.H. Wagoner: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 2143-2150.
B. Petit, N. Gey, M. Cherkaoui, B. Bolle, and M. Humbert, Int’l J. Plast., 2007, vol. 23, pp. 323-341.
K.S. Raghavan: AK Steel, unpublished research, 2013.
A.D. Krawitz: Introduction to Diffraction in Materials Science and Engineering, John Wiley, New York, 2001, pp. 128–43, 151–78, 240–60.
R.E. Smallmann and A.H.W. Ngan: Physical Metallurgy and Advanced Materials, 7th ed., Butterworth Heinemann, Amsterdam, 2007, pp. 414–20.
B. Fultz, and J.M. Howe, Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials, third ed., Springer, Berlin, 2008, pp. 119-266.
Acknowledgments
The help of Prof. J. Krzanowski and the graduate student Graham Cullen during this work is acknowledged with thanks, as is the support of the U.S. National Science Foundation through Grant CMMI-1031169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 1, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moser, N.H., Gross, T.S. & Korkolis, Y.P. Martensite Formation in Conventional and Isothermal Tension of 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel Measured by X-ray Diffraction. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 4891–4896 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2422-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2422-y