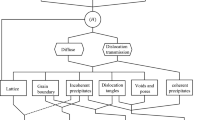
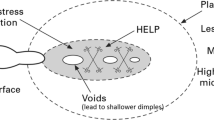
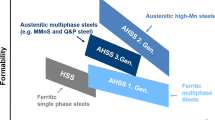
Abstract
Advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) have a better combination between strength and ductility than conventional HSS, and higher crash resistances are obtained in concomitance with weight reduction of car structural components. These steels have been developed in the last few decades, and their use is rapidly increasing. Notwithstanding, some of their important features have to be still understood and studied in order to completely characterize their service behavior. In particular, the high mechanical resistance of AHSS makes hydrogen-related problems a great concern for this steel grade. This article investigates the hydrogen embrittlement (HE) of four AHSS steels. The behavior of one transformation induced plasticity (TRIP), two martensitic with different strength levels, and one hot-stam** steels has been studied using slow strain rate tensile (SSRT) tests on electrochemically hydrogenated notched samples. The embrittlement susceptibility of these AHSS steels has been correlated mainly to their strength level and to their microstructural features. Finally, the hydrogen critical concentrations for HE, established by SSRT tests, have been compared to hydrogen contents absorbed during the painting process of a body in white (BIW) structure, experimentally determined during a real cycle in an industrial plant.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Iron & Steel Institute Committee on Automotive: Advanced High Strength Steel (AHSS) Application Guidelines, Version 3, 2006, www.worldautosteel.org.
C. Federici, S. Maggi, and S. Rigoni: Proc. Conf. on New Developments on Metallurgy and Applications of High Strength Steels, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2008.
Y. Mukai: Kobelco Tech. Rev., 2005, no. 26, pp. 26–31.
B.C. De Cooman, L. Chen, H.S. Kim, Y. Estrin, S.K. Kim, and H. Voswinckel: Proc. Conf. on New Developments on Metallurgy and Applications of High Strength Steels, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2008.
W. Bleck and K. Phiu-On: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vols. 500/501, pp. 97–114.
R.A. Oriani, J.P. Hirth, and M. Smialowski: Hydrogen Degradation of Ferrous Alloys, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985.
J.P. Hirth: Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 861–90.
ASM Materials Handbook: Metals Handbook, 9th ed., vol. 13, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1987, p. 330.
I.M. Bernstein: Proc. 5 th Int. Conf. on the Effect of Hydrogen on the Behavior of Materials, A.W. Thompson and N.R. Moody, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 3–11.
T.B. Hilditch, S-B. Lee, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock: SAE SP, 2003, no. 1764, pp. 47–56.
S-J. Lee, J.A. Ronevich, G. Krauss, and D. Matlock: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 294–301.
K.H. So, J.S. Kim, Y.S. Chun, K.T. Park, Y-K. Lee, and C.S. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 1952–1959.
H. Mohrbacher: Proc. Conf. on Steel Product Metallurgy and Application, Pittsburgh, PA, 2008.
J.A. Ronevich, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock: SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf., 2010, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 255–67.
W.J. Pollock: ASTM-STP 962, Hydrogen Embrittlement: Prevention and Control, L. Raymond, ed., ASTM STP 962, Philadelphia, PA, 1988, pp. 68–80.
I. Krylova: Progr. Org. Coating., 2001, vol. 42, pp. 119–31.
J. Cranck: The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed., Oxford Science Publications, Oxford, U.K., 1975, pp. 49–51.
M.A.V. Devanathan and Z. Stachurski: Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1962, vol. 270, no. 1340, pp. 90–102.
ASTM G129 – 00 (reapproved 2006): Standard Practice for Slow Strain Rate Testing to Evaluate the Susceptibility of Metallic Materials to Environmentally Assisted Cracking, ASTM International, West Conshohoken, PA, 2006.
D.A. Berman and V.S. Agarwala: ASTM-STP 962 Hydrogen Embrittlement: Prevention and Control, L. Raymond, ed., ASTM STP 962 Philadelphia, PA, 1988, pp. 98–104.
ASTM F 1113 – 87 (reapproved 2005): Standard Test Method for Electrochemical Measurement of Diffusible Hydrogen in Steels (Barnacle Electrode), ASTM International, West Conshohoken, PA, 2005.
M. Beghini, G. Benamati, L. Bertini, I. Ricapito, and R. Valentini: J. Nucl. Mater., 2001, vol. 288, pp. 1–6.
E. Akiyama, S. Li, Z. Zhang, M. Wang, K. Matsukado, K. Tsuzaki, and B. Zhang: Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf., B. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R. Jones, eds., ASM International Materials Park, OH, 2009, p. 54–61.
R. Valentini, A. Solina, S. Matera, and P. De Gregorio: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 3773–80.
G. Lovicu, M. De Sanctis, A. Dimatteo, R. Valentini, and P. Trombetti: 32° Convegno Nazionale AIM, Ferrara, Italy, 2008.
ASTM G148-97 (reapproved 2003), Standard Practice for Evaluation of Hydrogen Uptake, Permeation, and Transport in Metals by an Electrochemical Technique, 2003.
C.J. McMahon, X. Liu, J. Kameda, and M.J. Morgan: Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf., B. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R. Jones, eds., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2009, pp. 46–53.
Die Design Handbook, Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME), Dearborn MI, 1990, pp. 6–9.
S.M. Teus, V.N. Shyvanyuk, and V.G. Gavriljuk: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 497, pp. 290–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 28, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lovicu, G., Bottazzi, M., D’Aiuto, F. et al. Hydrogen Embrittlement of Automotive Advanced High-Strength Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 4075–4087 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1280-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1280-8