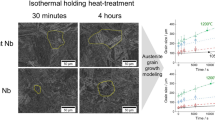
A novel processing route of cold rolling and reversion annealing for enhanced mechanical properties has been investigated in metastable 17Cr-7Ni-type austenitic stainless steels, i.e., commercial grades AISI 301LN and AISI 301, and in some experimental heats. The investigation was essentially aimed at studying the possibility of processing nano/submicron-grained structure in these steels and to rationalize the possible effects of alloying elements on the reversion mechanisms. The steels were cold rolled to various reductions between 45 and 78 pct to induce the formation of martensite, and subsequently annealed between 600 °C to 1000 °C for short annealing times (mostly 1 to 100 seconds). Microstructure examinations of the reversion-annealed 301LN steel revealed that an ultrafine-grained austenitic structure was formed by the diffusional transformation mechanism within a short holding time above 700 °C, even after the lowest cold-rolling reduction. In contrast, in 301 steel and experimental heats, the shear type of transformation occurred at temperatures above 650 °C, but fine austenite grains were only formed by recrystallization at higher temperatures or longer holding times, e.g., at 900 °C/100 s. An attempt has been made to determine the reversion mechanisms in various steels by modifying the criteria governing the Gibbs free energy change during the martensite-austenite reversion in Cr-Ni alloys. The room temperature (RT)-tensile property evaluation showed that excellent combinations of yield or tensile strength and elongation are possible to achieve, depending mainly on annealing conditions both in the 301LN and 301 steels, but the experimental heats were too unstable for high ductility. Ultrafine grain size of austenite contributed to this in 301LN and shear-transformed high-dislocated austenite in 301. Upon reversion annealing, the reversion mechanism did not affect the texture. The texture of the reverted fine-grained austenite is very strong compared to the typical texture of commercially cold-rolled and annealed 301LN steel.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Thermocalc is a trademark of Thermo-Calc Software, Stockholm, Sweden.
References
P.-J. Cunat and T. Pauly: Proc. 4th Eur. Stainless Steel Science and Market Congr., Association Technique De La Siderburgie Francaise, Paris, 2002, pp. 10–18
R. Andersson, E. Schedin, C. Magnusson, J. Ocklund, and A. Persson: Proc. 4th Eur. Stainless Steel Science and Market Congr., Association Technique De La Siderburgie Francaise, Paris, 2002, pp. 57–60
T. Christiansen, M.A.J. Somers: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 675–82
Design Manual for Structural Stainless Steel, 3rd ed., Euro Inox and The Steel Construction Institute, Luxembourg, 2006, p. 19
A. Kyröläinen: Outokumpu Stainless Oy, Tornio, Finland, process data, 2005
M. Buccioni, L. Alleva, and M. Barteri: Proc. 5th Eur. Stainless Steel Science and Market Congr., J.A. Odriozola and A. Paul, eds., Centro De Investigaciones Cientificas Isla De La Cartuja, Universidad de Sevilla, Seville, Spain, 2005, pp. 31–36
Y. Ma, J.-E. **, Y.-K. Lee: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 1311–15
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, Y. Tokunaga: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31 (12), pp. 1431–37
K. Tomimura , S. Takaki , S. Tanimoto, Y. Tokunaga: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31 (7), pp. 721–27
Y. Yagodzinskyy, J. Romu, P. Nenonen, H. Hänninen: 7th Int. Conf. High Nitrogen Steels 2004, Ostend, Belgium, Steel Grips, GRIPS' Sparkling World of Steel, 2004, vol. 2, Suppl., pp. 103–12.
S. Takaki and T. Suzaki: Proc. Stainless Steel ’9 Science and Market–3rd Eur. Congress, Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, Chia Laguna Sardinia, Italy, 1999, vol. 2, pp. 49–54
S. Takaki, K. Tomimura, S. Ueda: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34 (6), pp. 522–27
S. Takaki and Y. Tokunaga: Proc. 1st European Stainless Steel Conf., Florence, Italy, 1993, pp. 2.327–2.332
X.H. Chen, J. Lu, L. Lu, K. Lu: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 1039–44
D.L. Johanssen, A. Kyröläinen, P.J. Ferreira: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 2325–38
M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, M. Koljonen, P. Aspegren, T. Taulavuori, and A. Kyröläinen: Proc. 5th Eur. Stainless Steel Science and Market Congr., J.A. Odriozola and A. Paul, eds., Centro De Investigaciones Cientificas Isla De La Cartuja, Universidad de Sevilla, Seville, Spain, 2005, pp. 37–42
M. Somani, P. Karjalainen, P. Juntunen, S. Rajasekhara, P. Ferreira, A. Kyröläinen, T. Taulavuori, and P. Aspegren: Iron and Steel, vol. 40, pp. 283–89; Int. Conf. HSLA Steels 2005 and ISUGS 2005, Sanya, China, 2005
S. Rajasekhara, M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, A. Kyröläinen, and P.J. Ferreira: Iron and Steel, vol. 40, pp. 232–37; Int. Conf. of HSLA Steels 2005 and ISUGS 2005, Sanya, China, 2005
S. Rajasekhara, M.C. Somani, M. Koljonen, L.P. Karjalainen, A. Kyröläinen, and P.J. Ferreira: MRS 2005 Fall Meeting, Materials Research Society, Boston, MA, 2006, vol. 903E, pp. 40.1–40.6
M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, A. Kyröläinen, T. Taulavuori: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 539–543, pp. 4875–80
J. Talonen, P. Nenonen, G. Pape, H. Hänninen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 421–32
K. Nohara, Y. Ono, N. Ohashi: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1977, vol. 63, pp. 212–22
R.L. Miller: Trans. ASM, 1968, vol. 61, pp. 592–97
G.B. Olson, M. Cohen: Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 791–95
S. Rajasekhara, P.J. Ferreira, L.P. Karjalainen, and A. Kyröläinen: Proc. 6th Eur. Stainless Steel Conf. Science and Market, P. Karjalainen and S. Hertzman, eds., Jernkontoret, Helsinki, Finland, 2008, pp. 505–10
L. Kaufman, E.V. Clougherty, R.J. Weiss: Acta Metall., 1963, vol. 11, pp. 323–35
T. Takemoto, Y. Murata, T. Tanaka: ISIJ Int., 1990, vol. 30 (8), pp. 608–14
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, Y. Tokunaga: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1990, vol. 76 (10), pp. 1728–35
K.-E. Thelning: Steel and Its Heat Treatment, Bofors Handbook, Butterworth and Co., London, 1975, pp. 82–126
M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, R.D.K. Misra, P. Juntunen, and A. Kyröläinen: Proc. 6th Eur. Stainless Steel Conf. Science and Market, P. Karjalainen and S. Hertzman, eds., Jernkontoret, Helsinki, Finland, 2008, pp. 519–24
S. Rajasekhara, P.J. Ferreira, L.P. Karjalainen, and A. Kyröläinen: Proc. 6th Eur. Stainless Steel Conf. Science and Market, P. Karjalainen and S. Hertzman, eds., Jernkontoret, Helsinki, Finland, 2008, pp. 511–17
S.K. Varma, J. Kalyanam, L.E. Murr, V. Srinivas: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1994, vol. 13, pp. 107–11
M.A. Meyers, O. Vöhringer, V.A. Lubarda: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 4025–39
C.W. Sinclair, H. Proudhon, J.-D. Mithieux: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 539–543, pp. 4714–19
S. Rajasekhara, P.J. Ferreira, L.P. Karjalainen, A. Kyröläinen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 1202–10
G.V. Kurdjumov, G. Sachs: Z. Phys., 1930, vol. 64, pp. 325–43
M. Hölscher, D. Raabe, K. Lücke: Steel Res., 1991, vol. 62, pp. 567–75
B. Ravi Kumar, A.K. Singh, B. Mahato, P.K. De, N.R. Bandyopadhyay, D.K. Bhattacharya: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 429, pp. 205–11
Acknowledgments
The financial support from the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (Tekes), Outokumpu Oyj, LaserPlus Oy, and Sanmina-SCI Enclosure Systems Oy in the Tekes-project Nr: 40266/04-Dnr: 2044/31/03 is acknowledged with gratitude.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 24, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somani, M., Juntunen, P., Karjalainen, L. et al. Enhanced Mechanical Properties through Reversion in Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 40, 729–744 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9723-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9723-y