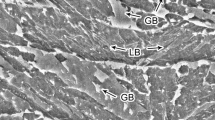
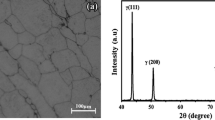
Abstract
Thermomechanical processing of microalloyed steels containing niobium can be performed to obtain deformed austenite prior to transformation. Accelerated cooling can be employed to refine the final microstructure and, consequently, to improve both strength and toughness. This general rule is fulfilled if the transformation occurs on a quite homogeneous austenite microstructure. Nevertheless, the presence of coarse austenite grains before transformation in different industrial processes is a usual source of concern, and regarding toughness, the coarsest high-angle boundary units would determine its final value. Sets of deformation dilatometry tests were carried out using three 0.06 pct Nb microalloyed steels to evaluate the effect of Mo alloying additions (0, 0.16, and 0.31 pct Mo) on final transformation from both recrystallized and unrecrystallized coarse-grained austenite. Continuous cooling transformation (CCT) diagrams were created, and detailed microstructural characterization was achieved through the use of optical microscopy (OM), field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEGSEM), and electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD). The resultant microstructures ranged from polygonal ferrite (PF) and pearlite (P) at slow cooling ranges to bainitic ferrite (BF) accompanied by martensite (M) for fast cooling rates. Plastic deformation of the parent austenite accelerated both ferrite and bainite transformation, moving the CCT curves to higher temperatures and shorter times. However, an increase in the final heterogeneity was observed when BF packets were formed, creating coarse high-angle grain boundary units.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIPS is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd.
References
G.I. Garcia: Int. Conf. Microalloying ‘95, ISS, Warrendale, PA, 1995, pp. 365–75.
S.G. Jansto: New Developments on Metallurgy and Applications of High Strength Steels Conf., Buenos Aires, 2008, TMS, Warrendale, PA, pp. 1313–26.
N.A. McPherson: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2009, vol. 36, pp. 193–200.
E.J. Czyryca, D.P. Kihl, and R. DeNale: AMPTIAC Q., 2003, vol. 7, pp. 63–70.
B. Dutta, E. Valdés, and C.M. Sellars: Acta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 652–62.
M.G. Akben, I. Weiss, and J.J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 111–21.
O. Kwon, and A.J. DeArdo: Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, vol. 39, pp. 529–38.
D.N. Hanlon, J. Sietsma, and S. van der Zwaag: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1028–36.
Y. van Leeuwen and J. Sietsma: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 539–543, pp. 4572–77.
S. Cai and J.D. Boyd: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vols. 500–501, pp. 171–78.
H. Asahi, A. Yagi, and M. Ueno: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 1375–81.
T. Tanaka: Int. Met. Rev., 1981, vol. 26, pp. 185–212.
H. Meuser, F. Grimpe, S. Meimeth, C.J. Heckmann, and C. Träger: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vols. 500–501, pp. 565–72.
D. Chakrabarti, M. Strangwood, and C. Davis: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 780–95.
P. Uranga, A.I. Fernández, B. López, and J.M. Rodriguez-Ibabe: 43rd Mechanical Working and Steel Processing Conf., ISS, Warrendale, PA, 2001, vol. 33, pp. 511–29.
B.L. Bramfitt and J.G. Speer: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 817–29.
T. Araki, I. Kozasu, H. Tankechi, K. Shibata, M. Enomoto, and H. Tamehiro, eds., Atlas for Bainitic Microstructures, ISIJ, Tokyo, 1992, vol. 1.
H.I. Aaronson and H.A. Domian: Trans. AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 781–96.
M. Hillert: in Solid-Solid Phase Transformations, H.I. Aaronson, D.E. Laughlin, R.F. Sekerka, and C.M. Wayman, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 789–806.
D.E. Coates: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 2313–25.
T.B. Massalski: in Phase Transformations, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1970, pp. 433–95.
M. Hillert: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 411–19.
J. Cawley, C.F. Harris, and E.A. Wilson: New Aspects of Microstructures in Modern Low Carbon High Strength Steels Symp., ISIJ, Tokyo, 1994, pp. 11–14.
K. Shibata and K. Asakura: New Aspects of Microstructures in Modern Low Carbon High Strength Steels Symp., ISIJ, Tokyo, 1994, pp. 31–34.
G. Krauss and S.W. Thompson: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 937–45.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels, Transformations, Microstructure and Properties, 2nd ed., The Institute of Materials, London, 2001, pp. 277–79.
H.J. Lee, G. Spanos, G.J. Shiflet, and H.I. Aaronson: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 1129–40.
S. Zajac, V. Schwinn, and K.H. Tacke: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vols. 500–501, pp. 387–94.
R.F. Speyer: Thermal Analysis of Material, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY, 1994.
C. García de Andrés, F.B. Caballero, C. Capdevila, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 39, pp. 791–96.
ABAQUS Reference Manuals, Dassault Systèmes, Providence, RI, 2009.
R. Petrov, L. Kestens, and Y. Houbaert: Mater. Charact., 2004, vol. 53, pp. 51–61.
P. Cizek, B.P. Wynne, C.H.J. Davies, B.C. Muddle, and P.D. Hodgson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 1331–49.
P.A. Manohar, T. Chandra, and C.R. Killmore: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 36, pp. 1486–93.
I. Tamura: Int. Conf. Thermec ‘88, ISIJ, Tokyo, 1988, pp. 1–10.
T. Tanaka: Int. Conf. Microalloying 95, M. Korchynsky, A.J. DeArdo, P. Repas, and G. Tither, eds., Pittsburgh, ISS, Warrendale, PA, 1995, pp. 165–81.
R. Bengochea, B. Lopez, and I. Gutierrez: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 417–26.
R. Bengochea, B. Lopez, and I. Gutierrez: in Microalloying in Steels (μ-as 98), J.M. Rodriguez-Ibabe, I. Gutierrez, and B. Lopez, eds., San Sebastian, Spain, 1998, pp. 201–08.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels, Transformations, Microstructure and Properties, 2nd ed., The Institute of Materials, London, 2001, pp. 201–24.
A. Kazimierz and J. Lis: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vol. 539–543, pp. 4620–25.
M. Umemoto, Z.H. Guo, and I. Tamura: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1987, vol. 3, pp. 249–55.
S. Zajac, T. Siwecki, B. Hutchinson, and M. Attlegard: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2681–94.
J.H. Beynon and C.M. Sellars: High Strength Low Alloy Steels Conf., Wollongong, 1984, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 142–50.
A. From and R. Sandström: Mater. Charact., 1999, vol. 42, pp. 111–22.
T. Hanamura, F. Yin, and K. Nagai: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 610–17.
T. Furuhara, H. Kawata, S. Morito, and T. Maki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. A431, pp. 228–36.
T. Furuhara, N. Takayama, and G. Miyamoto: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, vols. 638–642, pp. 3044–49.
A. Lambert-Perlade, A.F. Gourgues, and A. Pineau: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 2337–48.
K. Fujiwara, S. Okaguchi, and H. Ohtani: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 1006–12.
K. Fujiwara and S. Okaguchi: Mater. Sci. Forum, 1998, vols. 284–286, pp. 271–78.
R.Y. Zhang and J.D. Boyd: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 1448–59.
Acknowledgments
Financial support of this work by the Spanish Science and Innovation Department (MAT2009-09250 project) is gratefully acknowledged. One of the authors (NI) acknowledges a research grant from the University of Navarra. PU is grateful to NSF and TMS for the MS&T’10 Conference registration fee funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 16, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isasti, N., Jorge-Badiola, D., Taheri, M.L. et al. Effect of Composition and Deformation on Coarse-Grained Austenite Transformation in Nb-Mo Microalloyed Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 3729–3742 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0624-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0624-0